The use of herbal remedies to treat illness and disease goes back thousands of years, but the medical use of chemicals prepared in the laboratory has a much shorter history.
Barbiturates, a large class of drugs with a wide variety of uses, constitute one of the earliest successes of medicinal chemistry. The synthesis and medical use of barbiturates goes back to 1904 when Bayer, a German chemical company, first marketed a compound called barbital, trade named Veronal, as a treatment for insomnia. Since that time, more than 2500 different barbiturate analogs have been synthesized by drug companies, more than 50 have been used medicinally, and about a dozen are still in use as anesthetics, anticonvulsants, sedatives, and anxiolytics.

Figure 22.8 Different barbiturates come in a multitude of colors, giving rise to similarly colorful street names when the drugs are abused. (credit: “Medications” by freestocks.org/Flickr, Public Domain)
The synthesis of barbiturates is relatively simple and relies on reactions that are now familiar: enolate alkylations and nucleophilic acyl substitutions. Starting with diethylmalonate, alkylation of the corresponding enolate ion with simple alkyl halides provides a wealth of different disubstituted malonic esters. Reaction with urea, (H2N)2C═O, then gives the product barbiturates by a twofold nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of the ester groups with the –NH2 groups of urea (Figure 22.9). Amobarbital (Amytal), pentobarbital (Nembutal), and secobarbital (Seconal) are typical examples.
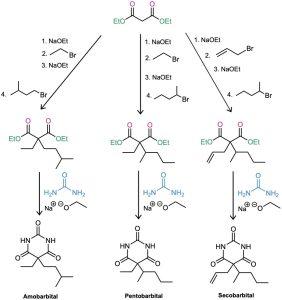
Figure 22.9 The synthesis of barbiturates relies on malonic ester alkylations and nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions. More than 2500 different barbiturates have been synthesized over the past 100 years.
In addition to their prescribed medical uses, many barbiturates have also found widespread illegal use as street drugs. Each barbiturate often comes as a tablet of regulated size, shape, and color. Although still used today, most barbiturates have been replaced by safer, more potent alternatives with markedly different structures.

