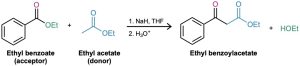
The mixed Claisen condensation of two different esters is similar to the mixed aldol condensation of two different aldehydes or ketones (Section 23.5). Mixed Claisen reactions are successful only when one of the two ester components has no α hydrogens and thus can’t form an enolate ion. For example, ethyl benzoate and ethyl formate can’t form enolate ions and thus can’t serve as donors. They can, however, act as the electrophilic acceptor components in reactions with other ester anions to give mixed β-keto ester products.
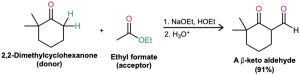
Mixed Claisen-like reactions can also be carried out between an ester and a ketone, resulting in the synthesis of a β-diketone. The reaction works best when the ester component has no α hydrogens and thus can’t act as the nucleophilic donor. For example, ethyl formate gives high yields in mixed Claisen condensations with ketones.
Worked Example 23.4 – Predicting the Product of a Mixed Claisen Condensation Reaction
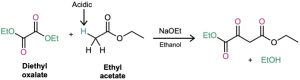
Diethyl oxalate, (CO2Et)2, often gives high yields in mixed Claisen reactions. What product would you expect to obtain from a mixed Claisen reaction of ethyl acetate with diethyl oxalate?
Strategy: A mixed Claisen reaction is effective when only one of the two partners has an acidic α hydrogen atom. In the present case, ethyl acetate can be converted into its enolate ion, but diethyl oxalate cannot. Thus, ethyl acetate acts as the donor and diethyl oxalate as the acceptor.
Solution:
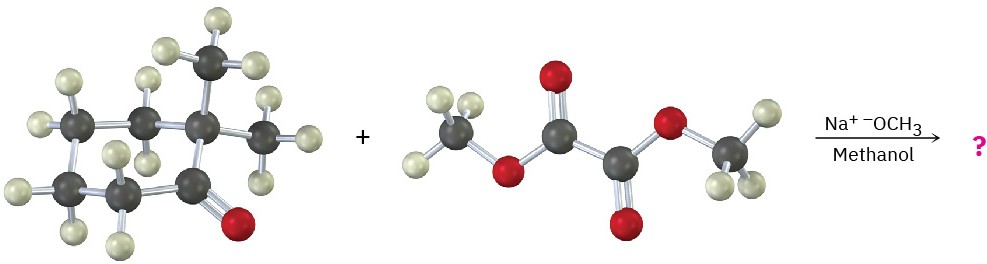
Problem 23-13
What product would you expect from the following mixed Claisen-like reaction?