Example Practical Exam Answers
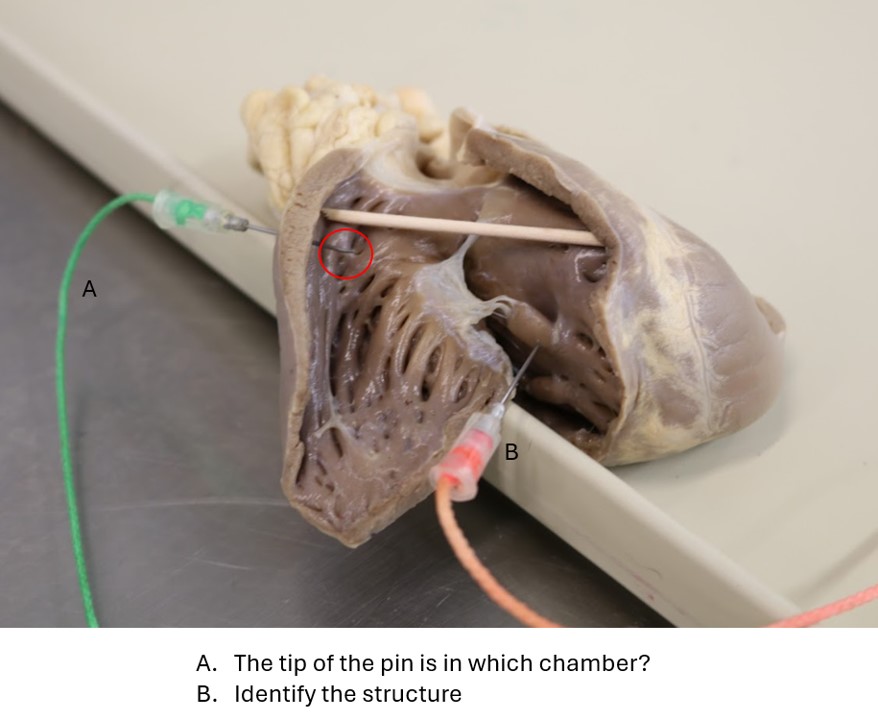
Lab 1 Heart 1
A. Right ventricle
B. Papillary muscle
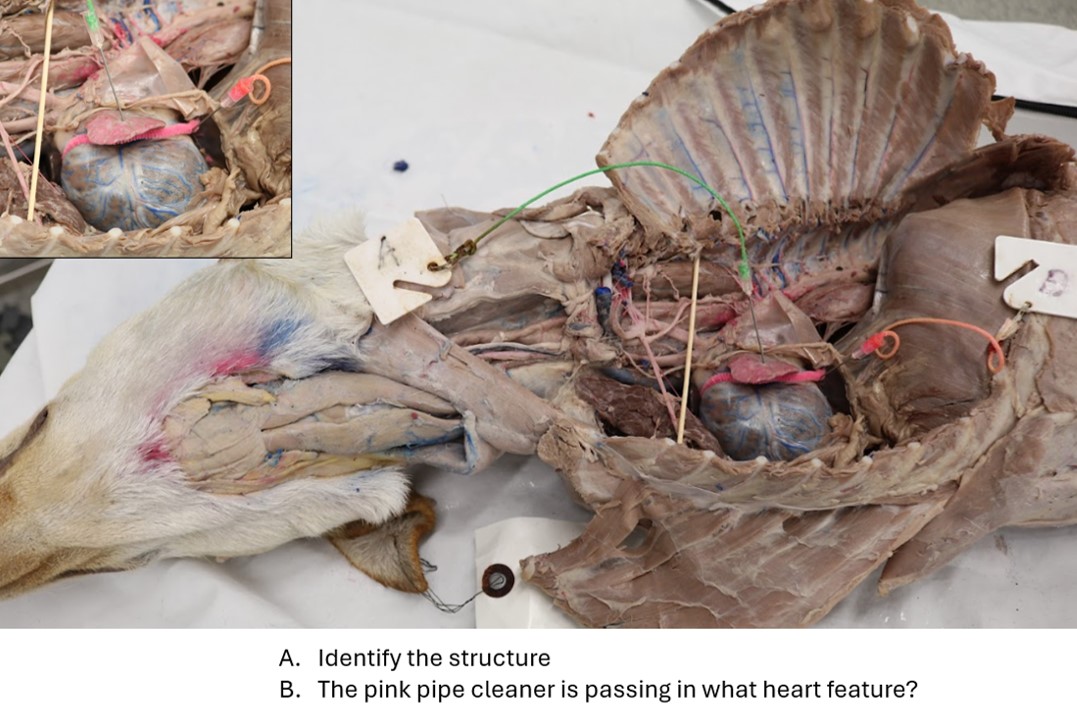
Lab 1 Heart 2
A. Left auricle
B. Coronary groove
Lab 2 Dog thorax
A. Costocervical trunk
B. Descending aorta
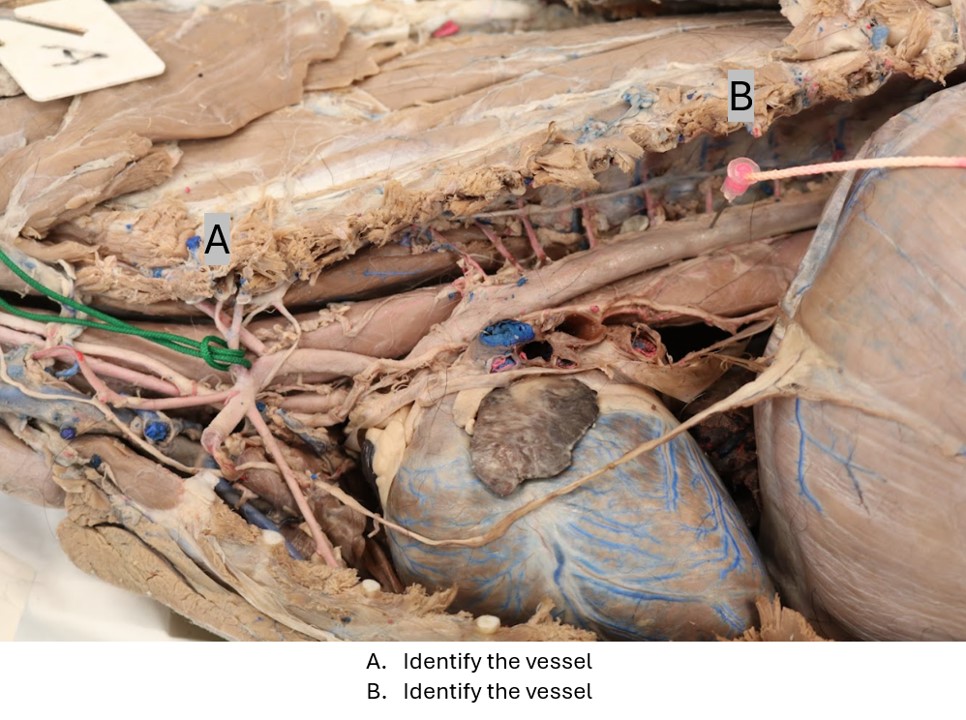
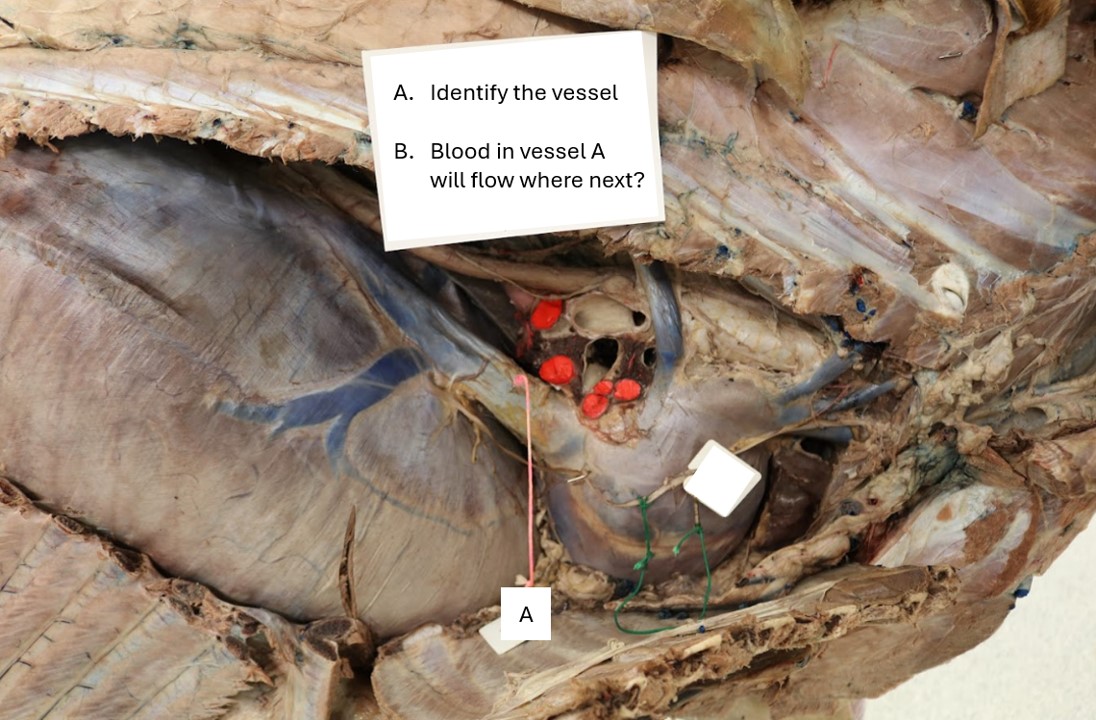
Lab 2 Horse thorax
A. Caudal vena cava
