Visualizing Chemistry
Problem 24-26
Name the following amines, and identify each as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
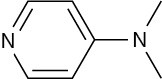
(a)
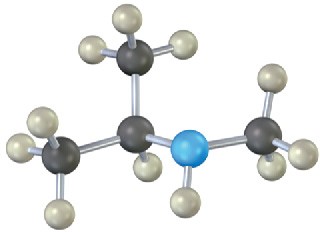
(b)
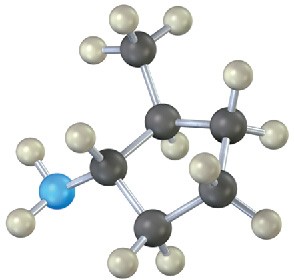
(c)
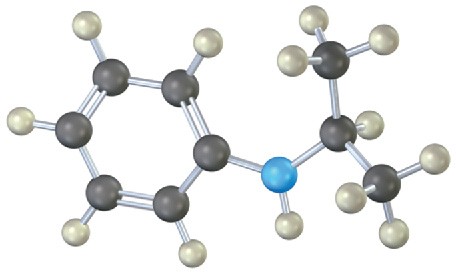
Problem 24-27
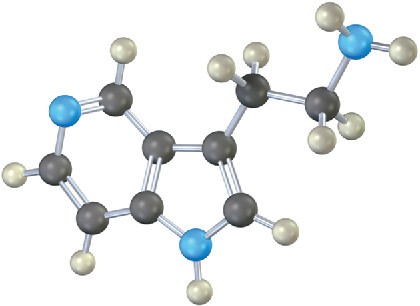
The following compound contains three nitrogen atoms. Rank them in order of increasing basicity.
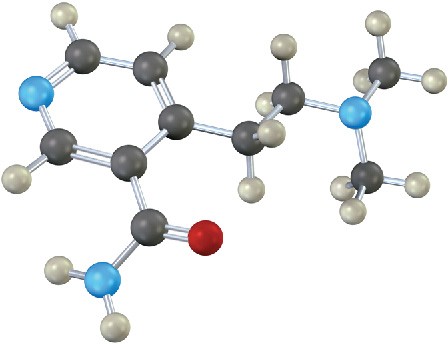
Problem 24-28
Name the following amine, including R,S stereochemistry, and draw the product of its reaction with excess iodomethane followed by heating with Ag2O (Hofmann elimination). Is the stereochemistry of the alkene product Z or E? Explain.
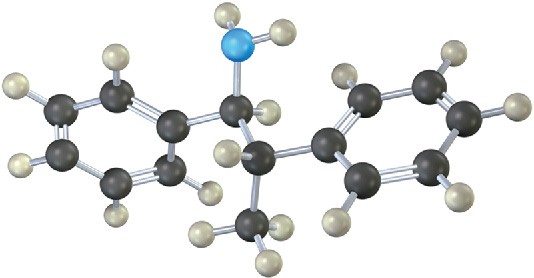
Problem 24-29
Which nitrogen atom in the following compound is most basic? Explain.
Mechanism Problems
Problem 24-30
Predict the product(s) and write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
(a)
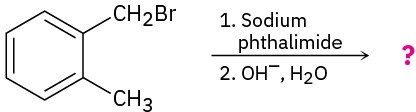
(b)
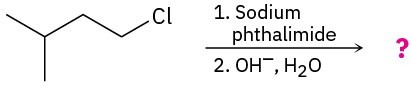
Problem 24-31
Predict the product(s) and write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
(a)
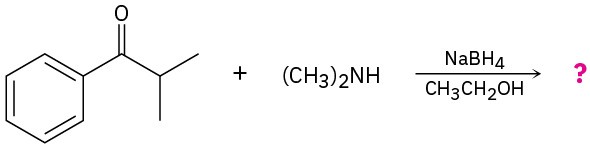
(b)
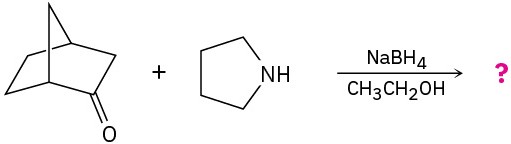
Problem 24-32
Predict the product(s) and write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
(a)
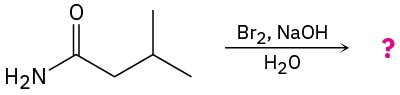
(b)
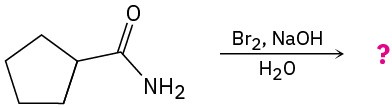
(c)
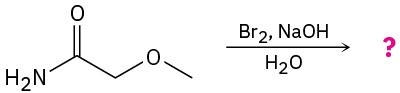
(d)
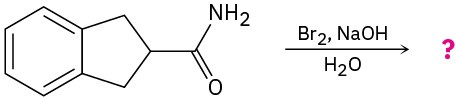
Problem 24-33
Predict the product(s) and write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
(a)
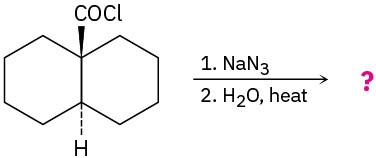
(b)
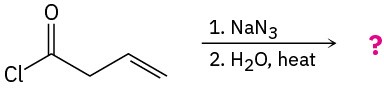
Problem 24-34
The diazotization of aniline first involves the formation of NO+ (nitrosonium ion) by the dehydration of nitrous acid with sulfuric acid. The aniline nitrogen then acts as a nucleophile and eventually loses water. Propose a mechanism for the formation of the dizaonium salt of aniline using curved arrows to show all electron movement.
Problem 24-35
Substituted pyrroles are often prepared by treatment of a 1,4-diketone with ammonia. Propose a mechanism.
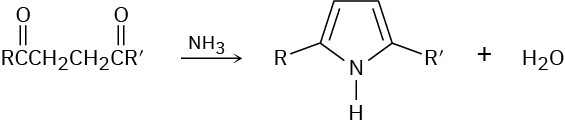
Problem 24-36
3,5-Dimethylisoxazole is prepared by reaction of 2,4-pentanedione with hydroxylamine. Propose a mechanism.
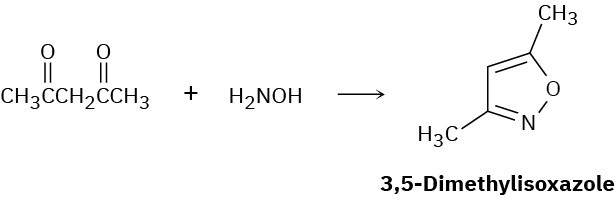
Problem 24-37
One problem with reductive amination as a method of amine synthesis is that by-products are sometimes obtained. For example, reductive amination of benzaldehyde with methylamine leads to a mixture of N-methylbenzylamine and N-methyldibenzylamine. How do you suppose the tertiary amine by-product is formed? Propose a mechanism.
Problem 24-38
Chlorophyll, heme, vitamin B12, and a host of other substances are biosynthesized from porphobilinogen (PBG), which is itself formed from condensation of two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate. The two 5-aminolevulinates are bound to lysine (Lys) amino acids in the enzyme, one in the enamine form and one in the imine form, and their condensation is thought to occur by the following steps. Use curved arrows to show the mechanism of each step.
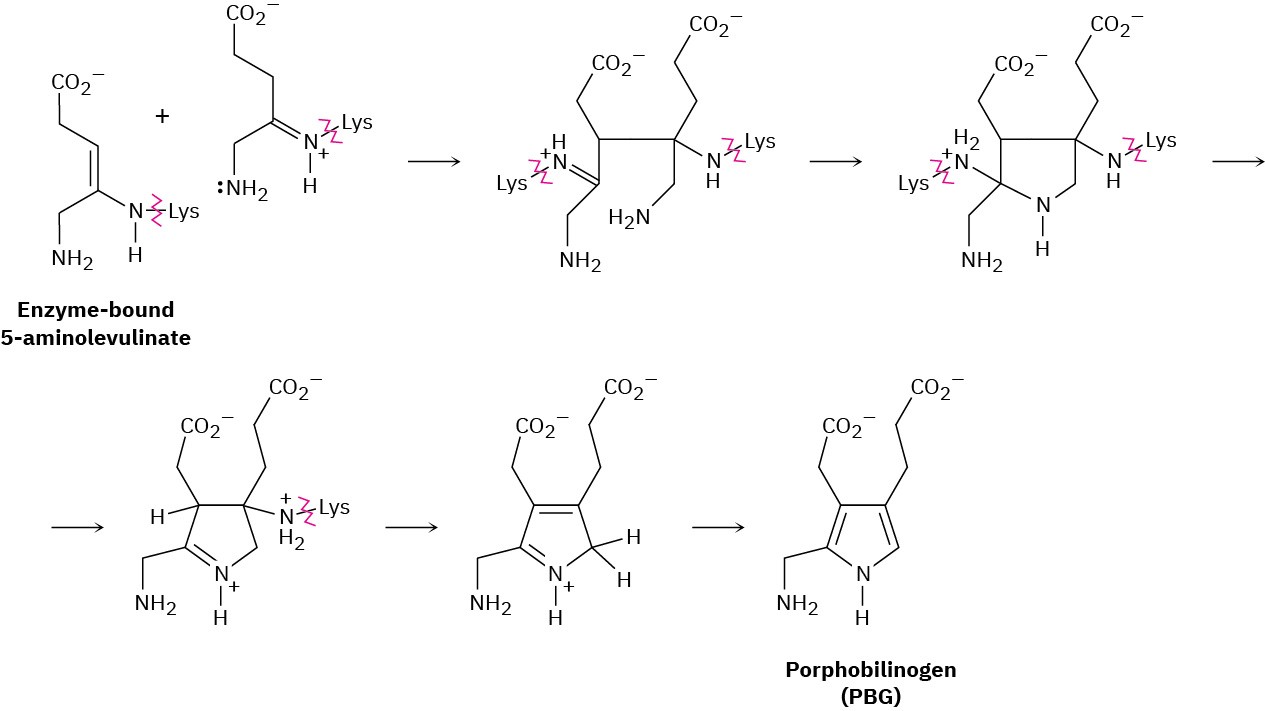
Problem 24-39
Choline, a component of the phospholipids in cell membranes, can be prepared by SN2 reaction of trimethylamine with ethylene oxide. Show the structure of choline, and propose a mechanism for the reaction.
