The primary cellular function of mRNA is to direct the biosynthesis of the thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by an organism—as many as 150,000 in a human. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of about 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific ribonucleotide sequence in mRNA forms a message that determines the order in which amino acid residues are to be joined. Each “word,” or codon, along the mRNA chain consists of a sequence of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. For example, the series UUC on mRNA is a codon directing incorporation of the amino acid phenylalanine into the growing protein. Of the 43 = 64 possible triplets of the four bases in RNA, 61 code for specific amino acids and 3 code for chain termination. Table 28.1 shows the meaning of each codon.
Table 28.1 Codon Assignments of Base Triplets
|
|
|
||||
|
First base (5′ end) |
Second base |
U |
C |
A |
G |
|
U |
U |
Phe |
Phe |
Leu |
Leu |
|
C |
Ser |
Ser |
Ser |
Ser |
|
|
A |
Tyr |
Tyr |
Stop |
Stop |
|
|
G |
Cys |
Cys |
Stop |
Trp |
|
|
C |
U |
Leu |
Leu |
Leu |
Leu |
|
C |
Pro |
Pro |
Pro |
Pro |
|
|
A |
His |
His |
Gln |
Gln |
|
|
G |
Arg |
Arg |
Arg |
Arg |
|
|
A |
U |
Ile |
Ile |
Ile |
Met |
|
C |
Thr |
Thr |
Thr |
Thr |
|
|
A |
Asn |
Asn |
Lys |
Lys |
|
|
G |
Ser |
Ser |
Arg |
Arg |
|
|
G |
U |
Val |
Val |
Val |
Val |
|
C |
Ala |
Ala |
Ala |
Ala |
|
|
A |
Asp |
Asp |
Glu |
Glu |
|
|
G |
Gly |
Gly |
Gly |
Gly |
|
The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation. There are 61 different tRNAs, one for each of the 61 codons that specify an amino acid. A typical tRNA is single-stranded and has roughly the shape of a cloverleaf, as shown in Figure 28.7. It consists of about 70 to 100 ribonucleotides and is bonded to a
specific amino acid by an ester linkage through the 3′ hydroxyl on ribose at the 3′ end of the tRNA. Each tRNA also contains on its middle leaf a segment called an anticodon, a sequence of three ribonucleotides complementary to the codon sequence. For example, the codon sequence UUC present on mRNA is read by a phenylalanine-bearing tRNA having the complementary anticodon base sequence GAA. [Remember that nucleotide sequences are written in the 5′ → 3′ direction, so the sequence in an anticodon must be reversed. That is, the complement to (5′)-UUC-(3′) is (3′)-AAG-(5′), which is written as (5′)-GAA-(3′).]
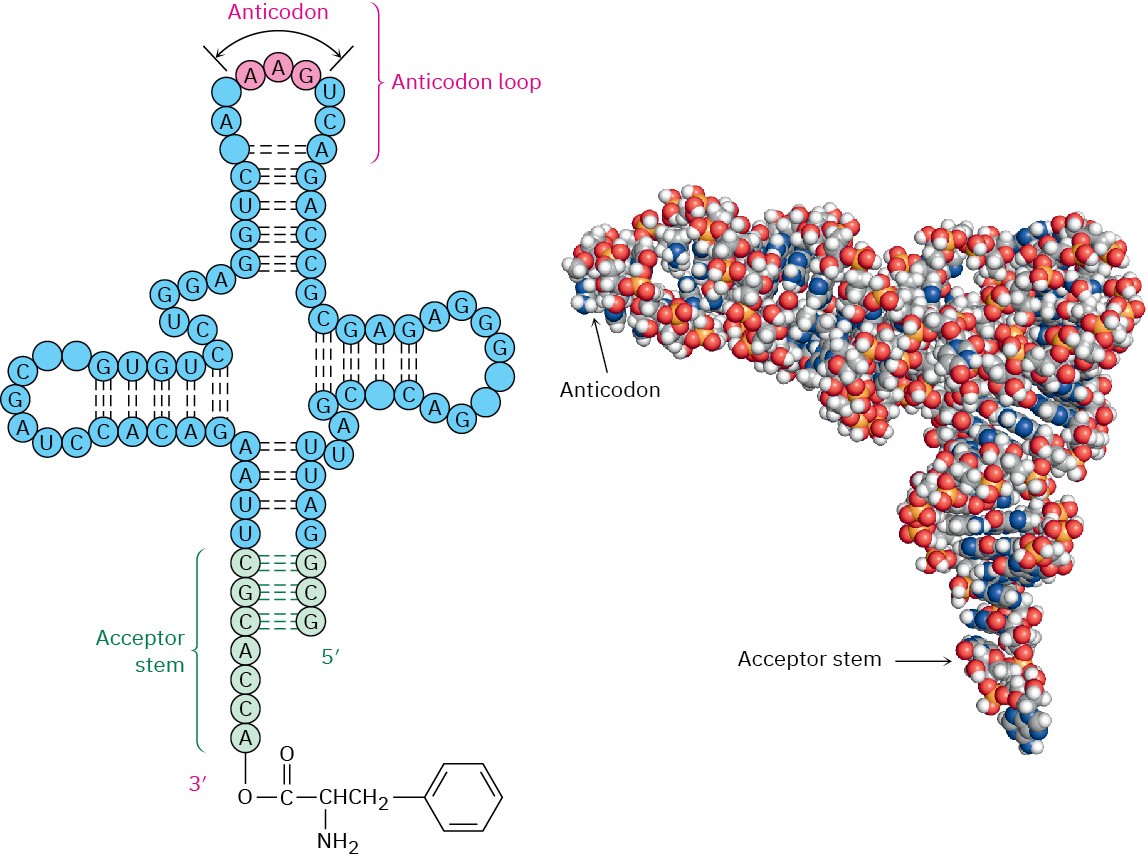
Figure 28.7 Structure of a tRNA molecule. The tRNA is a roughly cloverleaf-shaped molecule containing an anticodon triplet on one “leaf” and an amino acid unit attached covalently at its 3′ end. The example shown is a yeast tRNA that codes for phenylalanine. The nucleotides not specifically identified are chemically modified analogs of the four common nucleotides.
