Example Practical Exam Answers
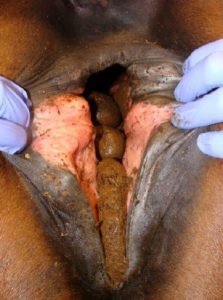
Lab 6 Rectal Tear
Examining a foaling injury about 3 months post foaling in a mare.
Q: What is your diagnosis?
Answer: 3rd degree perineal laceration – full tearing of rectal floor, perineal body, and vaginal roof through to skin surface. Hence feces dropping down into vagina and exiting vulva.
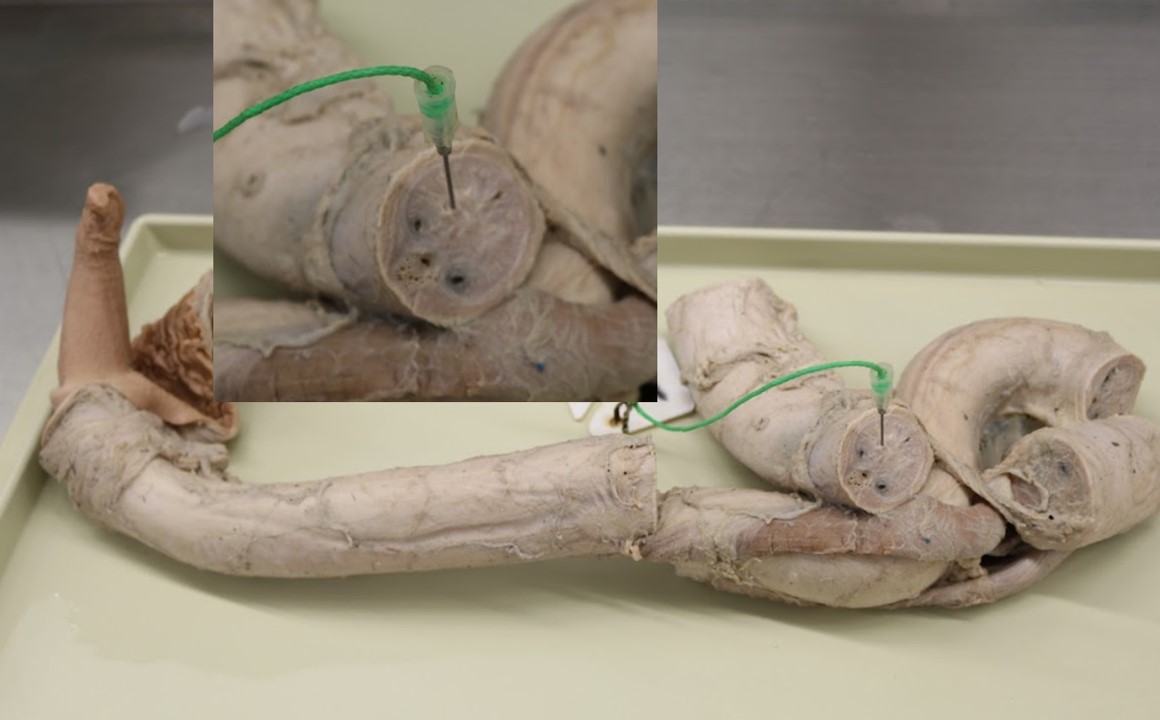
Lab 6 Dog
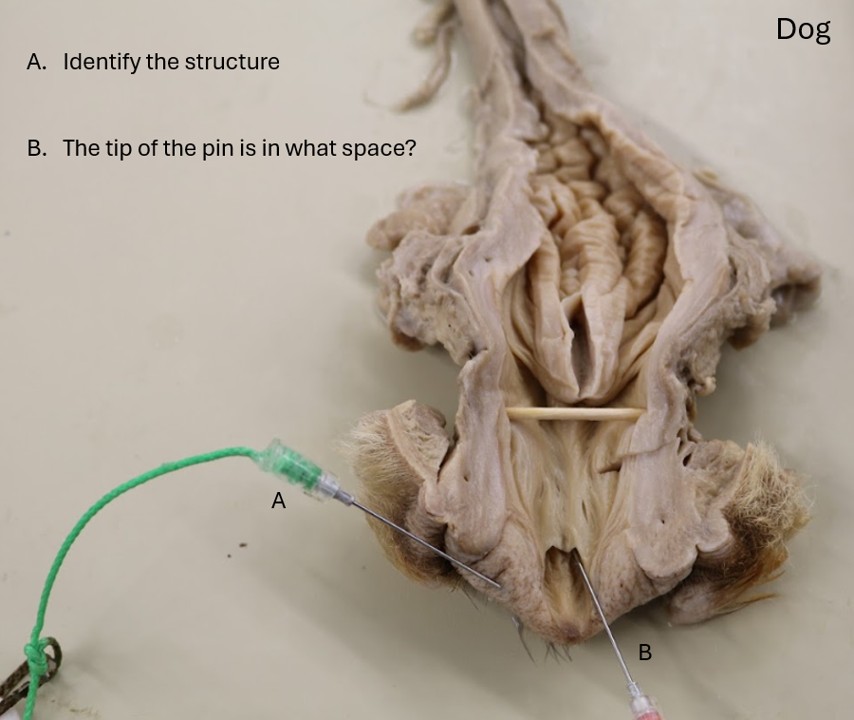
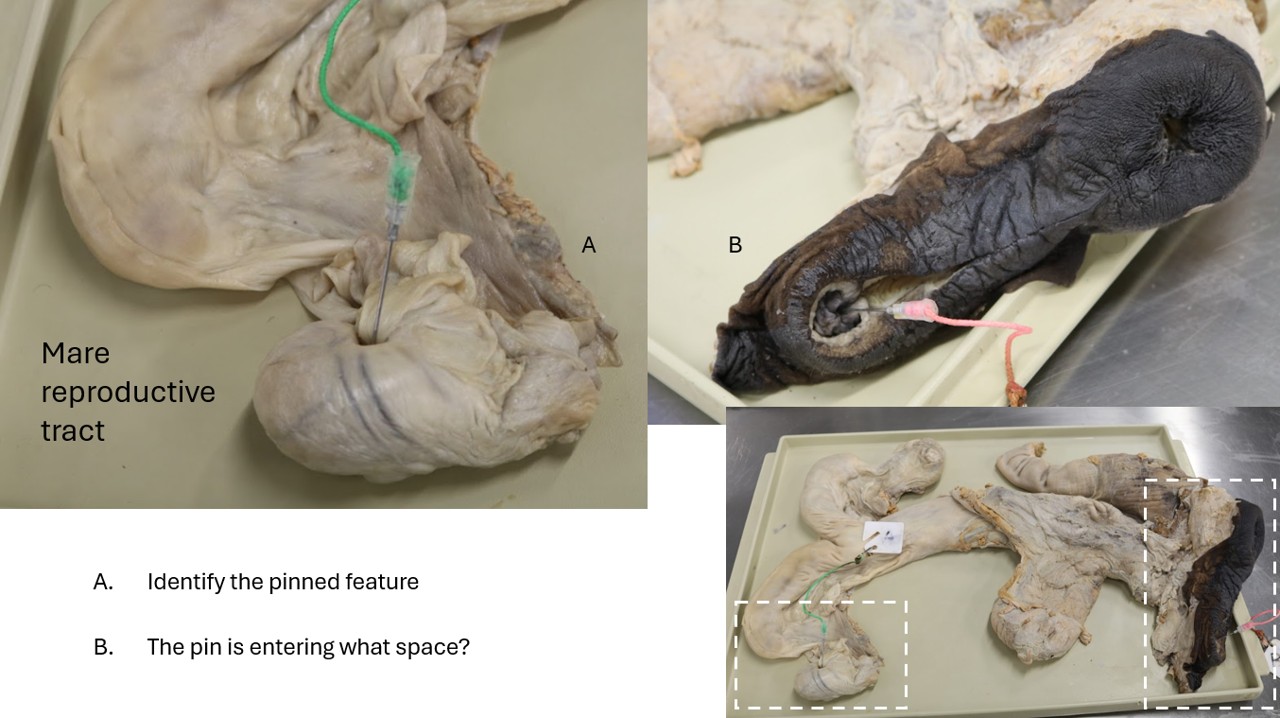
