Additional Problems 11: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
Visualizing Chemistry
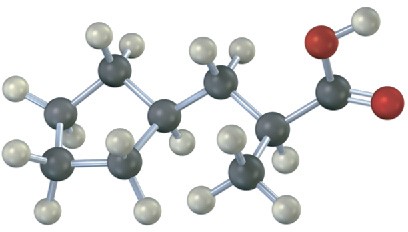
Problem 11.34
Give IUPAC names for the following carboxylic acids (reddish brown = Br):
(a)
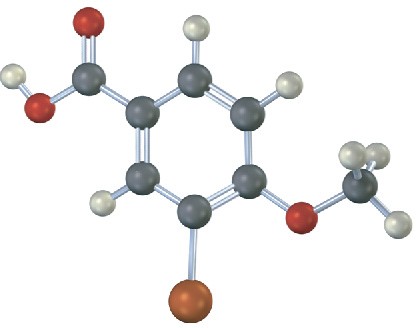
(b)
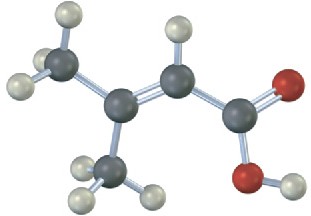
(c)
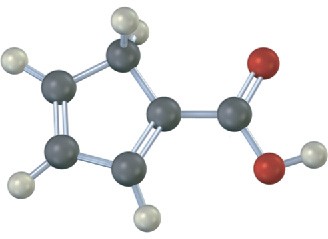
(d)
Problem 11.35
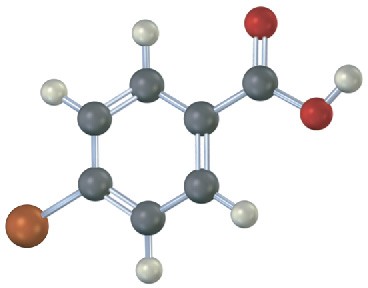
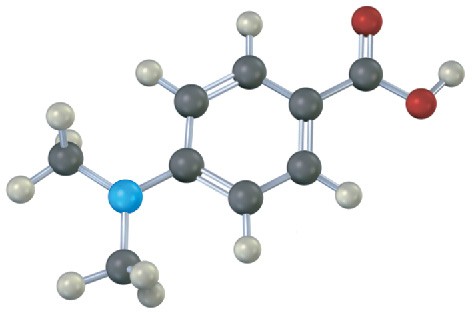
Would you expect the following carboxylic acids to be more acidic or less acidic than benzoic acid? Explain. (Reddish brown = Br.)
(a)
(b)
Problem 11.36
The following carboxylic acid can’t be prepared from an alkyl halide by either the nitrile hydrolysis route or the Grignard carboxylation route. Explain.
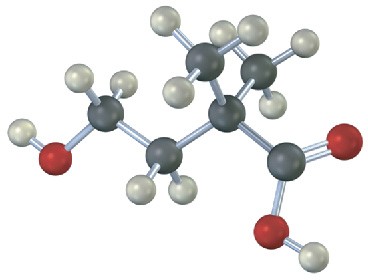
Problem 11.37
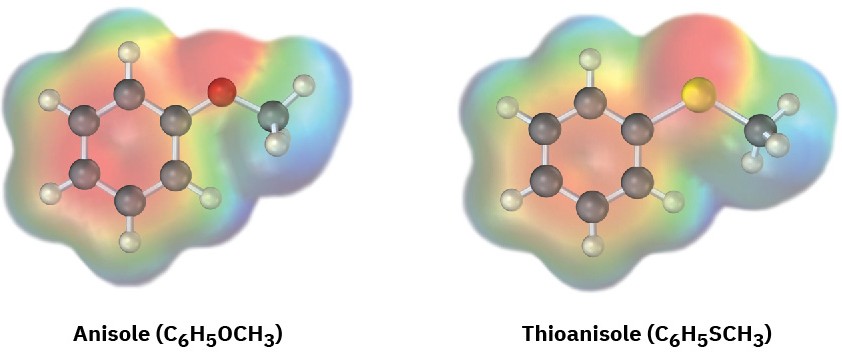
Electrostatic potential maps of anisole and thioanisole are shown. Which do you think is the stronger acid, p-methoxybenzoic acid or p-(methylthio)benzoic acid? Explain.
Mechanism Problems
Problem 11.38
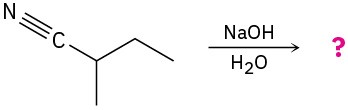
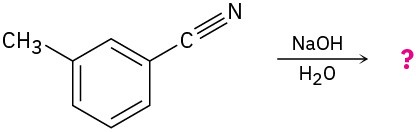
Predict the product(s) for each of the following reactions:
(a)
(b)
Problem 11.39
Predict the product(s) for of each of the following reactions:
(a)
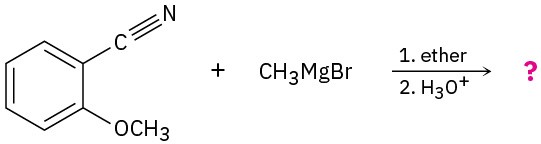
(b)
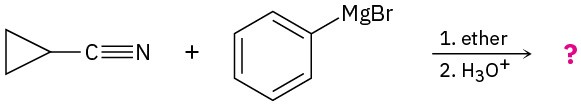
Problem 11.40
Predict the product(s) for the following reactions.
