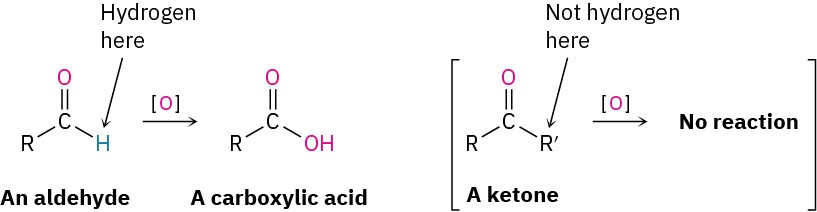
Aldehydes are easily oxidized to yield carboxylic acids, but ketones are generally inert toward oxidation. The difference is a consequence of structure: aldehydes have a –CHO proton that can be abstracted during oxidation, but ketones do not.
Many oxidizing agents, including alkaline KMnO4 and hot HNO3, convert aldehydes into carboxylic acids. The oxidation occurs rapidly at room temperature and generally works well.
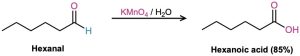
Aldehyde oxidations occur through intermediate 1,1-diols, or hydrates, which are formed by a reversible nucleophilic addition of water to the carbonyl group. Even though it’s formed to only a small extent at equilibrium, the hydrate reacts like any typical primary or secondary alcohol and is oxidized to a carbonyl compound (Section 17.7).

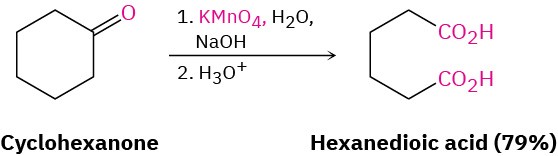
Ketones are inert to most oxidizing agents but undergo a slow cleavage reaction of the C–C bond next to the carbonyl group when treated with hot alkaline KMnO4. The reaction is not often used, however, and is mentioned here only for completeness.