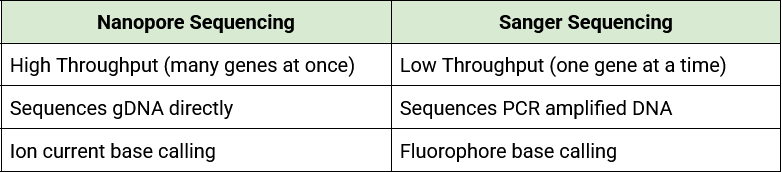
49 16S Gene PCR Amplification and Sanger Sequencing
After genomic DNA (gDNA) has been isolated and quantified, it can be used for many downstream applications. While we will use our genomic DNA samples for whole genome sequencing using Nanopore sequencing technology, we can also use the gDNA to amplify one gene for Sanger sequencing. These different sequencing methods contrast one another:
Table. Comparison of Nanopore and Sanger DNA Sequencing.
PCR amplification of 16S
We will amplify the bacterial 16S gene, which encodes a subunit of ribosomes.
Biologists use this gene to compare evolutionary relationships by sequence similarities and differences to organize biological taxonomies. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) enables scientists to amplify many copies of a gene, and we will target 16S for amplification.
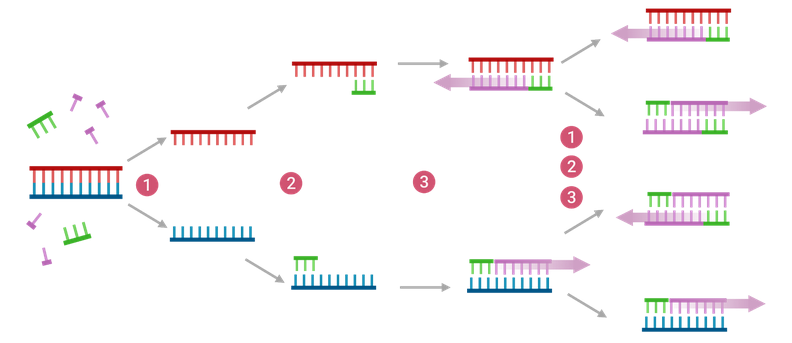
PCR Cycles Diagram indicating the three main steps: denaturation at 95-96°C, annealing at 68°C, and elongation at 72°C. Created with BioRender.com
You can learn about this reaction by watching the video “Polymerase Chain Reaction.”
After completing this lab you will gain the following lab skills:
Learning Objectives
- Lab safety and proper personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Setup of two PCR reactions.
- Proper use of a thermocycler for PCR.