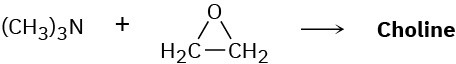
Problem 24-40
The antitumor antibiotic mitomycin C functions by forming cross-links in DNA chains.
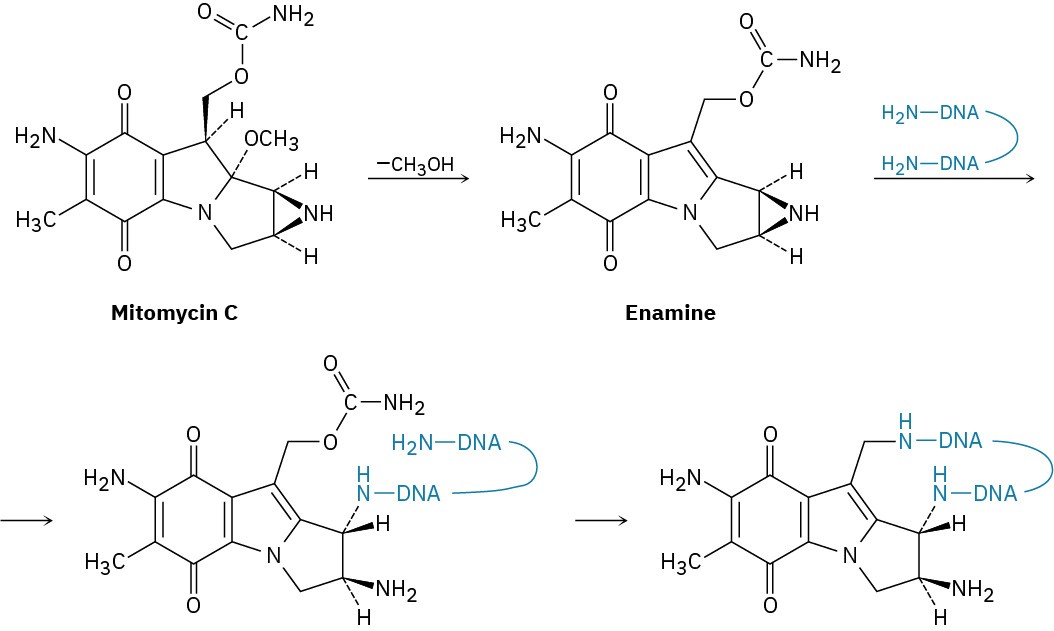
(a) The first step is loss of methoxide and formation of an iminium ion intermediate that is deprotonated to give an enamine. Show the mechanism.
(b) The second step is reaction of the enamine with DNA to open the three-membered, nitrogen-containing (aziridine) ring. Show the mechanism.
(c) The third step is loss of carbamate (NH2CO2–) and formation of an unsaturated iminium ion, followed by a conjugate addition of another part of the DNA chain. Show the mechanism.
Problem 24-41
α-Amino acids can be prepared by the Strecker synthesis, a two-step process in which an aldehyde is treated with ammonium cyanide followed by hydrolysis of the amino nitrile intermediate with aqueous acid. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
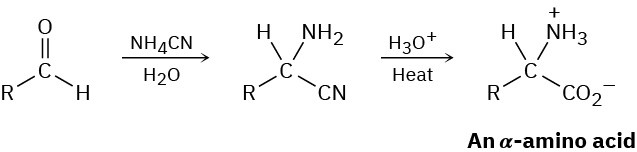
Problem 24-42
One of the reactions used in determining the sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA is reaction with hydrazine. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction, which occurs by an initial conjugate addition followed by internal amide formation.
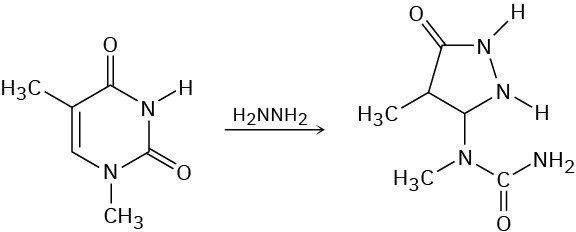
Problem 24-43
When an α-hydroxy amide is treated with Br2 in aqueous NaOH under Hofmann rearrangement conditions, loss of CO2 occurs and a chain-shortened aldehyde is formed. Propose a mechanism.
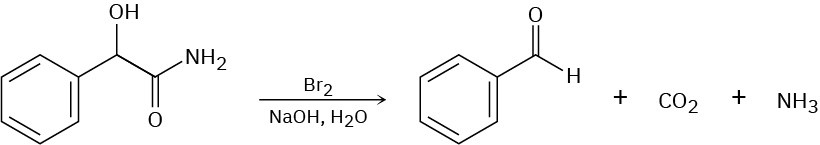
Problem 24-44
The following transformation involves a conjugate nucleophilic addition reaction (Section 19.13) followed by an intramolecular nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction (Section 21.2). Show the mechanism.
