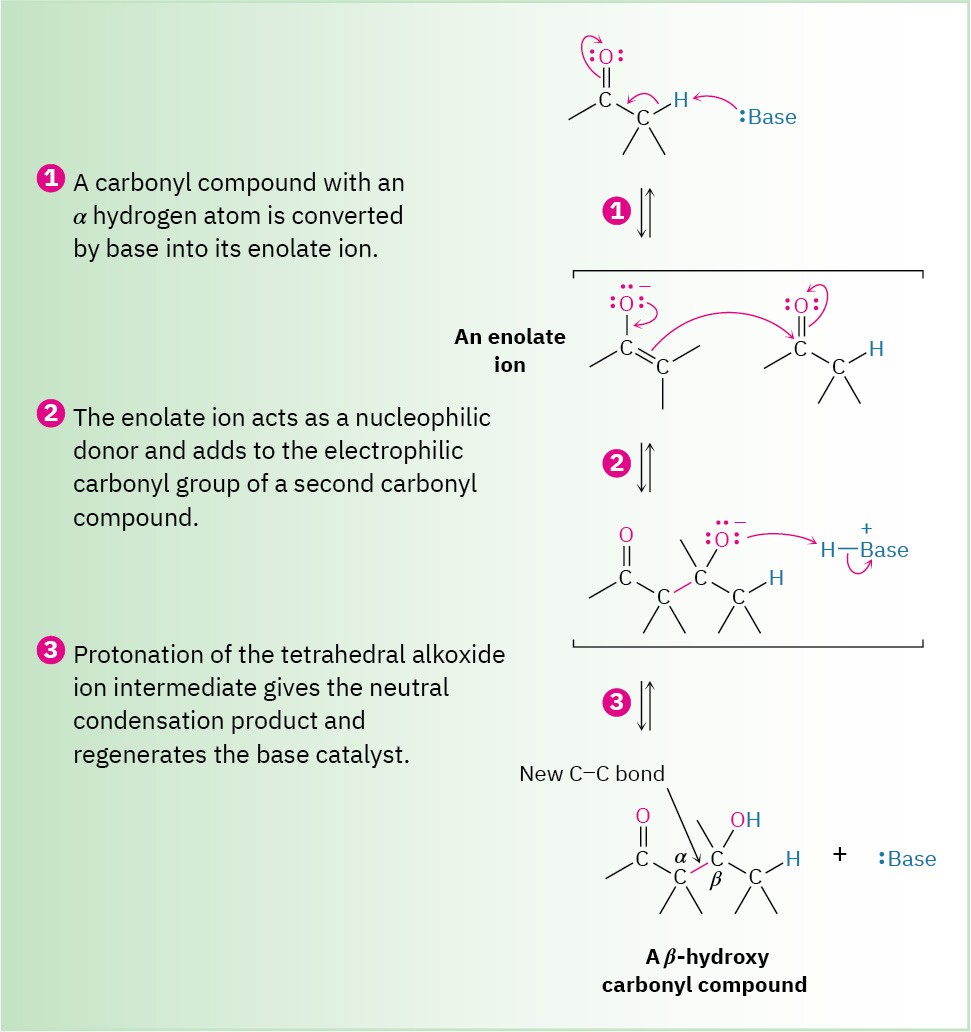
Carbonyl condensation reactions take place between two carbonyl partners and involve a combination of nucleophilic addition and α-substitution steps. One partner is converted into an enolate-ion nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group of the second partner. In so doing, the nucleophilic partner undergoes an α-substitution reaction and the electrophilic partner undergoes a nucleophilic addition. The general mechanism of the process is shown in Figure 23.2.
Figure 23.2 The general mechanism of a carbonyl condensation reaction.
One partner becomes a nucleophilic donor and adds to the second partner as an electrophilic acceptor. After protonation, the final product is a β-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
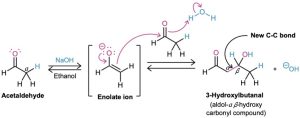
Aldehydes and ketones with an α hydrogen atom undergo a base-catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction called the aldol reaction. For example, treatment of acetaldehyde with a base such as sodium ethoxide or sodium hydroxide in a protic solvent leads to rapid and reversible formation of 3-hydroxybutanal, known commonly as aldol (aldehyde + alcohol), hence the general name of the reaction.
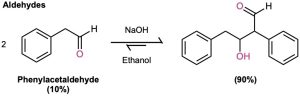
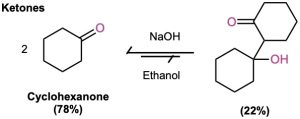
The exact position of the aldol equilibrium depends both on reaction conditions and on substrate structure. The equilibrium generally favors the condensation product in the case of aldehydes with no α substituent (RCH2CHO) but favors the reactant for disubstituted aldehydes (R2CHCHO) and for most ketones. Steric factors are probably responsible for these trends, since increased substitution near the reaction site increases steric congestion in the aldol product.
Worked Example 23.1 – Predicting the Product of an Aldol Reaction
What is the structure of the aldol product from propanal?
Strategy: An aldol reaction combines two molecules of reactant by forming a bond between the α-carbon of one partner and the carbonyl carbon of the second partner. The product is a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone, meaning that the two oxygen atoms in the product have a 1,3 relationship.
Solution:
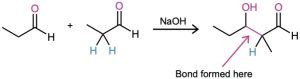
Problem 23-1
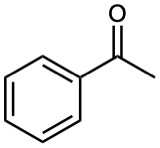
Predict the aldol reaction product of the following compounds:
(a)
![]()
(b)
(c)
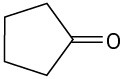
Problem 23-2
Using curved arrows to indicate the electron flow in each step, show how the base-catalyzed reverse-aldol reaction of 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone takes place to yield 2 equivalents of acetone.