Lab 6 Mare tract
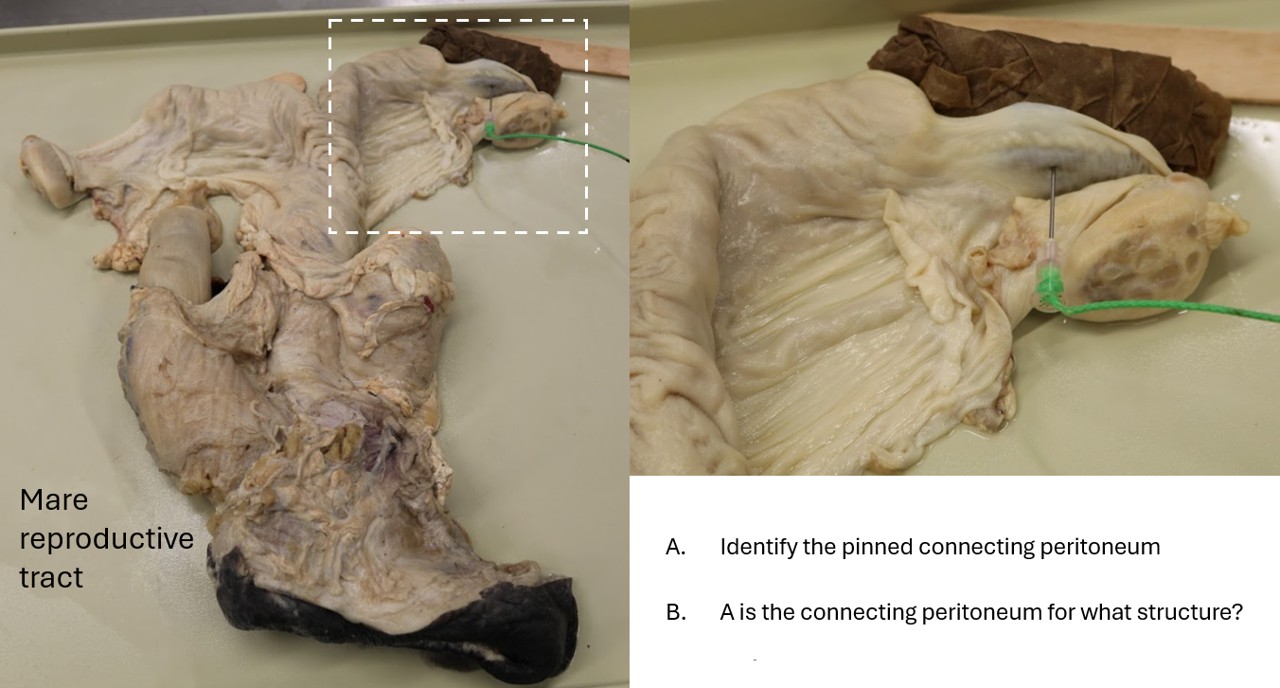
Lab 6 Mare Tract
Review question:
The caudal gluteal a. gives rise to the cranial gluteal artery (any chance you remember what muscles these old friends supply?
Answer: middle and deep gluteal muscles
Lab 10 Clinical Relevance: Patent Urachus
Patent urachus is not an uncommon condition in foals and an ascending infection at the site with abscess formation or systemic septicemia is a concern. Ruptured bladder/urachus, most commonly in the male foal, is also well recognized clinically with development of uroperitoneum and consequent electrolyte and acid-base disturbances. Surgical and medical therapies are utilized to manage these conditions.
Q4: What does not appear normal? What might be a cause?
Answer: Enlarged umbilicus; infection, hernia are two possible causes.
Lab 10 Placenta

A. Identify the tissue layer
B. Describe this placenta using two words (how is it classified?)
Answer:
A. Chorion
B. Diffuse epitheliochorial
Lab 10 Udder
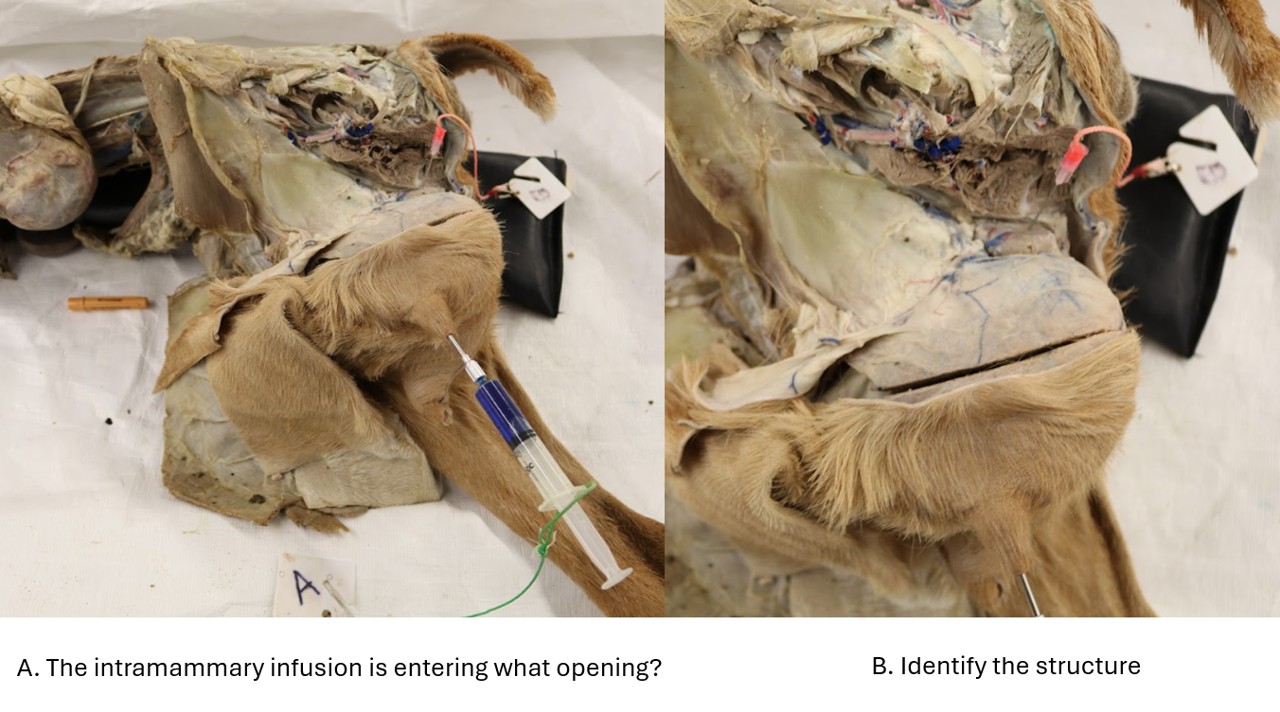
A. The intramammary infusion is entering what opening?
B. Identify the structure
Answer:
A. Teat orifice
B. Mammary (or superficial inguinal) lymph node
Lab 11 Innervation
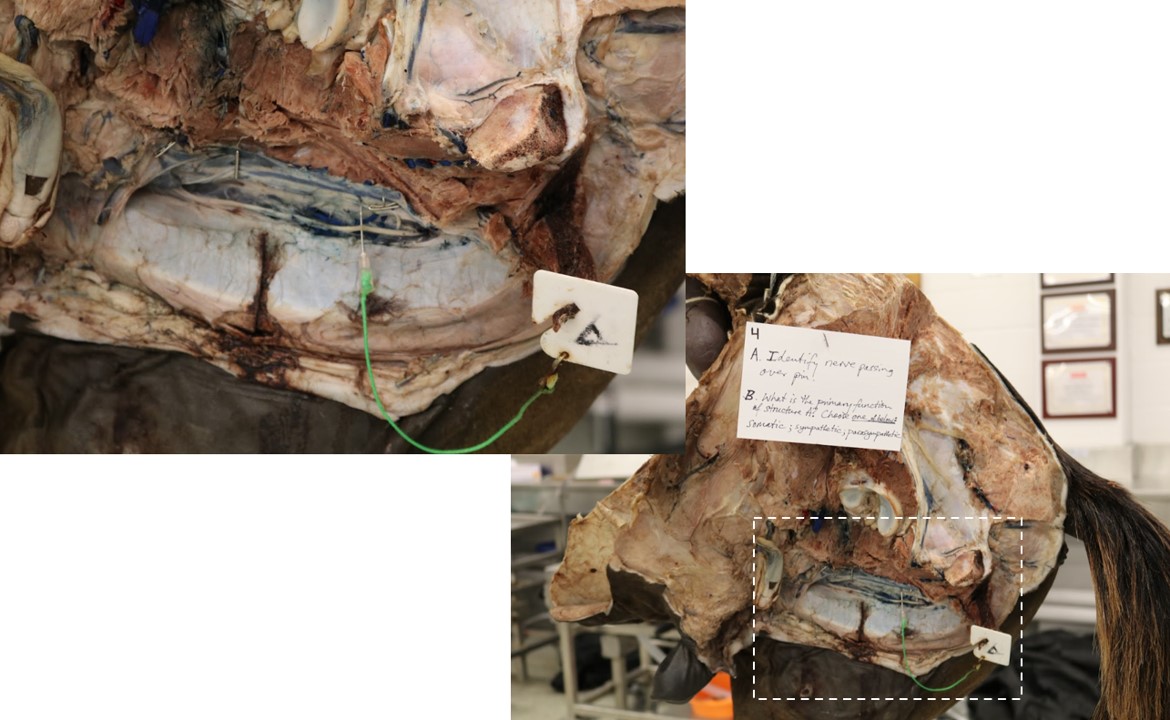

A. Identify the nerve passing over the pin
B. What is the primary function of nerve A? Choose one: somatic, sympathetic, parasympathetic.
Answer
A. Dorsal nerve of the penis
B. Somatic
Lab 11 Vasculature
A. Identify the erectile tissue
B. Identify the blood supply to the pinned erectile tissue
Answer
A. Corpus cavernosum
B. Deep artery of the penis