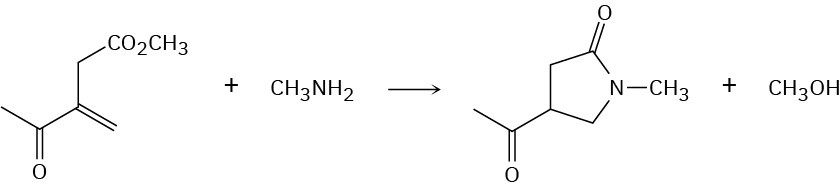
Problem 24-45
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:

Problem 24-46
One step in the biosynthesis of morphine is the reaction of dopamine with p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde to give (S)-norcoclaurine. Assuming that the reaction is acid-catalyzed, propose a mechanism.
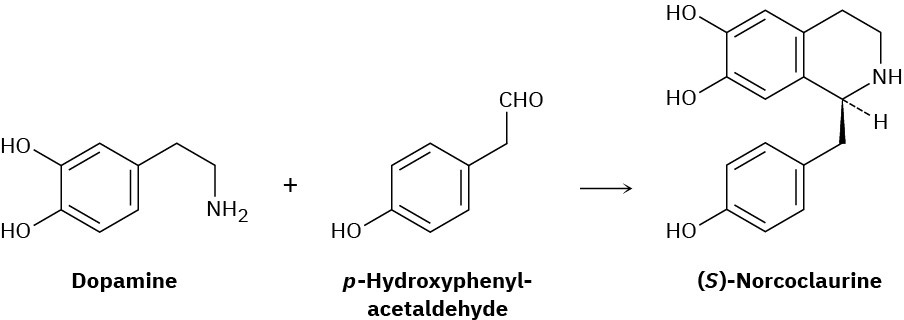
Naming Amines
Problem 24-47
Name the following compounds:
(a)
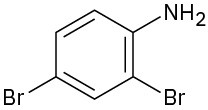
(b)
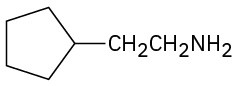
(c)
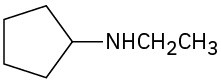
(d)
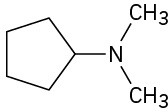
(e)
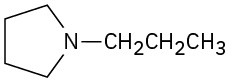
(f)

Problem 24-48
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
(a) N,N-Dimethylaniline
(b) (Cyclohexylmethyl)amine
(c) N-Methylcyclohexylamine
(d) (2-Methylcyclohexyl)amine
(e) 3-(N,N-Dimethylamino)propanoic acid
Problem 24-49
Classify each of the amine nitrogen atoms in the following substances as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
(a)
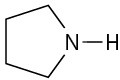
(b)
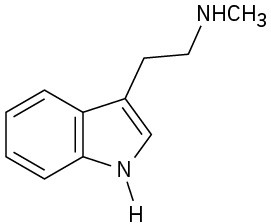
(c)
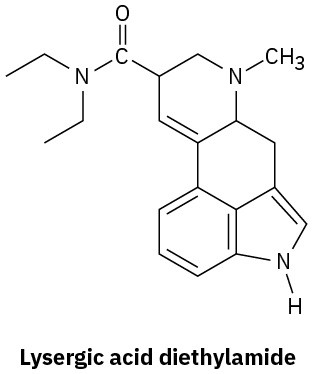
Amine Basicity
Problem 24-50
Although pyrrole is a much weaker base than most other amines, it is a much stronger acid (pKa ≈ 15 for the pyrrole versus 35 for diethylamine). The N–H hydrogen is readily abstracted by base to yield the pyrrole anion, C4H4N–. Explain.
Problem 24-51
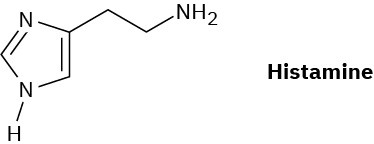
Histamine, whose release in the body triggers nasal secretions and constricted airways, has three nitrogen atoms. List them in order of increasing basicity and explain your ordering.
Problem 24-52
Account for the fact that p-nitroaniline (pKa = 1.0) is less basic than m-nitroaniline (pKa = 2.5) by a factor of 30. Draw resonance structures to support your argument. (The pKa values refer to the corresponding ammonium ions.)
Synthesis of Amines
Problem 24-53
How would you prepare the following substances from 1-butanol?
(a)Butylamine
(b) Dibutylamine
(c) Propylamine
(d) Pentylamine
(e) N,N-Dimethylbutylamine
(f) Propene
Problem 24-54
How would you prepare the following substances from pentanoic acid?
(a) Pentanamide
(b) Butylamine
(c) Pentylamine
(d) 2-Bromopentanoic acid
(e) Hexanenitrile
(f) Hexylamine
Problem 24-55
How would you prepare aniline from the following starting materials?
(a) Benzene
(b) Benzamide
(c) Toluene
Problem 24-56
How would you prepare benzylamine, C6H5CH2NH2, from benzene? More than one step is needed.
Problem 24-57
How might you prepare pentylamine from the following starting materials?
(a) Pentanamide
(b) Pentanenitrile
(c) 1-Butene
(d) Hexanamide
(e) 1-Butanol
(f) 5-Decene
(g) Pentanoic acid
Problem 24-58
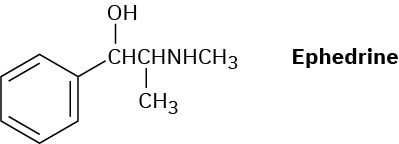
How might a reductive amination be used to synthesize ephedrine, an amino alcohol that was widely used for the treatment of bronchial asthma?
Reactions of Amines
Problem 24-59
How would you convert aniline into each of the following products?
(a) Benzene
(b) Benzamide
(c) Toluene
Problem 24-60
Write the structures of the major organic products you would expect from reaction of m-toluidine (m-methylaniline) with the following reagents:
(a)Br2 (1 equivalent)
(b)CH3I (excess)
(c) CH3COCl in pyridine
(d) The product of (c), then HSO3Cl
Problem 24-61
Show the products from reaction of p-bromoaniline with the following reagents:
(a) CH3I (excess)
(b)HCl
(c) HNO2, H2SO4
(d) CH3COCl
(e) CH3MgBr
(f) CH3CH2Cl, AlCl3
(g) Product of (c) with CuCl, HCl
(h) Product of (d) with CH3CH2Cl, AlCl3
Problem 24-62
What are the major products you would expect from Hofmann elimination of the following amines?
(a)
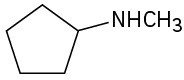
(b)
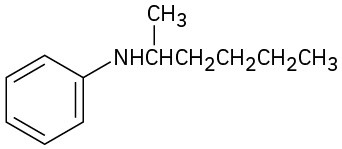
(c)
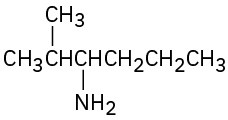
Problem 24-63
How would you prepare the following compounds from toluene? A diazonio replacement reaction is needed in some instances.
(a)
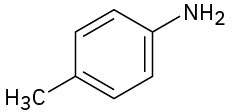
(b)
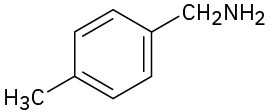
(c)
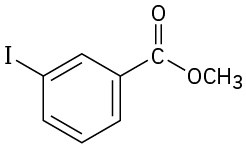
Problem 24-64
Predict the product(s) of the following reactions. If more than one product is formed, tell which is major.
(a)
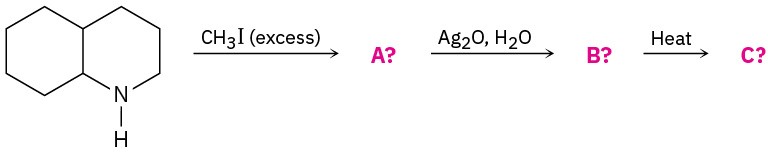
(b)
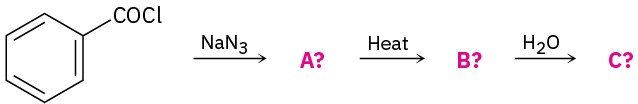
(c)
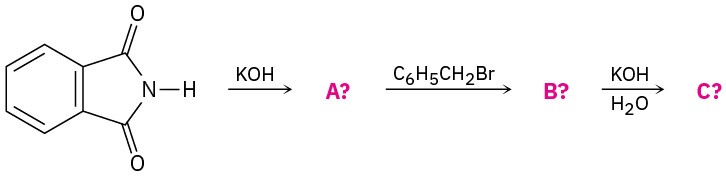
(d)
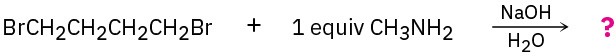
Spectroscopy
Problem 24-65
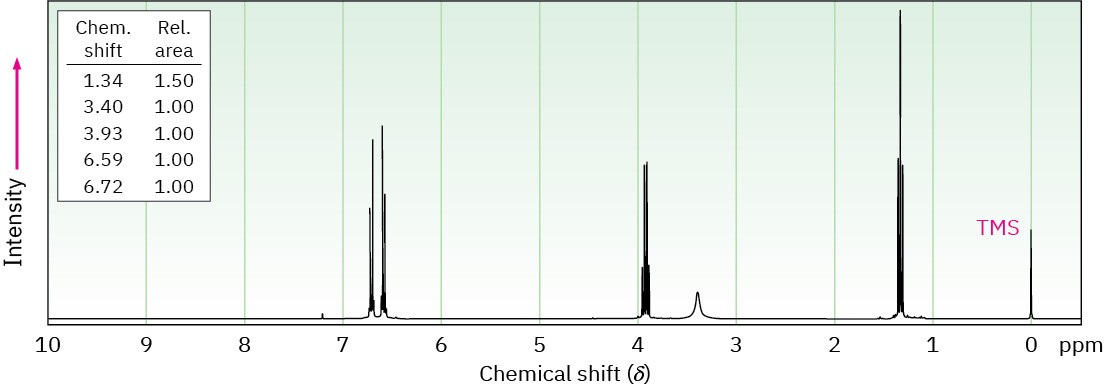
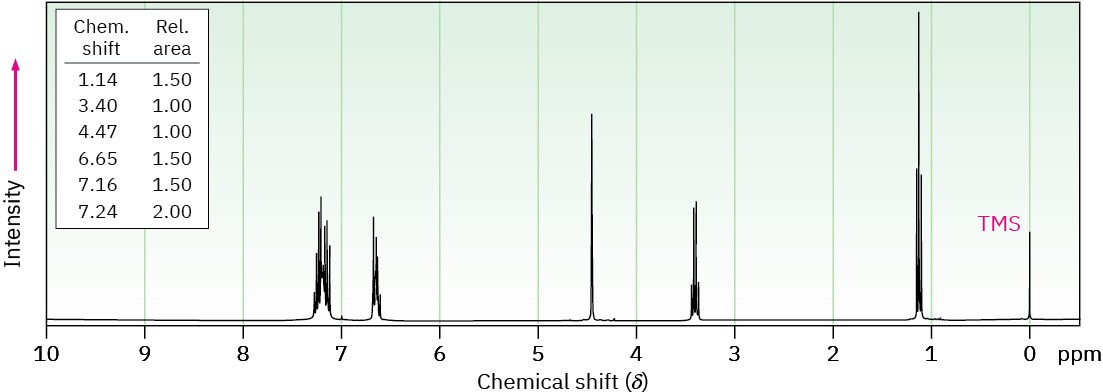
Phenacetin, a substance formerly used in over-the-counter headache remedies, has the formula C10H13NO2. Phenacetin is neutral and does not dissolve in either acid or base. When warmed with aqueous NaOH, phenacetin yields an amine, C8H11NO, whose 1H NMR spectrum is shown. When heated with HI, the amine is cleaved to an aminophenol, C6H7NO. What is the structure of phenacetin, and what are the structures of the amine and the aminophenol?