B. Right atrium
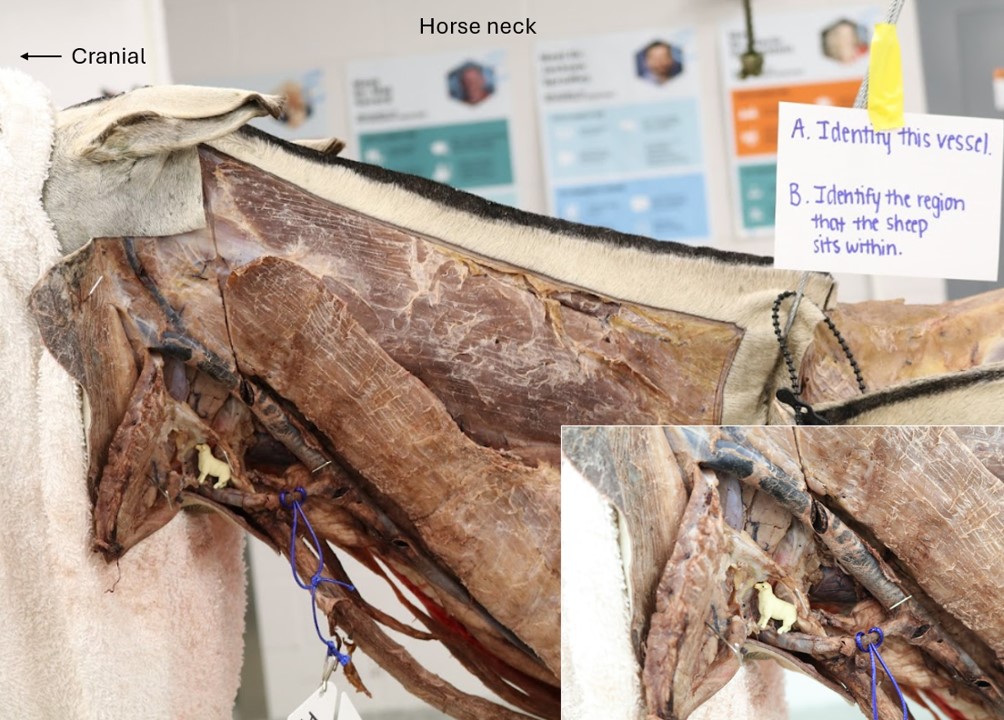
Lab 4 Horse neck
A. Linguofacial vein
B. Viborg’s triangle
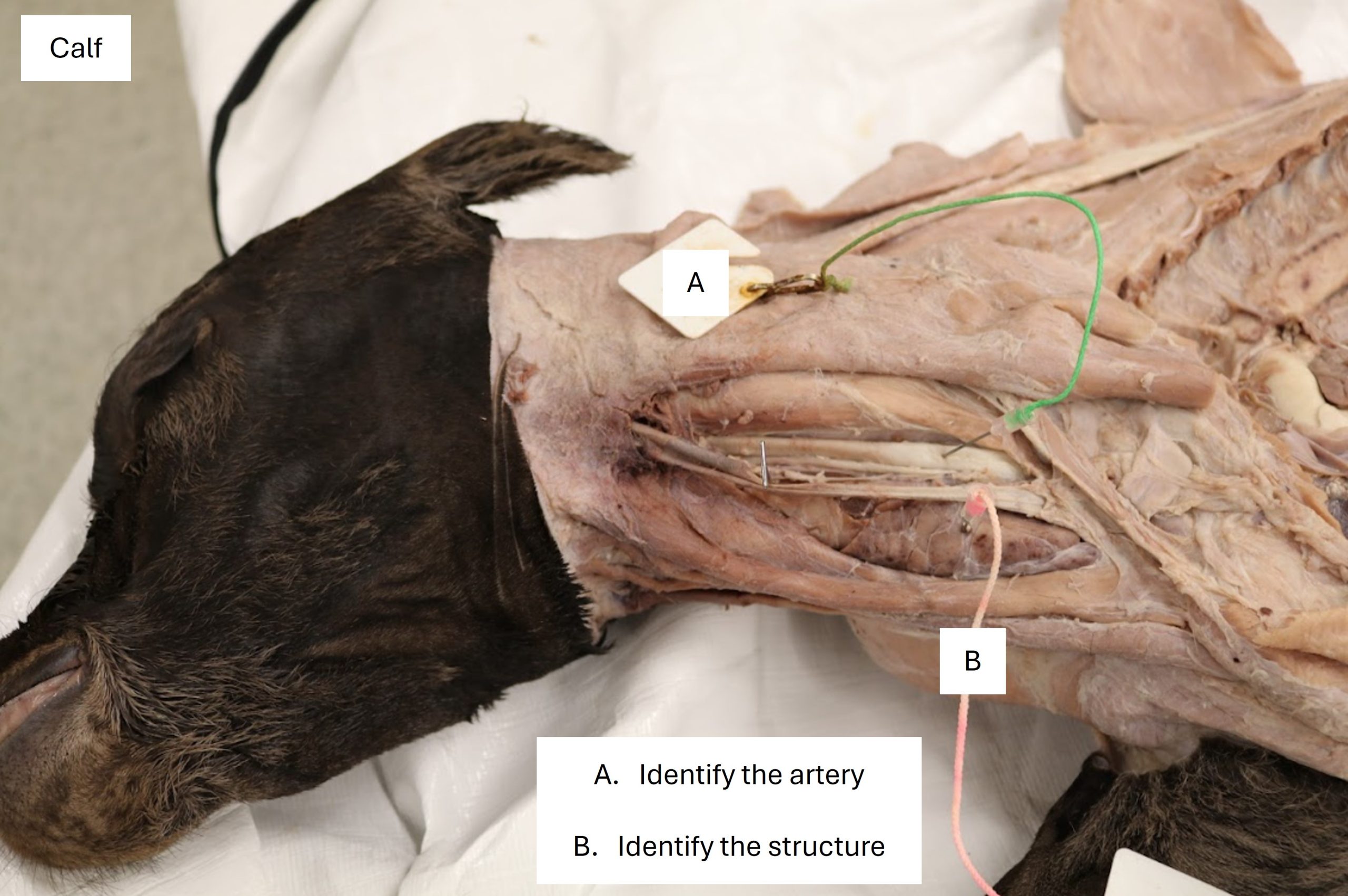
Lab 4 Calf
A. Common carotid a. (calf is unlatexed)
B. Thymus (cervical part)
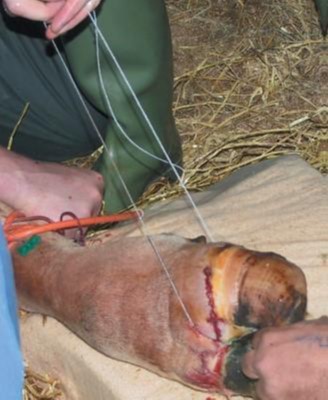
Cow Digit Amputation
Review the image and ponder the following questions.
1) What common cutting device is being used to amputate the digit (claw)?
