Example Practical Exam Answers
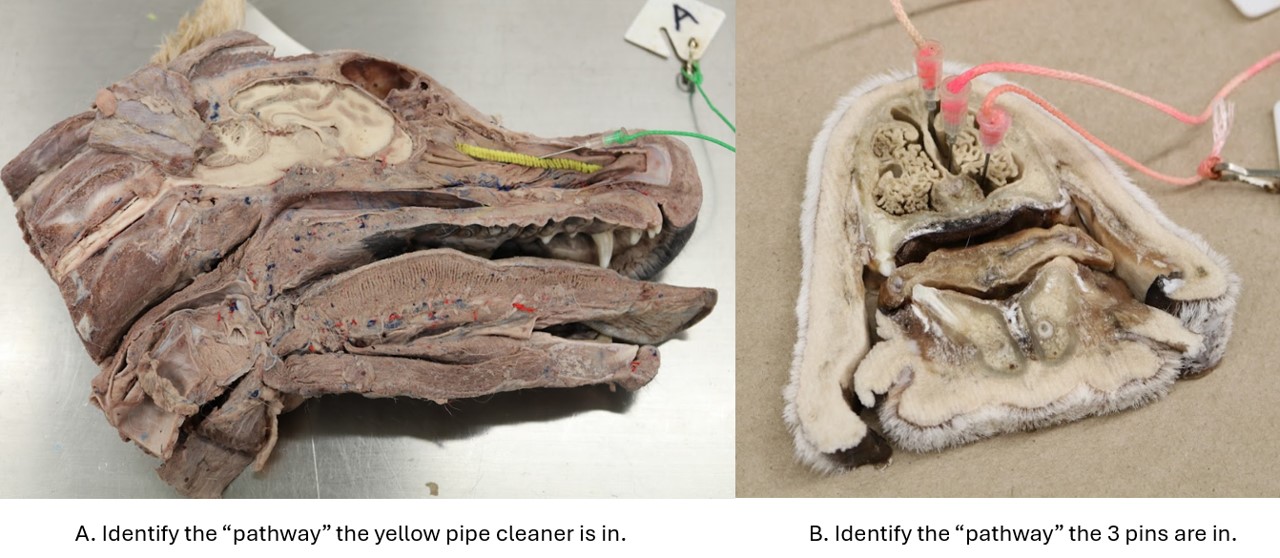
Lab 1 Dog
A. Middle nasal meatus
B. Common nasal meatus
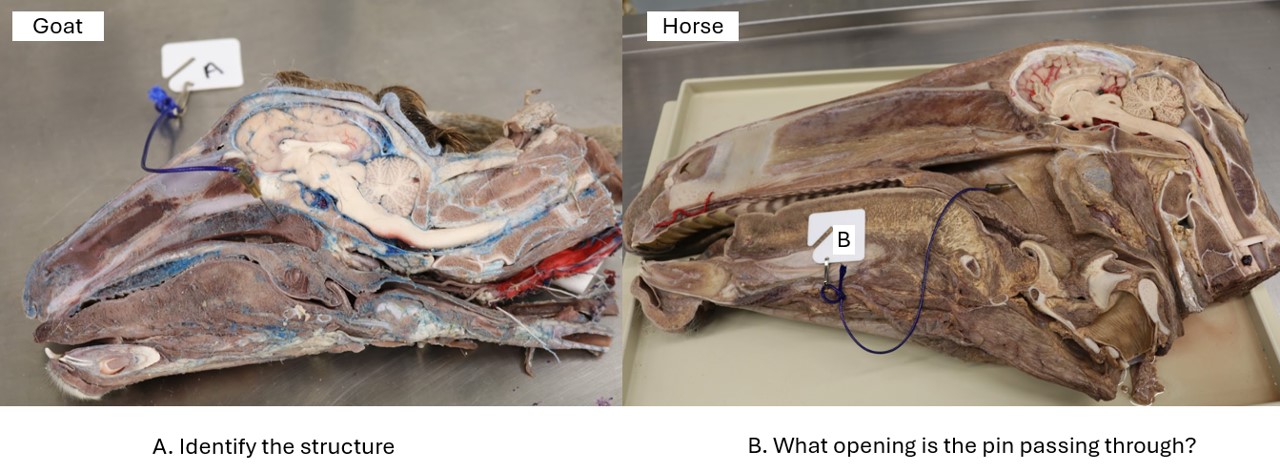
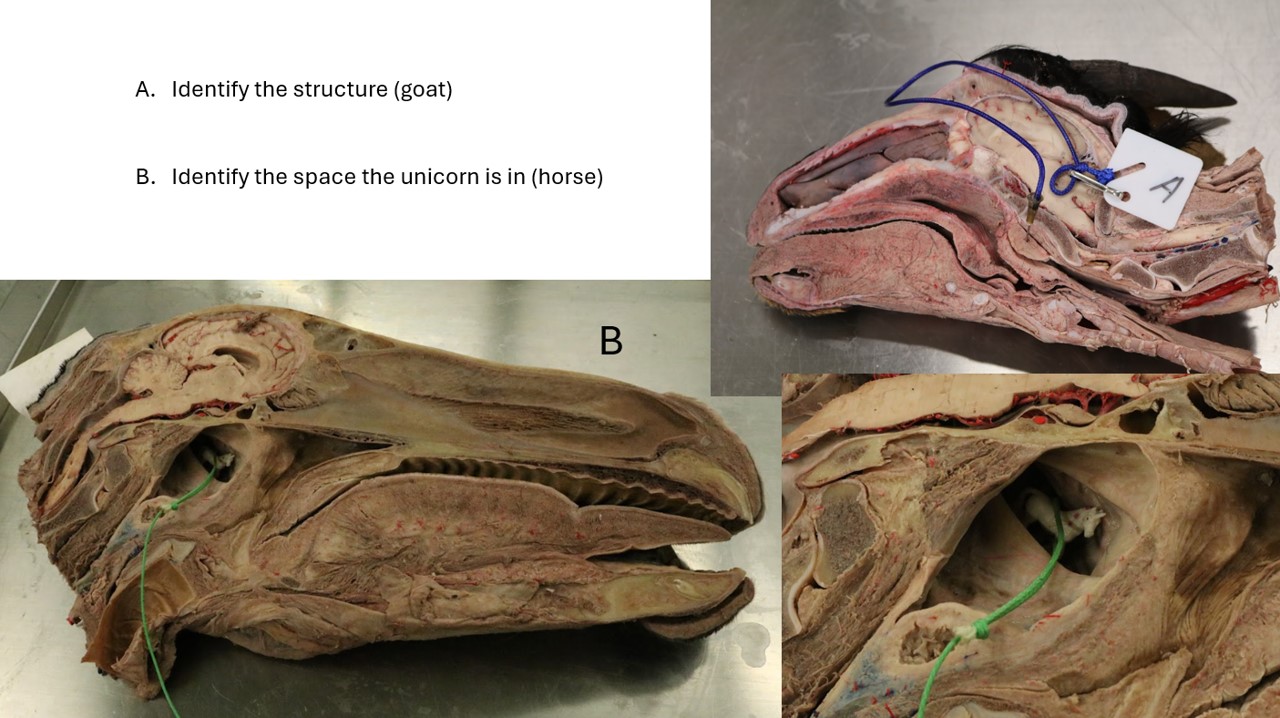
Lab 1 Goat & Horse
A. Pharyngeal septum
B. Nasopharyngeal opening of the auditory tube
Lab 1 Clinical application
B – Atheroma. This is a type of epidermal cyst that grows in the nasal diverticulum.
Lab 2 Dog larynx
A. Thyroid cartilage
B. Laryngeal ventricle
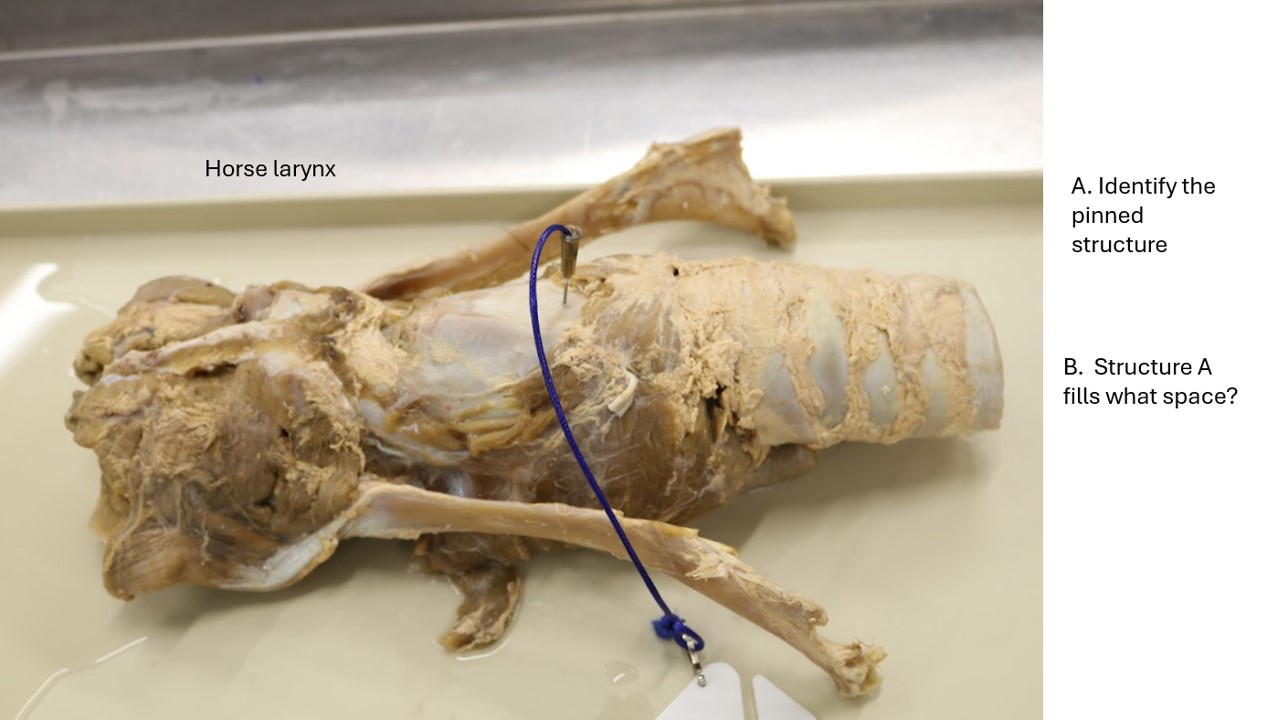
Lab 2 horse larynx
A. Cricothyroid ligament
B. Thyroid notch
Lab 3 clinical case
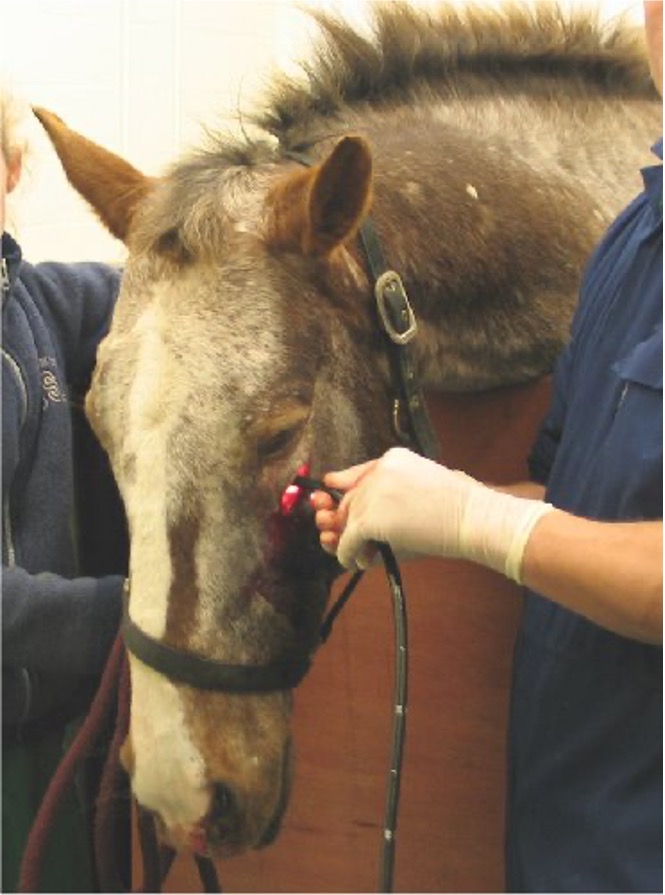
This horse is having sinoscopy performed, with the endoscope passed through a hole made into the paranasal sinuses. Based on the location of the entry point, which paranasal sinus is the endoscope entering (review figures of paranasal sinus anatomy).
