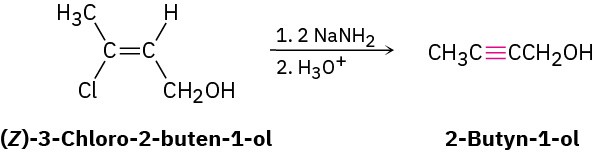Alkynes can be prepared by the elimination of HX from alkyl halides in a similar manner as alkenes (Section 8.1). Treatment of a 1,2-dihaloalkane (called a vicinal dihalide) with an excess amount of a strong base such as KOH or NaNH2 results in a twofold elimination of HX and formation of an alkyne. As with the elimination of HX to form an alkene, we’ll defer a full discussion of this topic and the relevant reaction mechanisms to Chapter 11.
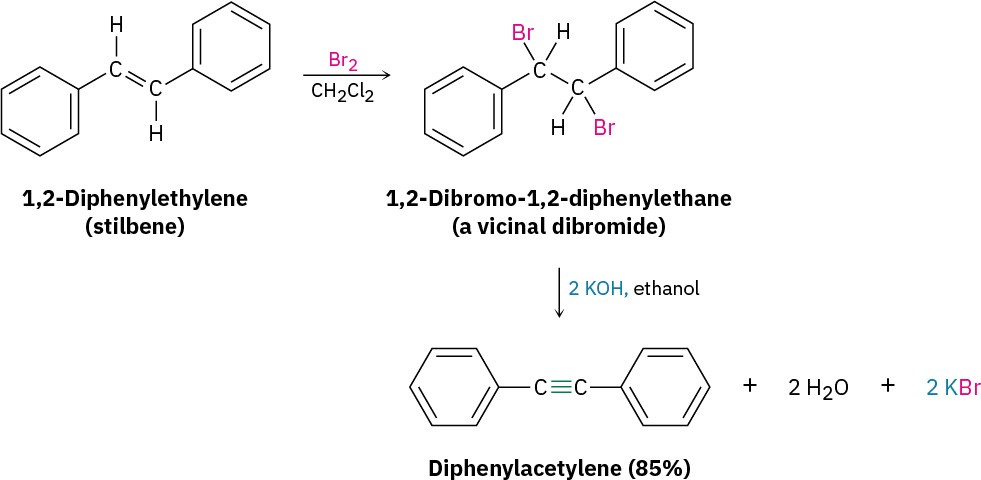
The starting vicinal dihalides are themselves readily available by addition of Br2 or Cl2 to alkenes. Thus, the overall halogenation/dehydrohalogenation sequence makes it possible to go from an alkene to an alkyne. For example, diphenylethylene is converted into diphenylacetylene by reaction with Br2 and subsequent base treatment.
The twofold dehydrohalogenation takes place through a vinylic halide intermediate, which suggests that vinylic halides themselves should give alkynes when treated with strong base. (A vinylic substituent is one that is attached to a double-bond.) This is indeed the case. For example: