Visualizing Chemistry
Problem 31-13
Identify the structural class to which the following polymer belongs, and show the structure of the monomer units used to make it:
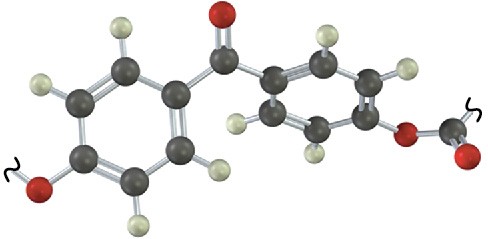
Problem 31-14
Show the structures of the polymers that could be made from the following monomers (green = Cl):
(a)
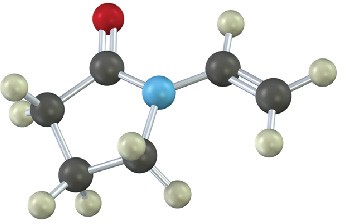
(b)
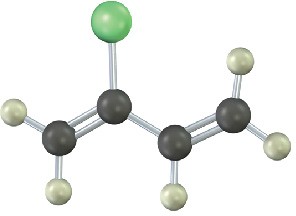
Mechanism Problems
Problem 31-15
Poly(ethylene glycol), or Carbowax, is made by anionic polymerization of ethylene oxide using NaOH as catalyst. Propose a mechanism.

Problem 31-16
The polyurethane foam used for home insulation uses methanediphenyldiisocyanate (MDI) as monomer. The MDI is prepared by acid-catalyzed reaction of aniline with formaldehyde, followed by treatment with phosgene, COCl2. Propose mechanisms for both steps.
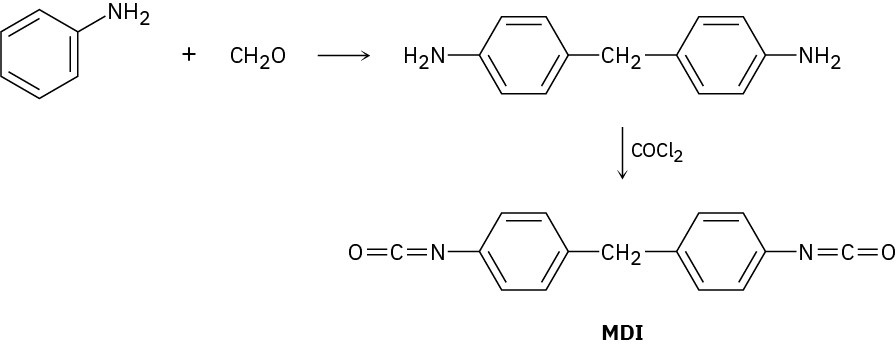
Problem 31-17
Write the structure of a representative segment of polyurethane prepared by reaction of ethylene glycol with MDI (Problem 31-16).
Problem 31-18
The polymeric resin used for Merrifield solid-phase peptide synthesis (Section 26.8) is prepared by treating polystyrene with N-(hydroxymethyl)phthalimide and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, followed by reaction with hydrazine. Propose a mechanism for both steps.