Problem 24-66
Propose structures for amines with the following 1H NMR spectra:
(a) C3H9NO
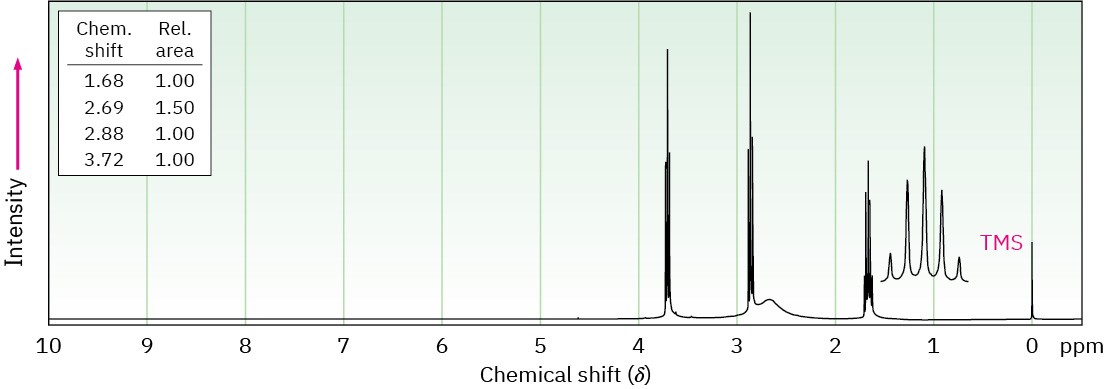
(b) C4H11NO2
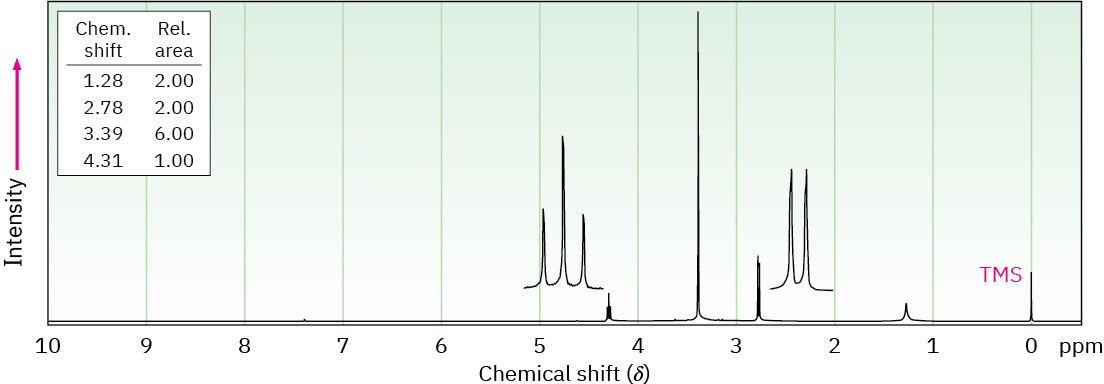
(c) C8H11N
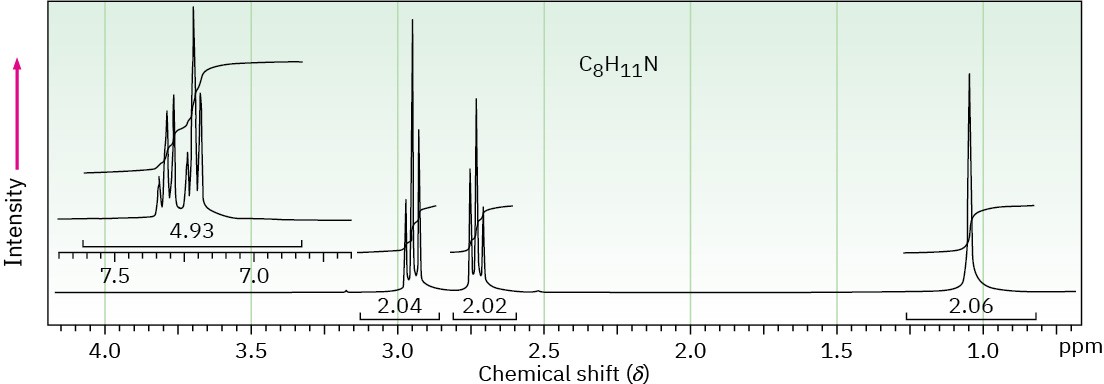
Problem 24-67
Draw the structure of the amine that produced the 1H NMR spectrum shown in Problem 24-66(c). This compound has a single strong peak in its IR spectrum at 3280 cm–1.