Gigli wire is the cutting device.
2) What ligament of the ruminant foot must be transected to allow removal of one digit, if amputation is through the mid shaft of the proximal phalanx?
The distal interdigital ligament.
3) Note the green butterfly catheter and orange torniquet – what vessel has likely been catheterized? What drug may have been injected?
The dorsal common digital v. 3
Local anesthetic.
Dog thoracic limb artery
A. Cranial circumflex humeral artery
B. Superficial brachial artery
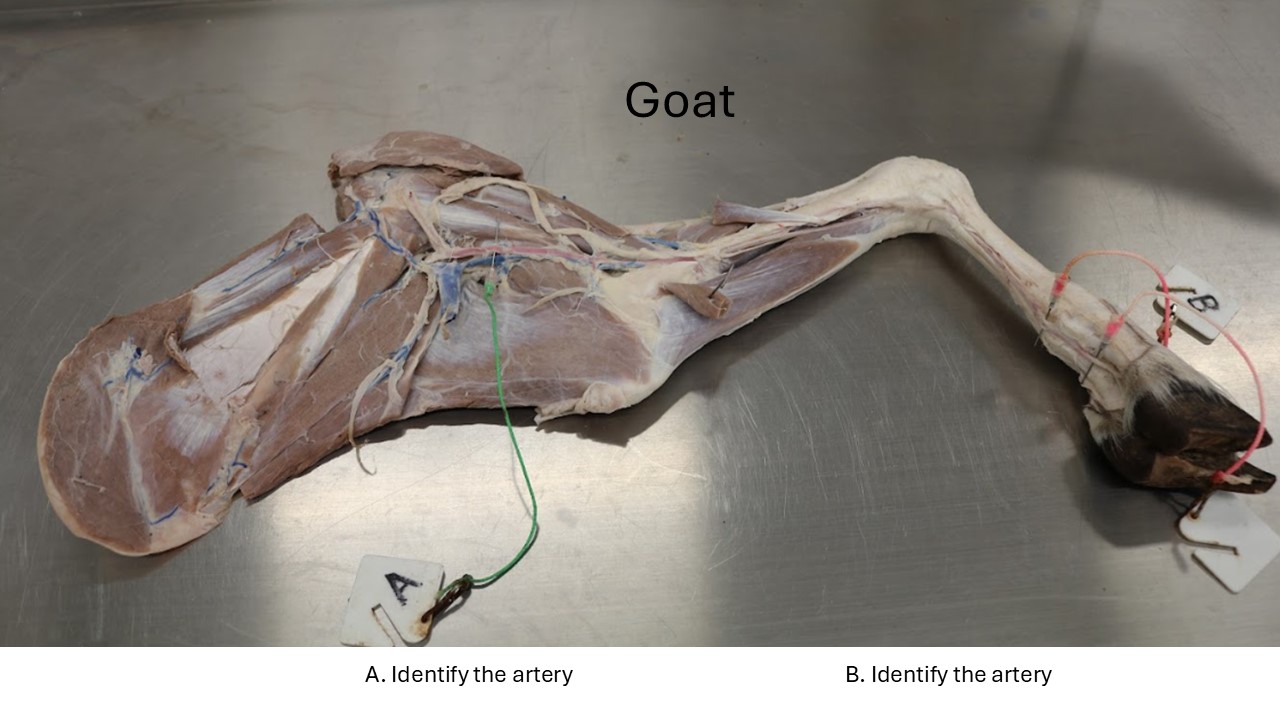
Goat thoracic limb artery
A. Brachial artery
B. Palmar common digital artery III
Lab 1 Clinical Application:
Q: In what intercostal space, and on what side of the patient, would you perform a pericardiocentesis in a dog? And in a cat? Why?
