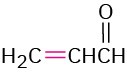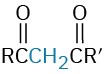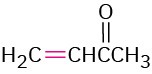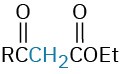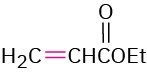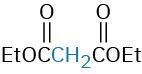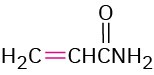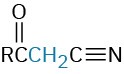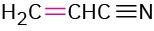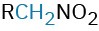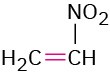We saw in Section 19.13 that certain nucleophiles, such as amines, react with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones to give a conjugate addition product, rather than a direct addition product.
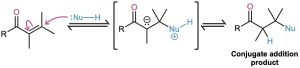
Exactly the same kind of conjugate addition can occur when a nucleophilic enolate ion reacts with an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound—a process known as the Michael reaction after Arthur Michael at Tufts College and Harvard University.
The best Michael reactions are those that take place when a particularly stable enolate ion, such as that derived from a β-keto ester or other 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, adds to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketone. For example, ethyl acetoacetate reacts with 3-buten-2-one in the presence of sodium ethoxide to yield the conjugate addition product.
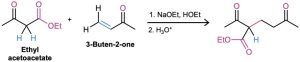
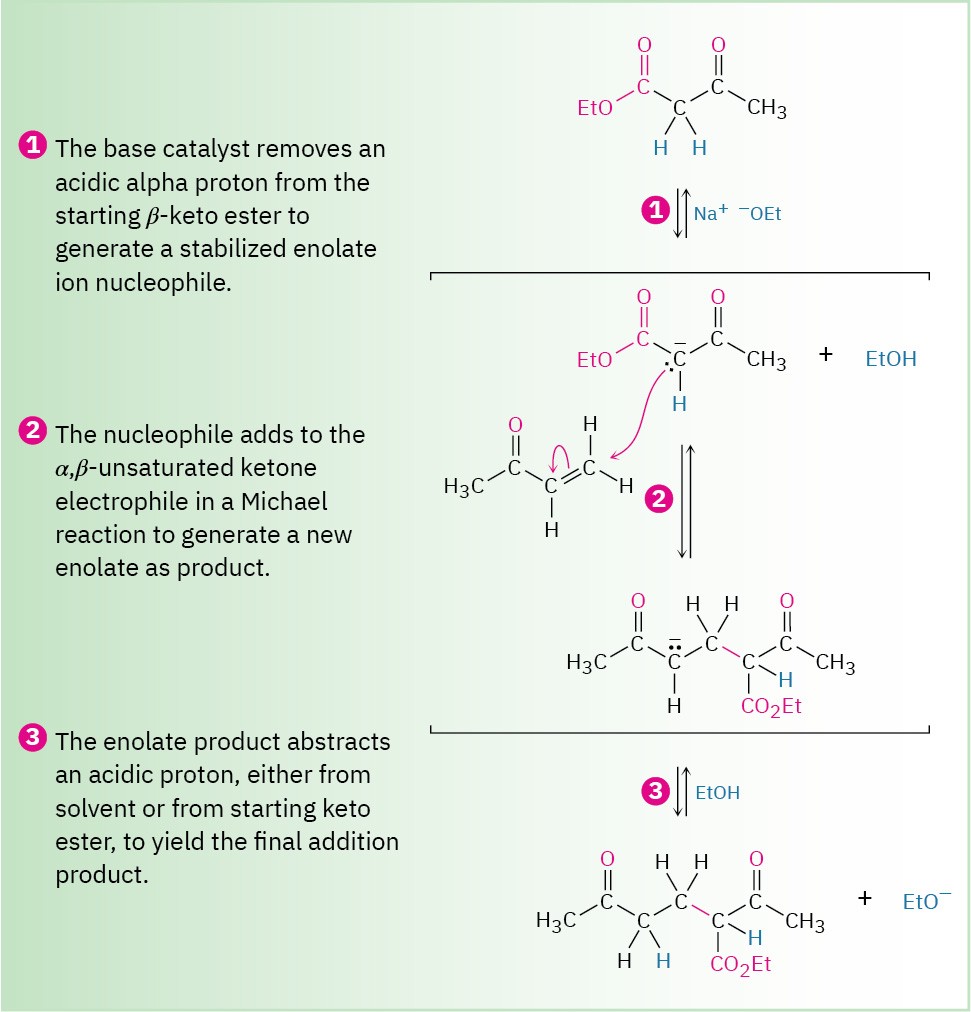
Michael reactions take place by addition of a nucleophilic enolate ion donor to the β carbon of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl acceptor, according to the mechanism shown in Figure 23.7.
Figure 23.7 Mechanism of the Michael reaction between a β-keto ester and an α,β-unsaturated ketone.
The reaction is a conjugate addition of an enolate ion to the unsaturated carbonyl compound.
The Michael reaction occurs with a variety of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, not just conjugated ketones. Unsaturated aldehydes, esters, thioesters, nitriles, amides, and nitro compounds can all act as the electrophilic acceptor component in Michael reactions (Table 23.1). Similarly, a variety of different donors can be used, including β-diketones, β-keto esters, malonic esters, β-keto nitriles, and nitro compounds.
Table 23.1 Some Michael Acceptors and Michael Donors
|
Michael acceptors |
Michael donors |
||
|
|
Propenal |
|
β-Diketone |
|
|
3-Buten-2-one |
|
β-Keto ester |
|
|
Ethyl propenoate |
|
Diethyl malonate |
|
|
Propenamide |
|
β-Keto nitrile |
|
|
Propenenitrile |
|
Nitro compound |
Worked Example 23.5 – Using the Michael Reaction
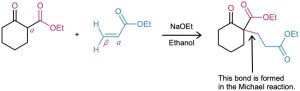
How might you obtain the following compound using a Michael reaction?
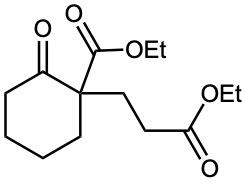
Strategy: A Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion donor to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl acceptor, yielding a 1,5-dicarbonyl product. Usually, the stable enolate ion is derived from a β-diketone, β-keto ester, malonic ester, or similar compound. The C–C bond formed in the conjugate addition step is the one between the α carbon of the acidic donor and the β carbon of the unsaturated acceptor.
Solution:
Problem 23-16
What product would you obtain from a base-catalyzed Michael reaction of 2,4-pentanedione with each of the following α,β-unsaturated acceptors?
(a) cyclohexenone
(b) propenenitrile
(c) ethyl 2-butenoate
Problem 23-17
What product would you obtain from a base-catalyzed Michael reaction of 3-buten-2-one with each of the following nucleophilic donors?
(a)
![]()
(b)
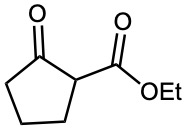
Problem 23-18
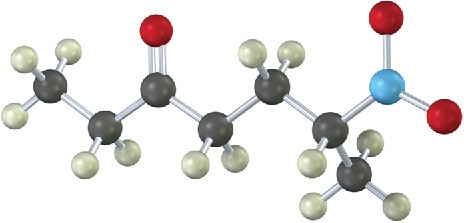
How would you prepare the following compound using a Michael reaction (gray = H, black = C, red = O, blue = N)?