(a)
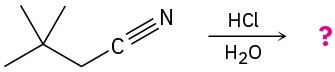
(b)
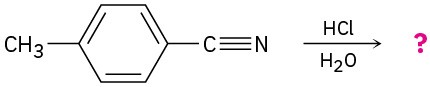
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
Problem 11.41
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:
(a)
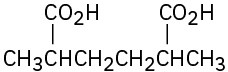
(b)
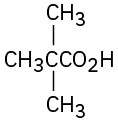
(c)
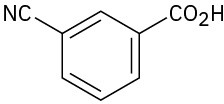
(d)
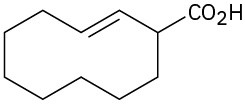
(e)
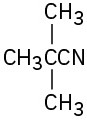
(f)
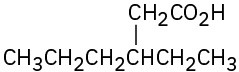
(g)
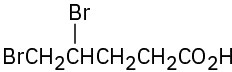
(h)
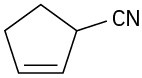
Problem 11.42
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
(a) cis-1,2-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid
(b) Heptanedioic acid
(c) 2-Hexen-4-ynoic acid
(d) 4-Ethyl-2-propyloctanoic acid
(e) 3-Chlorophthalic acid
(f) Triphenylacetic acid
(g) 2-Cyclobutenecarbonitrile
(h) m-Benzoylbenzonitrile
Problem 11.43
Draw and name the following compounds:
(a) The eight carboxylic acids with the formula C6H12O2
(b) Three nitriles with the formula C5H7N
Problem 11.44
Pregabalin, marketed as Lyrica, is an anticonvulsant drug that is also effective in treating chronic pain. The IUPAC name of pregabalin is (S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. (An aminomethyl group is –CH2NH2.) Draw the structure of pregabalin.
Problem 11.45
Isocitric acid, an intermediate in the citric acid cycle of food metabolism, has the systematic name (2R,3S)-3-carboxy-2-hydroxypentanedioic acid. Draw the structure.
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
Problem 11.46
Order the compounds in each of the following sets with respect to increasing acidity:
(a) Acetic acid, oxalic acid, formic acid
(b) p-Bromobenzoic acid, p-nitrobenzoic acid, 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid
(c) Fluoroacetic acid, 3-fluoropropanoic acid, iodoacetic acid
Problem 11.47
Arrange the compounds in each of the following sets in order of increasing basicity:
(a) Magnesium acetate, magnesium hydroxide, methylmagnesium bromide
(b) Sodium benzoate, sodium p-nitrobenzoate, sodium acetylide
(c) Lithium hydroxide, lithium ethoxide, lithium formate
Problem 11.48
Calculate the pKa’s of the following acids:
(a) Lactic acid, Ka = 8.4 × 10–4
(b) Acrylic acid, Ka = 5.6 × 10–6
Problem 11.49
Calculate the Ka’s of the following acids:
(a) Citric acid, pKa = 3.14
(b)Tartaric acid, pKa = 2.98
Problem 11.50
Some pKa data for simple dibasic acids is shown. How can you account for the fact that the difference between the first and second ionization constants decreases with increasing distance between the carboxyl groups?
|
Name |
Structure |
pKa1 |
pKa2 |
|
Oxalic |
HO2CCO2H |
1.2 |
4.2 |
|
Succinic |
HO2CCH2CH2CO2H |
4.2 |
5.6 |
|
Adipic |
HO2C(CH2)4CO2H |
4.4 |
5.4 |
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
Problem 11.51
How could you convert butanoic acid into the following compounds? Write each step showing the reagents needed.
(a) 1-Butanol
(b) 1-Bromobutane
(c) Pentanoic acid
(d) 1-Butene
Problem 11.52
How could you convert each of the following compounds into butanoic acid? Write each step showing all reagents.
(a) 1-Butanol
(b) 1-Bromobutane
Problem 11.53
How could you convert butanenitrile into the following compounds? Write each step showing the reagents needed.
(a) Butanol
(b) Butylamine
(c) Methyl-3-hexanone
Problem 11.54
How would you prepare the following compounds from benzene? More than one step is needed in each case.
(a) m-Chlorobenzoic acid
(b) p-Bromobenzoic acid
Problem 11.55
Predict the product of the reaction of p-methylbenzoic acid with each of the following:
(a) LiAlH4, then H3O+
(b) CH3MgBr in ether, then H3O+
(c) KMnO4, H3O+
Problem 11.56
1,6-Hexanediamine, a starting material needed for making nylon, can be made from 1,3- butadiene. How would you accomplish the synthesis?
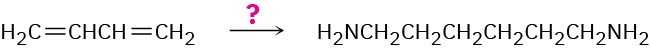
General Problems
Problem 11.57
A chemist in need of 2,2-dimethylpentanoic acid decided to synthesize some by reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane with NaCN, followed by hydrolysis of the product. After the reaction sequence was carried out, however, none of the desired product could be found. What do you suppose went wrong?
Problem 11.58
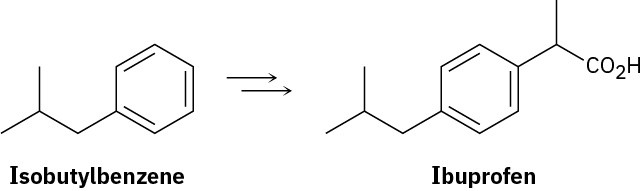
Show how you might prepare the anti-inflammatory agent ibuprofen starting from isobutylbenzene. More than one step is needed.
Problem 11.59
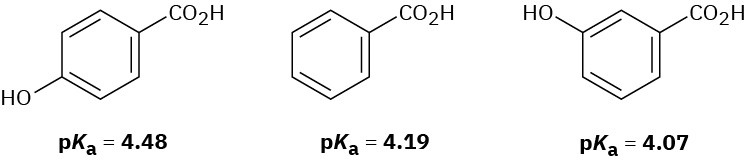
The following pKa values have been measured. Explain why a hydroxyl group in the para position decreases the acidity while a hydroxyl group in the meta position increases the acidity.