A: Right 4th ICS of the dog and 5th ICS of the cat. The cardiac notch allows for passage of the needle into the pericardial cavity while avoiding the lungs.
Lab 5 Clinical Application (mammary mass):
Question: You are presented with a twelve year old, intact, female domestic shorthair cat. On physical examination, you noted an approximately 1 cm, firm, non-movable mass on the left, cranial-most mamma/teat. Afferent lymph from the affected region flows to which lymph node first? Where does efferent lymph from this node go next?
Answer: Left axillary lymph node to tracheal trunk or thoracic duct or venous system.
Lab 5 Clinical Application (digit amputation):
Question: How many arteries provide blood supply to this digit at the level of the third phalange?
Four
Question: On physical examination, you had noted that the ipsilateral superficial cervical lymph node was enlarged. What is another important diagnostic step you should take in this case?
Perform a fine needle aspirate of the superficial cervical lymph node to determine if metastatic cells are observed.
Question: What information are you obligated to give about the patient given you will be removing the third phalanx in particular?
Digits three and four are weight-bearing in the carnivores. The owners should expect on-going lameness on the affected limb which may not resolve fully.
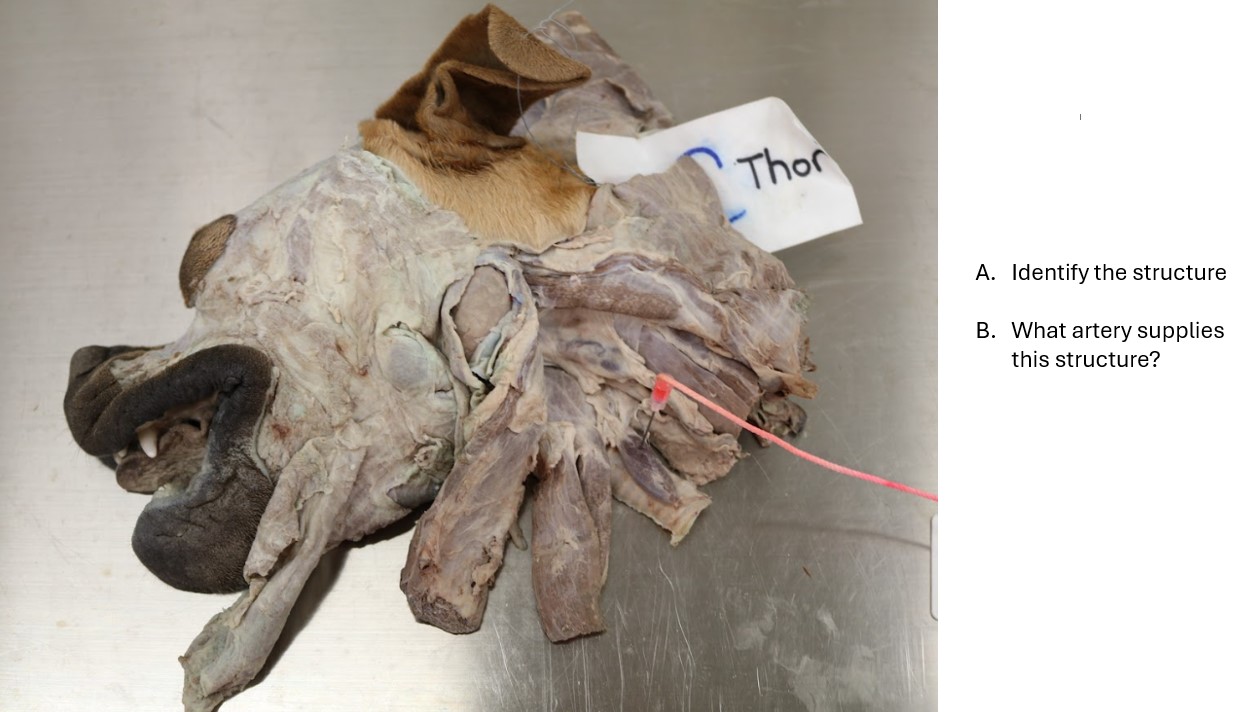
Dog thyroid gland
A. Thyroid gland
B. Cranial thyroid artery
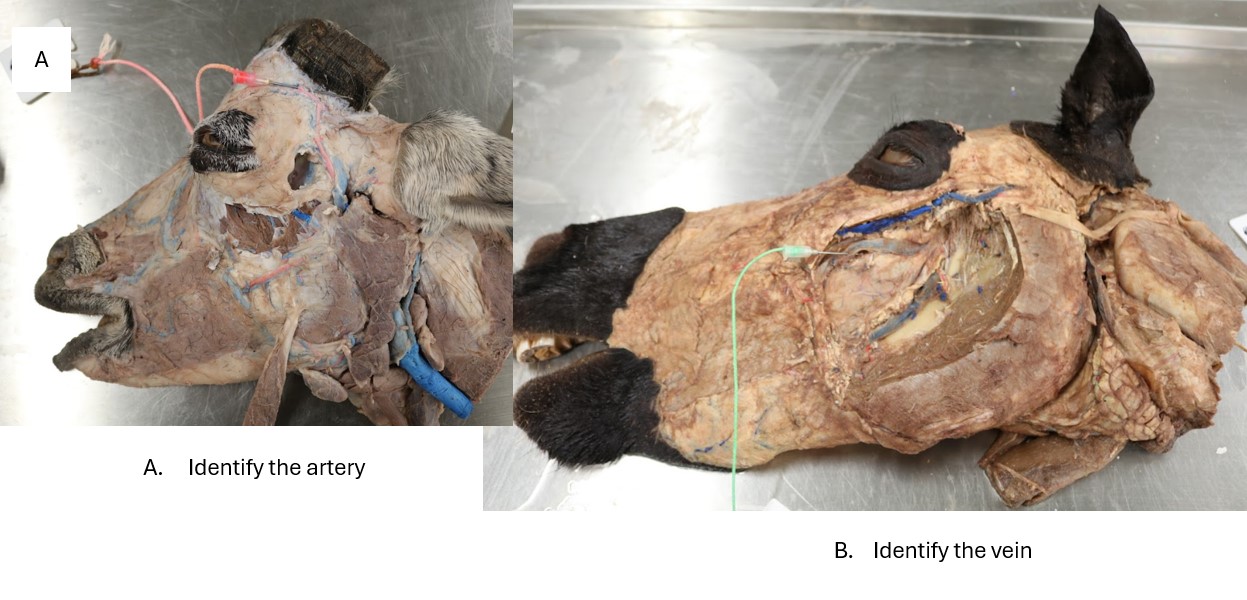