A – frontal sinus; B – rostral maxillary sinus; C – caudal maxillary sinus; D – dorsal conchal sinus; E – sphenopalatine sinus.
Answer = C-caudal maxillary sinus. To enter the caudal maxillary sinus the portal is made about 2 cm rostral to the rim of the orbit and 2 cm ventral to the line joining the medial canthus and the infraorbital foramen on that side (which approximates the nasolacrimal duct pathway).
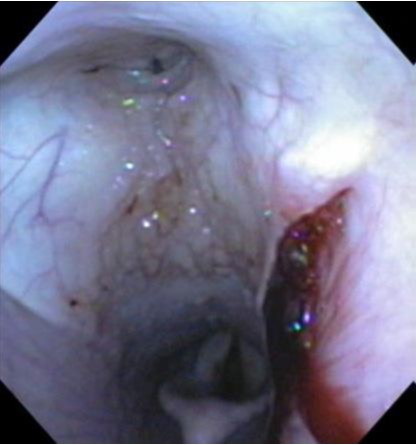
Lab 3 Clinical case
This is an endoscopic view of a horse’s nasopharynx, looking caudally towards the larynx. This horse has a history of sudden onset profuse nasal hemorrhage (epistaxis), that slowed after a few minutes, and the horse was referred on emergency for work up. From what opening is the blood exiting?
A – the laryngopharynx and start of the esophagus
B – the entrance to the larynx
C – the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube
D – the nasomaxillary opening.
Answer = C – the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube
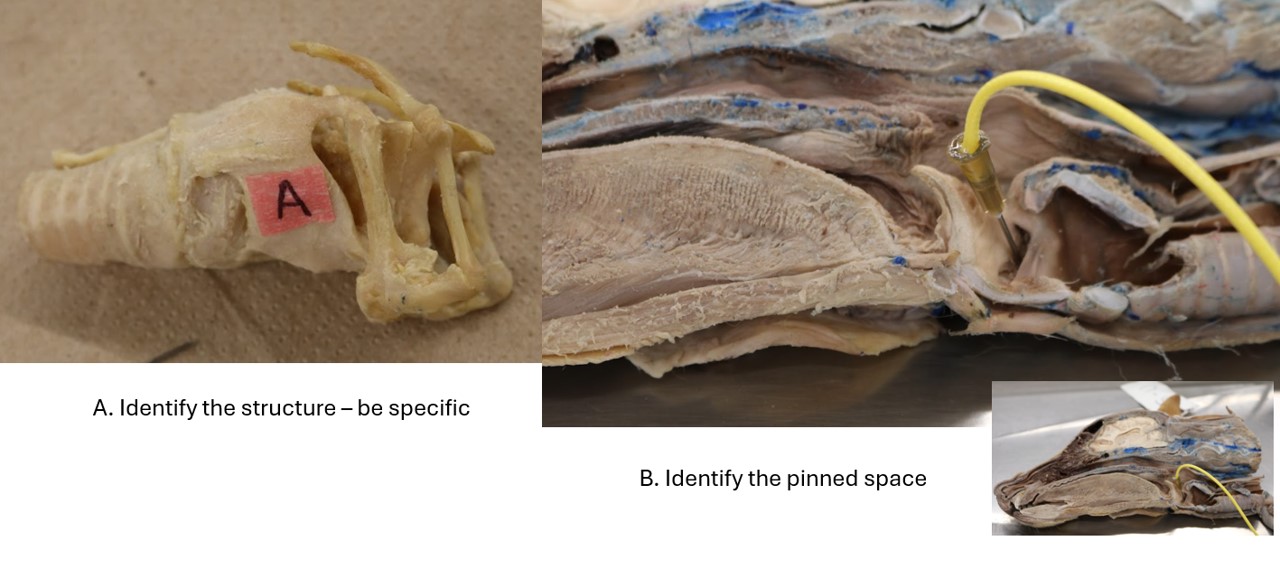
Lab 3 Sinus
A. Conchofrontal sinus
B. Palatine sinus
Lab 3 exam
A. Medial retropharyngeal lymph node
B. Lateral compartment of the guttural pouch
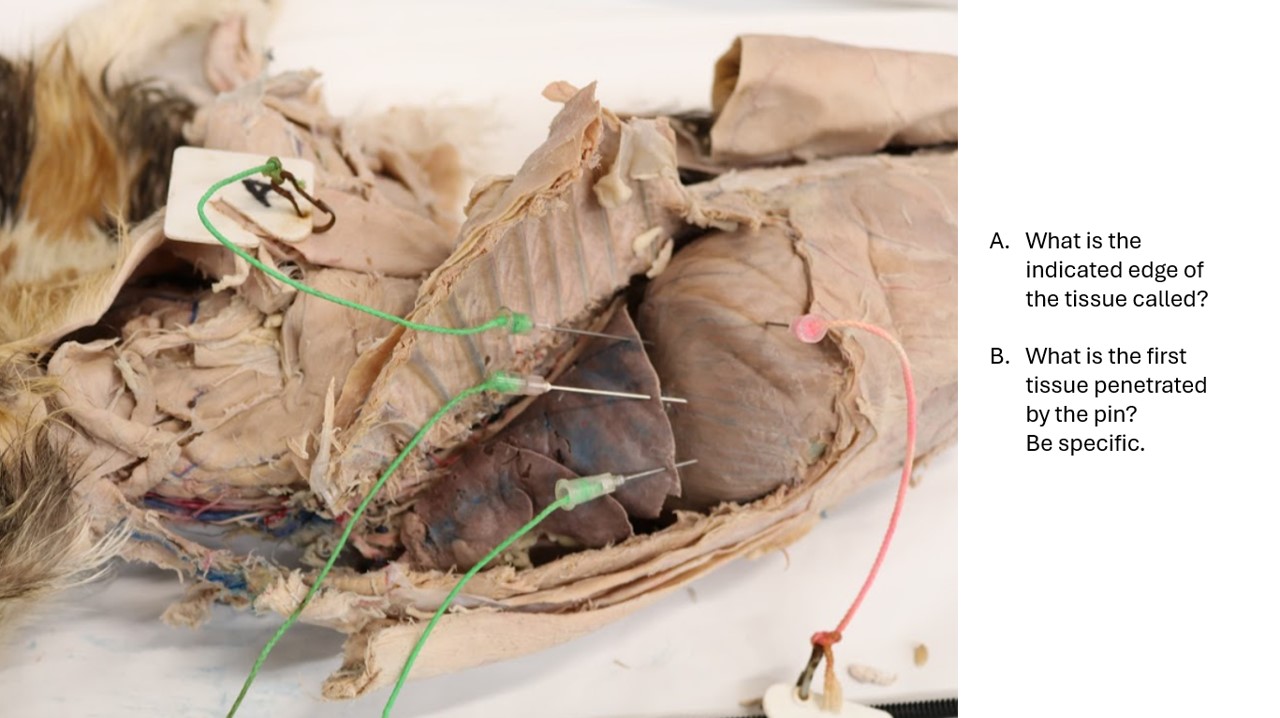
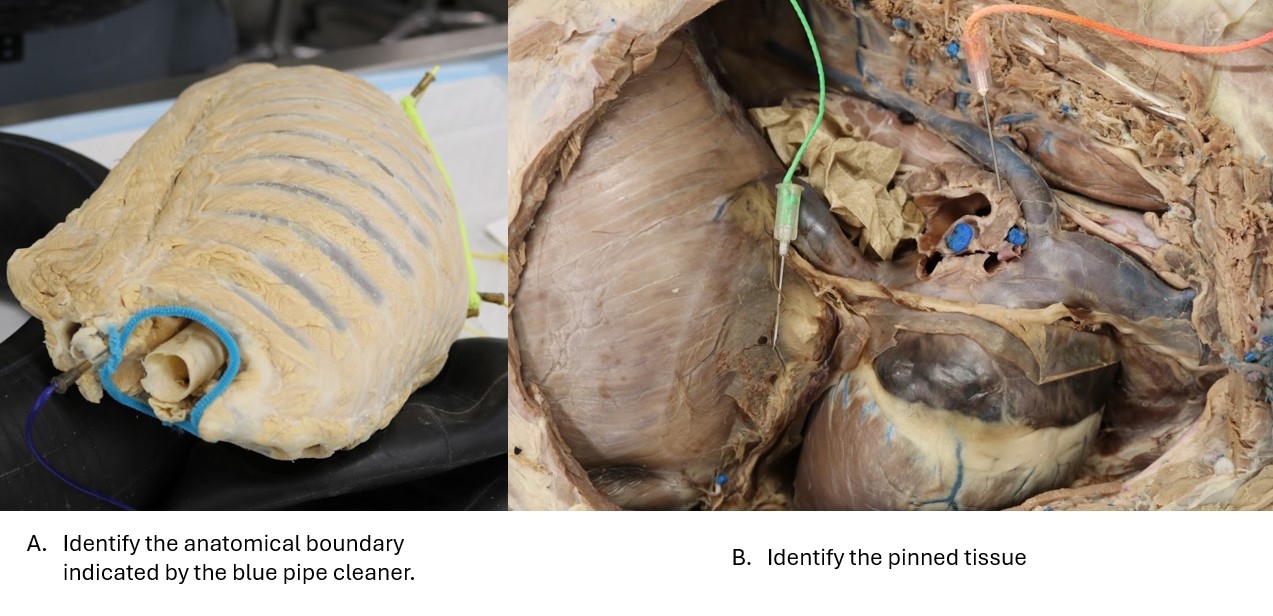
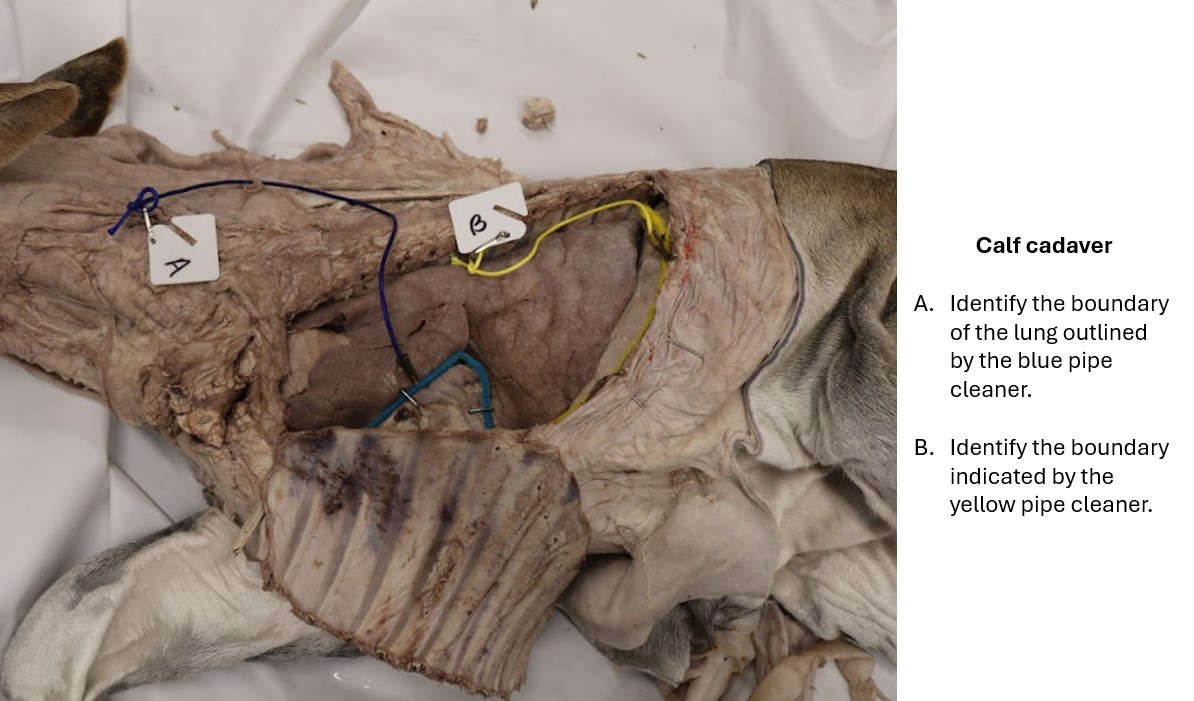
Lab 5 cat lung
A. Basal border of the lung
B. Diaphragmatic parietal pleura
Lab 5 Pleura
A. Thoracic inlet
B. Plica vena cava
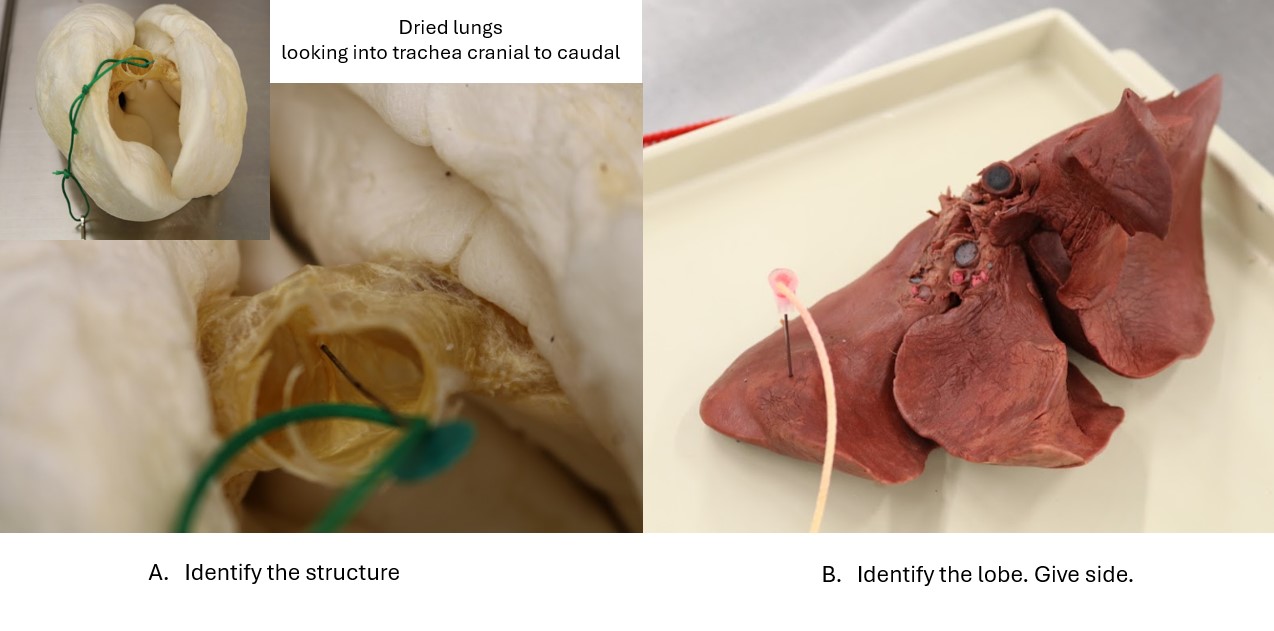
Lab 7 Clinical relevance: tracheal bronchus and intubation
A pig is induced for general anesthesia and will be maintained on gas anesthesia for its procedure. If the tracheal bronchus was inadvertently intubated when passing the endotracheal tube, what single lung lobe will be aerated (and therefore lead to significant complications with anesthesia)?
Answer: Right cranial lung lobe
Lab 7 Dog lungs
A: Carina
B. Right cranial