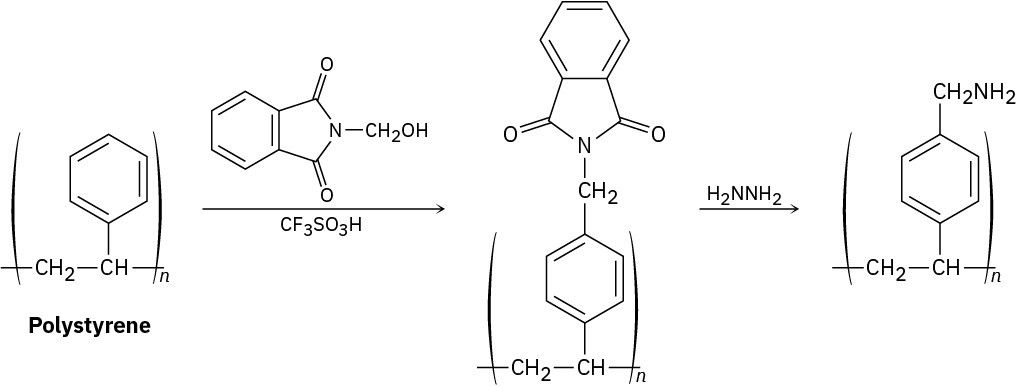
Problem 31-19
Polydicyclopentadiene (PDCPD), marketed as Telene or Metton, is a highly cross-linked thermosetting resin used for molding such impact-resistant parts as cabs for large trucks and earth-moving equipment. PDCPD is prepared by ring-opening metathesis polymerization of dicyclopentadiene, which is itself prepared from 1,3-cyclopentadiene. The polymerization occurs by initial metathesis of the more highly strained double bond in the bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane part of the molecule (Section 4.9) to give a linear polymer,
followed by cross-linking of different chains in a second metathesis of the remaining cyclopentene double bond.
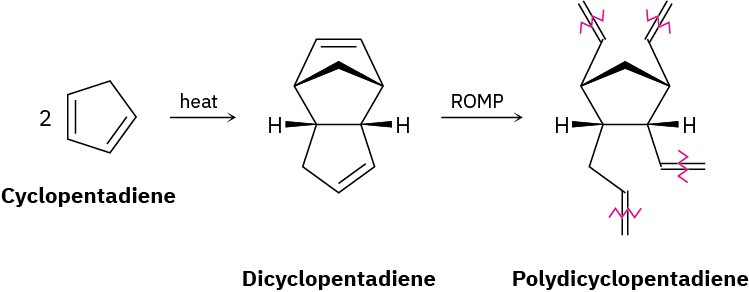
(a) Show the mechanism of the formation of dicyclopentadiene from cyclopentadiene.
(b) Draw the structure of a representative sample of the initially formed linear polymer containing three monomer units.
(c) Draw the structure of a representative sample of PDCPD that shows how cross-linking of the linear chains takes place.
General Problems
Problem 31-20
Identify the monomer units from which each of the following polymers is made, and tell whether each is a chain-growth or a step-growth polymer:
(a)
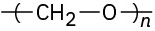
(b)
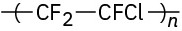
(c)
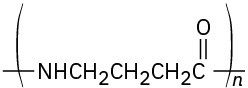
(d)
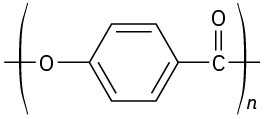
(e)
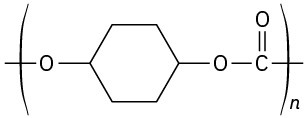
Problem 31-21
Draw a three-dimensional representation of segments of the following polymers:
(a) Syndiotactic polyacrylonitrile
(b) Atactic poly(methyl methacrylate)
(c) Isotactic poly(vinyl chloride)
Problem 31-22
Draw the structure of Kodel, a polyester prepared by heating dimethyl 1,4- benzenedicarboxylate with 1,4-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane.
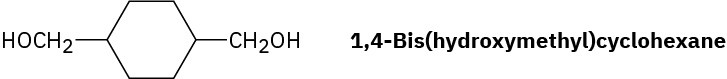
Problem 31-23
Show the structure of the polymer that results from heating the following diepoxide and diamine:
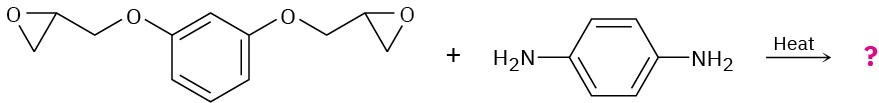
Problem 31-24
Nomex, a polyamide used in such applications as fire-retardant clothing, is prepared by reaction of 1,3-benzenediamine with 1,3-benzenedicarbonyl chloride. Show the structure of Nomex.