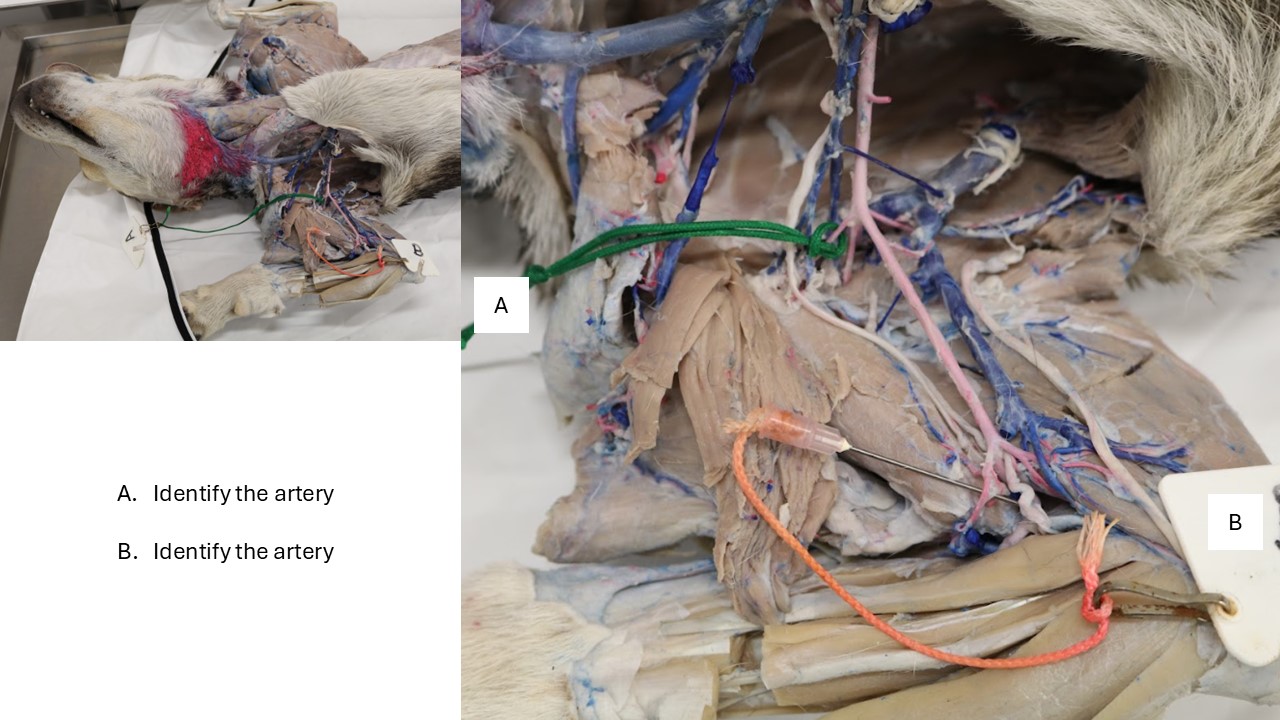
Goat and horse arteries
A. Cornual artery
B. Deep facial vein
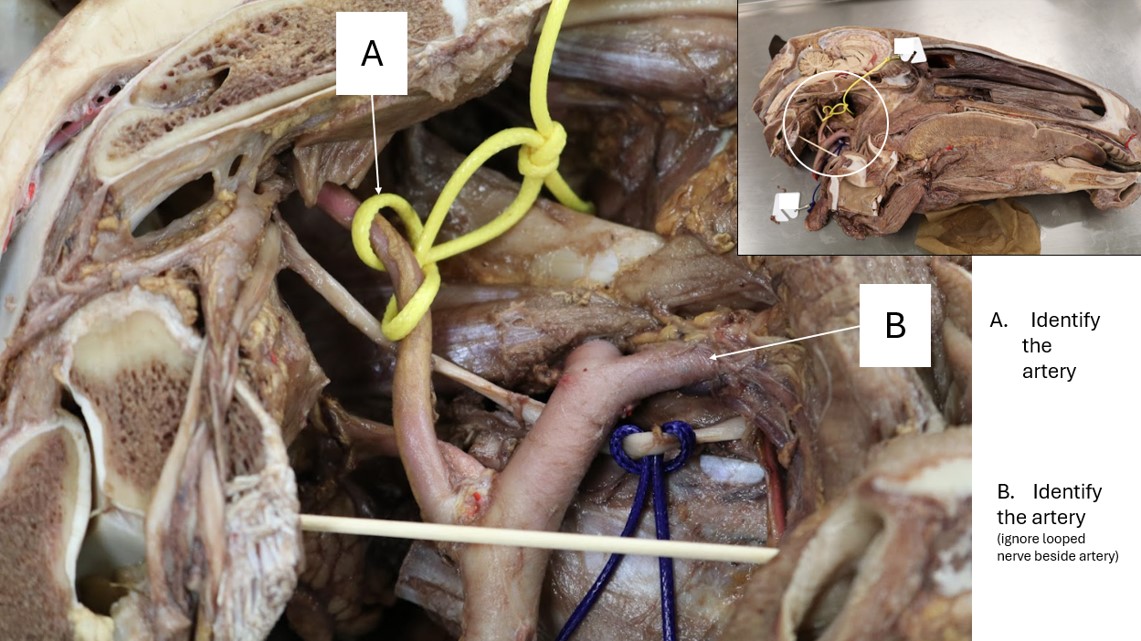
Horse arteries
A. Internal carotid artery
B. Linguofacial trunk (FYI: running with looped hypoglossal nerve)
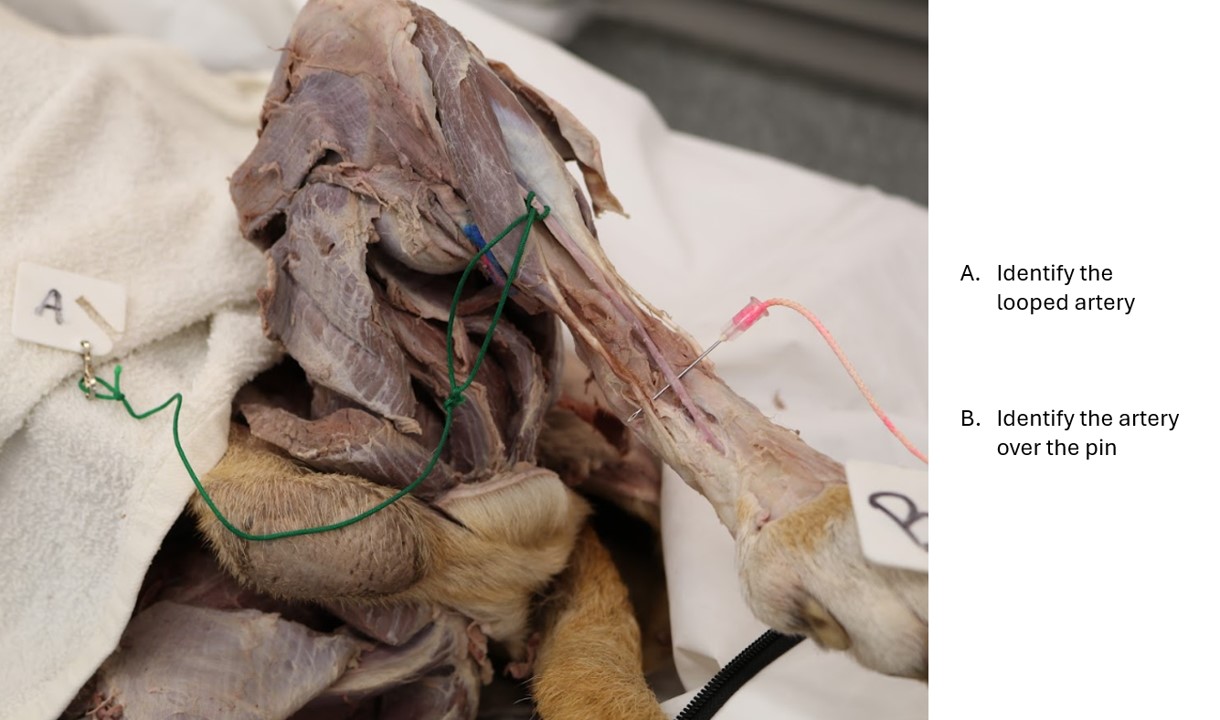
Dog pelvic limb arteries
A. Cranial tibial a.
B. Dorsal pedal a.
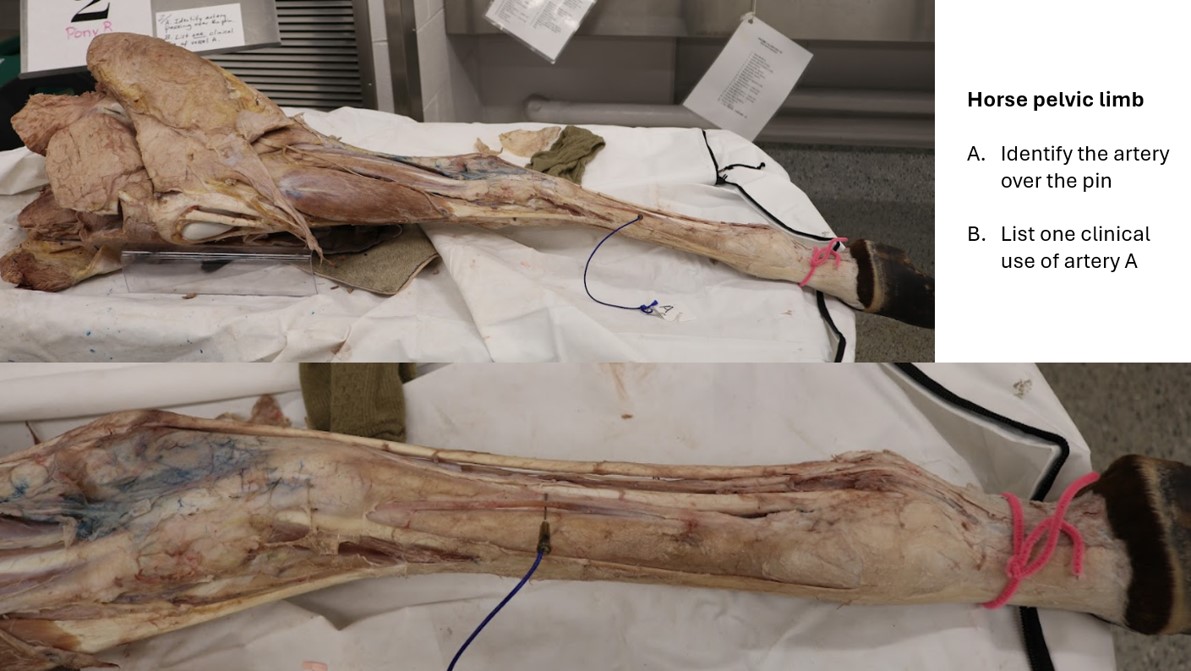
Horse pelvic limb artery
A. Dorsal metatarsal a. III
B. Taking a pulse; blood pressure monitoring; arterial blood gas