Additional Problems 12
Visualizing Chemistry
Problem 12.14
Name the following amines, and identify each as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
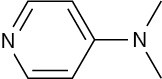
(a)
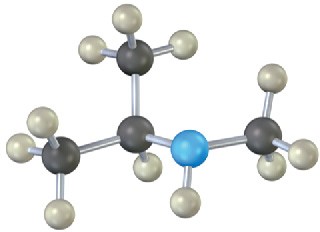
(b)
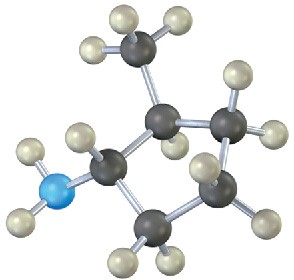
(c)
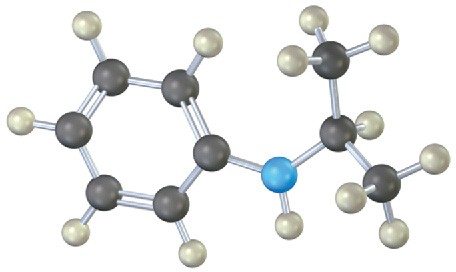
Problem 12.15
The following compound contains three nitrogen atoms. Rank them in order of increasing basicity.
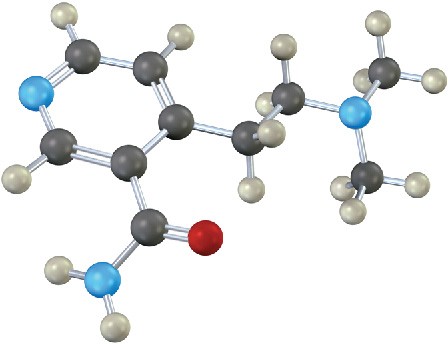
Problem 12.16
Name the following amine, including R,S stereochemistry.
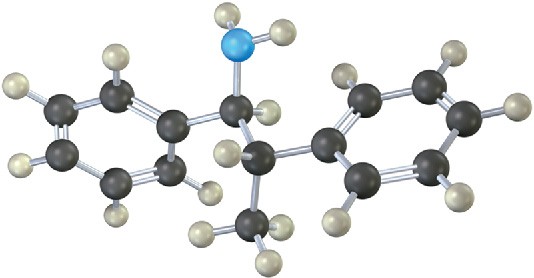
Problem 12.17
Which nitrogen atom in the following compound is most basic? Explain.
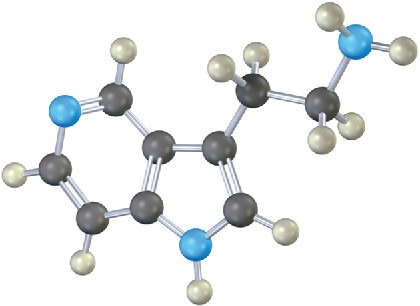
Mechanism Problems
Problem 12.18
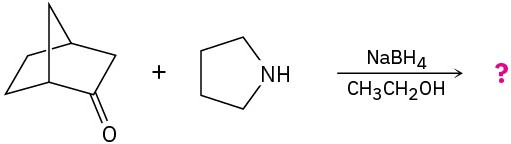
Predict the product(s) for each of the following reactions:
(a)
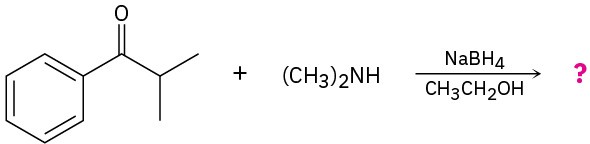
(b)
Naming Amines
Problem 12.19
Name the following compounds:
(a)
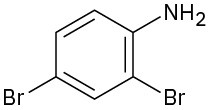
(b)
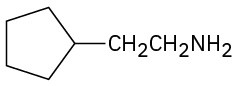
(c)
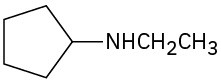
(d)
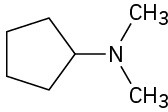
(e)
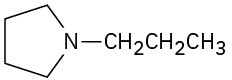
(f) ![]()
Problem 12.20
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
(a) N,N-Dimethylaniline
(b) (Cyclohexylmethyl)amine
(c) N-Methylcyclohexylamine
(d) (2-Methylcyclohexyl)amine
(e) 3-(N,N-Dimethylamino)propanoic acid
Problem 12.21
Classify each of the amine and amide nitrogen atoms in the following substances as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
(a)
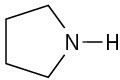
(b)
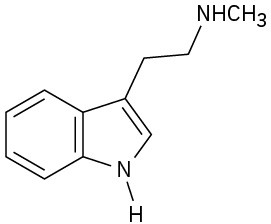
(c)
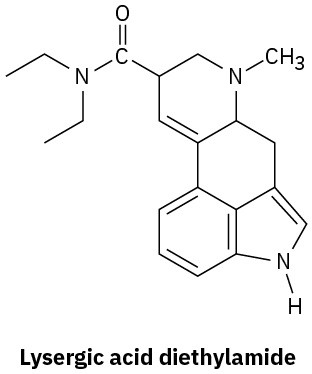
Amine Basicity
Problem 12.22
Although pyrrole is a much weaker base than most other amines, it is a much stronger acid (pKa ≈ 15 for the pyrrole versus 35 for diethylamine). The N–H hydrogen is readily abstracted by base to yield the pyrrole anion, C4H4N–. Explain.
Problem 12.23
Histamine, whose release in the body triggers nasal secretions and constricted airways, has three nitrogen atoms. List them in order of increasing basicity and explain your ordering.
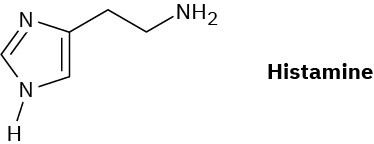
Problem 12.24
Account for the fact that p-nitroaniline (pKa = 1.0) is less basic than m-nitroaniline (pKa = 2.5) by a factor of 30. Draw resonance structures to support your argument. (The pKa values refer to the corresponding ammonium ions.)
Synthesis of Amines
Problem 12.25
How would you prepare the following substances from 1-butanol?
(a) Butylamine
(b) Dibutylamine
(c) Pentylamine
(d) N,N-Dimethylbutylamine
Problem 12.26
How would you prepare the following substances from pentanoic acid?
(a) Pentanamide
(b) Pentylamine
(c) Hexanenitrile
(d) Hexylamine
Problem 12.27
How would you prepare aniline from the following starting materials?
(a) Benzene
(b) Benzamide
(c) Toluene
Problem 12.28
How might you prepare pentylamine from the following starting materials?
(a) Pentanamide
(b) Pentanenitrile
(c) 1-Butene
(d) Hexanamide
(e) 1-Butanol
(f) 5-Decene
(g) Pentanoic acid
Problem 12.29
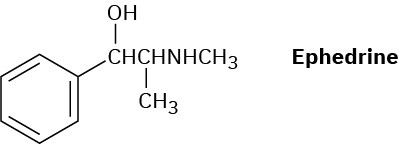
How might a reductive amination be used to synthesize ephedrine, an amino alcohol that was widely used for the treatment of bronchial asthma?
General Problems
Problem 12.30
Oxazole is a five-membered aromatic heterocycle. Would you expect oxazole to be more basic or less basic than pyrrole? Explain.
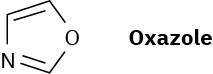
Problem 12.31
Protonation of an amide using strong acid occurs on oxygen rather than on nitrogen. Suggest a reason for this behavior, taking resonance into account.
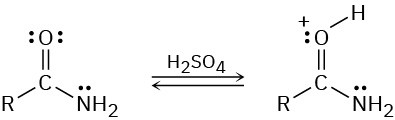
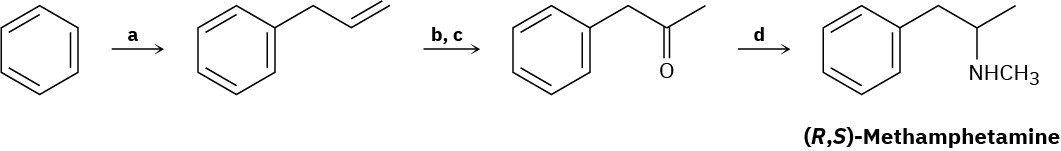
Problem 12.32
Fill in the missing reagents a–d in the following synthesis of racemic methamphetamine from benzene.
Problem 12.33
Cyclopentamine is an amphetamine-like central nervous system stimulant. Propose a synthesis of cyclopentamine from materials of five carbons or less.
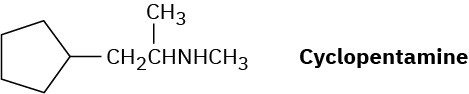
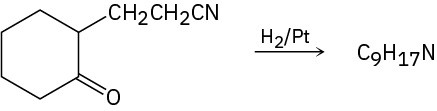
Problem 12.34
Propose a structure for the product with formula C9H17N that results when 2-(2-cyanoethyl)cyclohexanone is reduced catalytically.
Problem 12.35
4-Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) acts as a catalyst in acyl transfer reactions. DMAP’s catalytic activity stems from its nucleophilic character at the pyridine nitrogen, not the dimethylamino group. Explain this behavior, taking resonance into account.