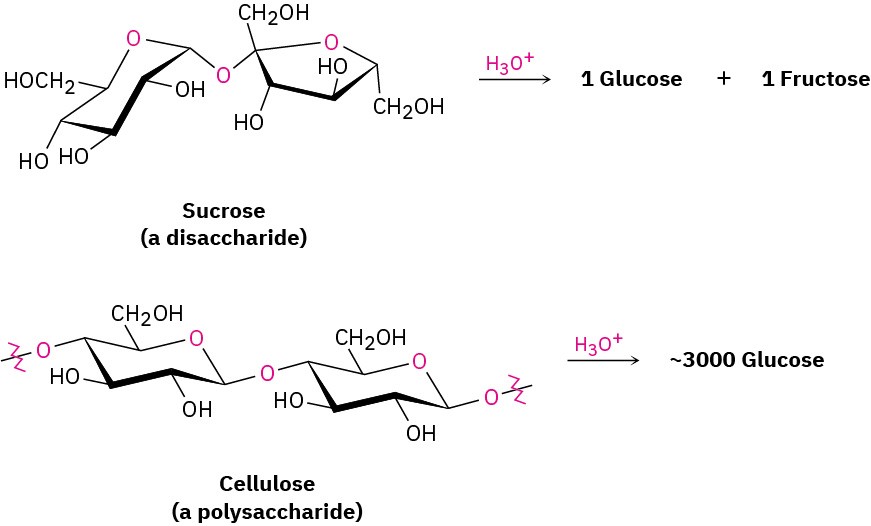
Carbohydrates are generally classified as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates like glucose and fructose that can’t be converted into smaller sugars by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two or more simple sugars linked together by acetal bonds (Section 19.10). Sucrose (table sugar), for instance, consists of one glucose linked to one fructose. Similarly, cellulose is made up of several thousand glucose units linked together. Enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of a complex carbohydrate breaks it down into its constituent monosaccharides.
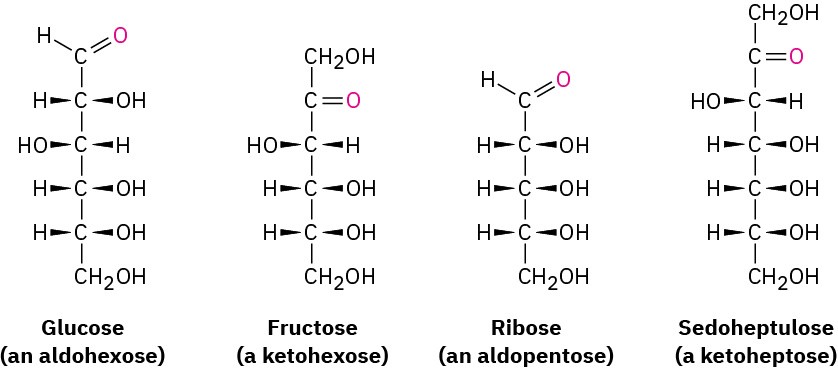
Monosaccharides are further classified as either aldoses or ketoses. The –ose suffix designates a carbohydrate, and the prefixes aldo– and keto– identify the kind of carbonyl group in the molecule, whether aldehyde or ketone. The number of carbon atoms in the monosaccharide is indicated by the appropriate numerical prefix tri-, tetr-, pent-, hex-, and so forth, in the name. Putting it all together, glucose is an aldohexose, a six-carbon aldehyde sugar; fructose is a ketohexose, a six-carbon keto sugar; ribose is an aldopentose, a five-carbon aldehyde sugar; and sedoheptulose is a ketoheptose, a seven-carbon keto sugar.
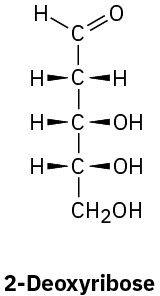
Most of the common simple sugars are either pentoses or hexoses.
Problem 25-1
Classify each of the following monosaccharides:
(a)
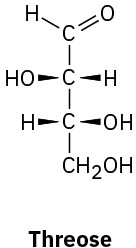
(b)
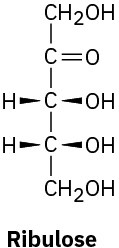
(c)
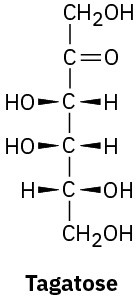
(d)