As each successive codon on mRNA is read, different tRNAs bring the correct amino acids into position for enzyme-mediated transfer to the growing peptide. When synthesis of the proper protein is completed, a “stop” codon signals the end, and the protein is released from the ribosome. This process is illustrated in Figure 28.8.
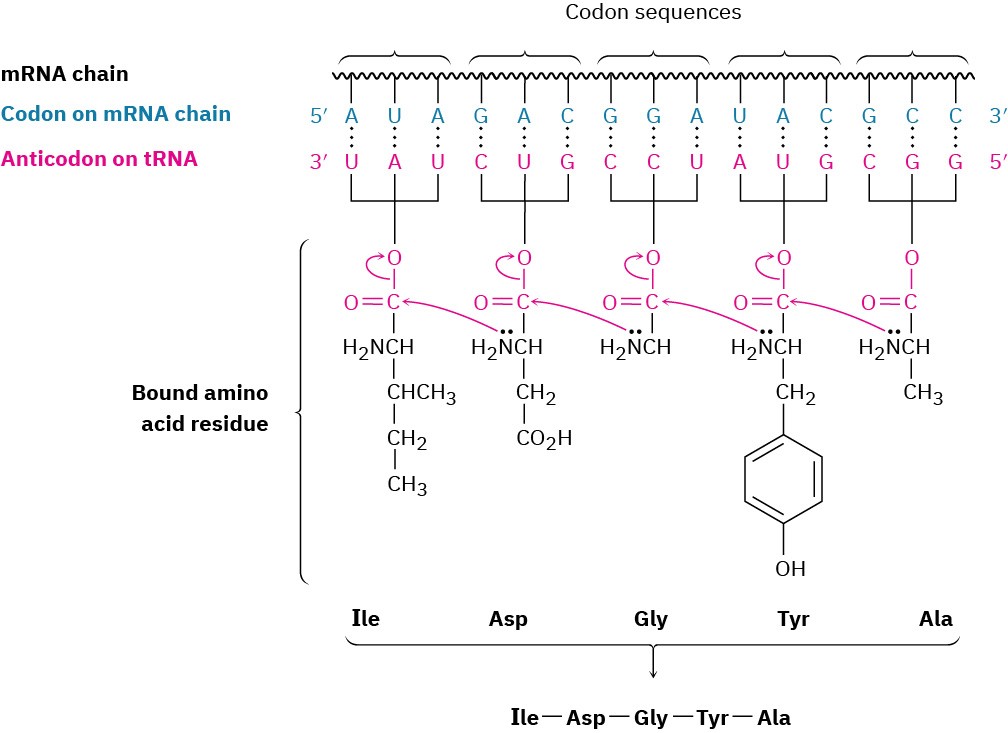
Figure 28.8 A representation of protein biosynthesis. The codon base sequences on mRNA are read by tRNAs containing complementary anticodon base sequences.
Transfer RNAs assemble the proper amino acids into position for incorporation into the growing peptide.
Worked Example 28.2Predicting the Amino Acid Sequence Transcribed from DNAWhat amino acid sequence is coded by the following segment of a DNA coding strand (sense strand)?(5′) CTA-ACT-AGC-GGG-TCG-CCG (3′)StrategyThe mRNA produced during translation is a copy of the DNA coding strand, with each T replaced by U. Thus, the mRNA has the sequence(5′) CUA-ACU-AGC-GGG-UCG-CCG (3′)Each set of three bases forms a codon, whose meaning can be found in Table 28.1.SolutionLeu-Thr-Ser-Gly-Ser-Pro.
Problem 28-7
List codon sequences for the following amino acids: (a)
Ala (b) Phe (c) Leu (d) Tyr
Problem 28-8
List anticodon sequences on the tRNAs carrying the following amino acids. (a)
Ala (b) Phe (c) Leu (d) Tyr
Problem 28-9
What amino acid sequence is coded by the following mRNA base sequence? CUU-AUG-GCU-UGG-CCC-UAA
Problem 28-10
What is the base sequence in the original DNA strand on which the mRNA sequence in Problem 28-9 was made?