General Problems
Problem 24-68
Fill in the missing reagents a–e in the following scheme:
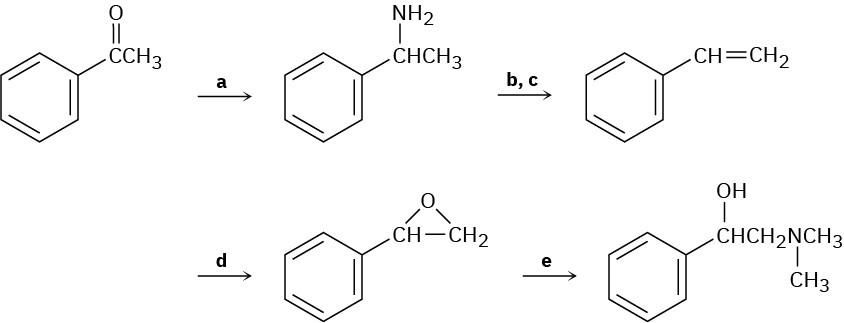
Problem 24-69
Oxazole is a five-membered aromatic heterocycle. Would you expect oxazole to be more basic or less basic than pyrrole? Explain.
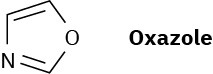
Problem 24-70
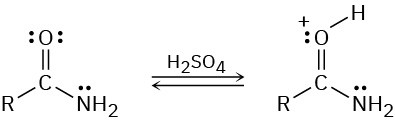
Protonation of an amide using strong acid occurs on oxygen rather than on nitrogen. Suggest a reason for this behavior, taking resonance into account.
Problem 24-71
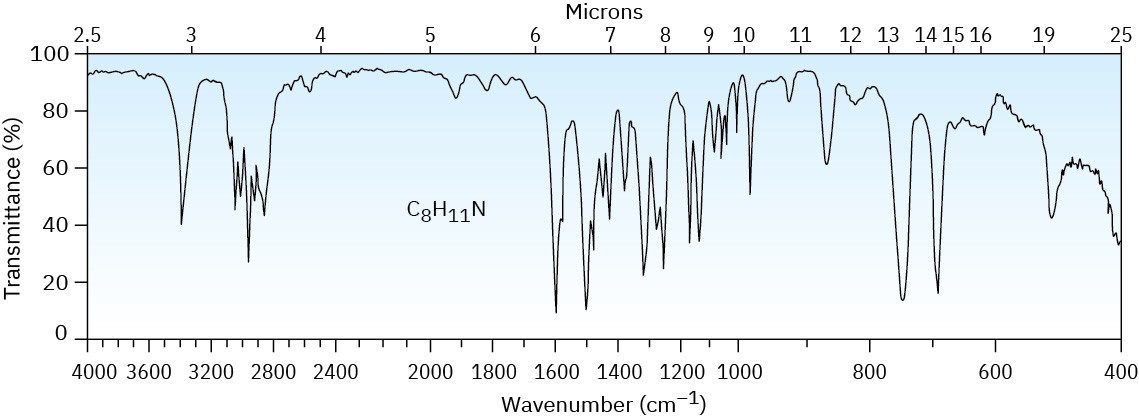
What is the structure of the compound with formula C8H11N that produced the following IR spectrum?
Problem 24-72
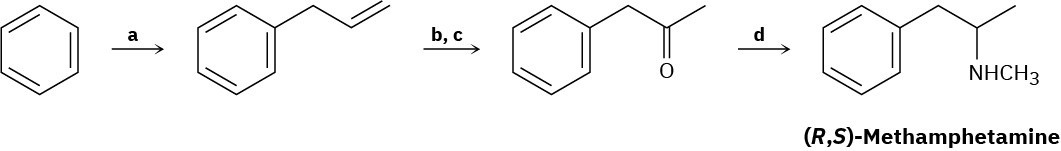
Fill in the missing reagents a–d in the following synthesis of racemic methamphetamine from benzene.
Problem 24-73
Cyclopentamine is an amphetamine-like central nervous system stimulant. Propose a synthesis of cyclopentamine from materials of five carbons or less.
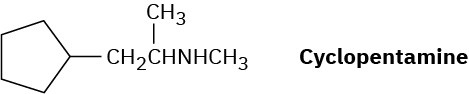
Problem 24-74
Tetracaine is a substance used as a spinal anesthetic.
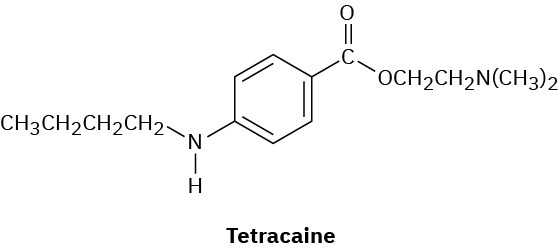
(a) How would you prepare tetracaine from the corresponding aniline derivative, ArNH2?
(b) How would you prepare tetracaine from p-nitrobenzoic acid?
(c) How would you prepare tetracaine from benzene?
Problem 24-75
Atropine, C17H23NO3, is a poisonous alkaloid isolated from the leaves and roots of Atropa belladonna, the deadly nightshade. In small doses, atropine acts as a muscle relaxant; 0.5 ng (nanogram, 10–9 g) is sufficient to cause pupil dilation. On basic hydrolysis, atropine yields tropic acid, C6H5CH(CH2OH)CO2H, and tropine, C8H15NO. Tropine is an optically inactive alcohol that yields tropidene on dehydration with H2SO4. Propose a structure for atropine.
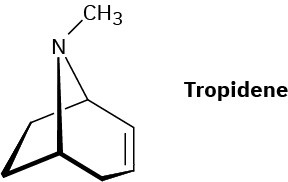
Problem 24-76
Tropidene (Problem 24-75) can be converted by a series of steps into tropilidene (1,3,5-cycloheptatriene). How would you accomplish this conversion?
Problem 24-77
Propose a structure for the product with formula C9H17N that results when 2-(2-cyanoethyl)cyclohexanone is reduced catalytically.
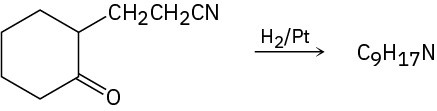
Problem 24-78
Coniine, C8H17N, is the toxic principle of the poison hemlock drunk by Socrates. When subjected to Hofmann elimination, coniine yields 5-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-octene. If coniine is a secondary amine, what is its structure?
Problem 24-79
How would you synthesize coniine (Problem 24-78) from acrylonitrile (H2C═CHCN) and ethyl 3-oxohexanoate (CH3CH2CH2COCH2CO2Et)? (See Problem 24-77.)
Problem 24-80
Tyramine is an alkaloid found, among other places, in mistletoe and ripe cheese. How would you synthesize tyramine from benzene? From toluene?
Problem 24-81
Reaction of anthranilic acid (o-aminobenzoic acid) with HNO2 and H2SO4 yields a diazonium salt that can be treated with base to yield a neutral diazonium carboxylate.
(a) What is the structure of the neutral diazonium carboxylate?
(b) Heating the diazonium carboxylate results in the formation of CO2, N2, and an intermediate that reacts with 1,3-cyclopentadiene to yield the following product:
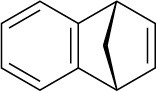
What is the structure of the intermediate, and what kind of reaction does it undergo with cyclopentadiene?
Problem 24-82
Cyclooctatetraene was first synthesized in 1911 by a route that involved the following transformation:
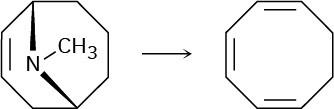
How might you use the Hofmann elimination to accomplish this reaction? How would you finish the synthesis by converting cyclooctatriene into cyclooctatetraene?
Problem 24-83
Propose structures for compounds that show the following 1H NMR spectra.
(a) C9H13N
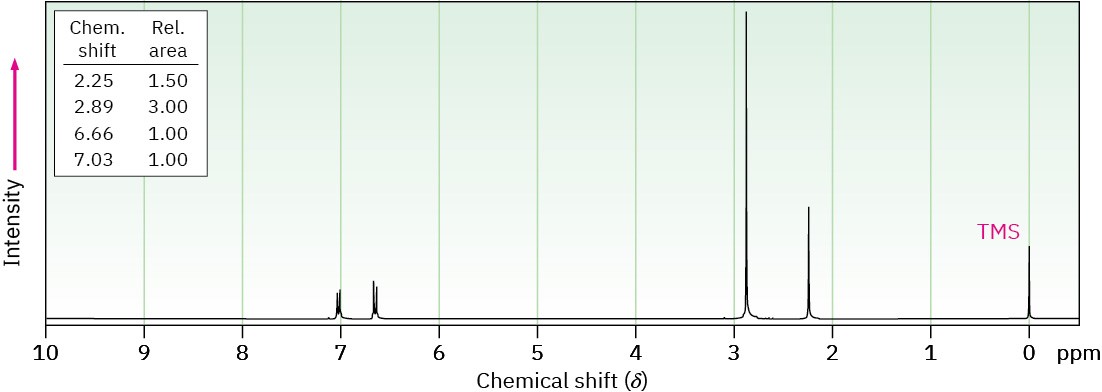
(b) C15H17N
Problem 24-84
4-Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) acts as a catalyst in acyl transfer reactions. DMAP’s catalytic activity stems from its nucleophilic character at the pyridine nitrogen, not the dimethylamino group. Explain this behavior, taking resonance into account.