Problem 31-25
Nylon 10,10 is an extremely tough, strong polymer used to make reinforcing rods for concrete. Draw a segment of nylon 10,10, and show its monomer units.
Problem 31-26
1,3-Cyclopentadiene undergoes thermal polymerization to yield a polymer that has no double bonds in the chain. Upon strong heating, the polymer breaks down to regenerate cyclopentadiene. Propose a structure for the polymer.
Problem 31-27
When styrene, C6H5CH═CH2, is copolymerized in the presence of a few percent p– divinylbenzene, a hard, insoluble, cross-linked polymer is obtained. Show how this cross- linking of polystyrene chains occurs.
Problem 31-28
Nitroethylene, H2C═CHNO2, is a sensitive compound that must be prepared with great care. Attempted purification of nitroethylene by distillation often results in low recovery of product and a white coating on the inner walls of the distillation apparatus. Explain.
Problem 31-29
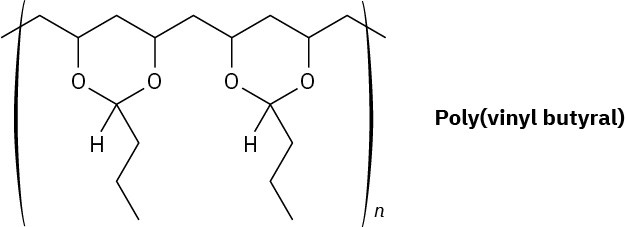
Poly(vinyl butyral) is used as the plastic laminate in the preparation of automobile windshield safety glass. How would you synthesize this polymer?
Problem 31-30
What is the structure of the polymer produced by anionic polymerization of β– propiolactone using NaOH as catalyst?
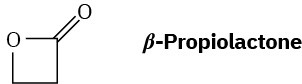
Problem 31-31
Glyptal is a highly cross-linked thermosetting resin produced by heating glycerol and phthalic anhydride (1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid anhydride). Show the structure of a representative segment of glyptal.
Problem 31-32
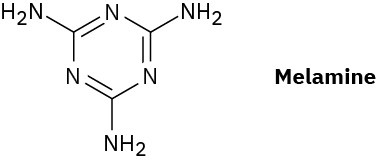
Melmac, a thermosetting resin often used to make plastic dishes, is prepared by heating melamine with formaldehyde. Look at the structure of Bakelite shown in Section 31.7, and then propose a structure for Melmac.
Problem 31-33
Epoxy adhesives are cross-linked resins prepared in two steps. The first step involves SN2 reaction of the disodium salt of bisphenol A with epichlorohydrin to form a low-molecular- weight prepolymer. This prepolymer is then “cured” into a cross-linked resin by treatment with a triamine such as H2NCH2CH2NHCH2CH2NH2.
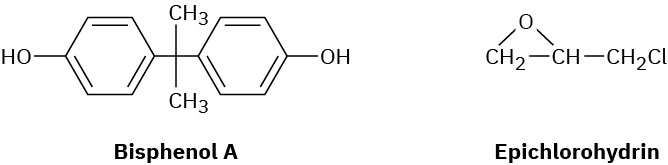
(a) What is the structure of the prepolymer?
(b) How does addition of the triamine to the prepolymer result in cross-linking?
Problem 31-34
The smoking salons of the Hindenburg and other hydrogen-filled dirigibles of the 1930s were insulated with urea–formaldehyde polymer foams. The structure of this polymer is highly cross-linked, like that of Bakelite (Section 31.7). Propose a structure.
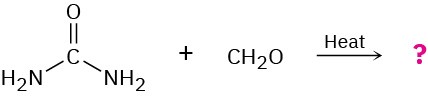
Problem 31-35
2-Ethyl-1-hexanol, used in the synthesis of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate plasticizer, is made commercially from butanal. Show the likely synthesis route.

