Additional Problems 4
Visualizing Chemistry
Problem 4.22
Name the following alkenes, and convert each drawing into a skeletal structure:
(a)
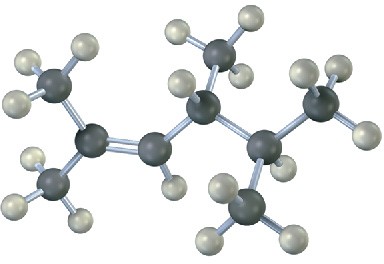
(b)
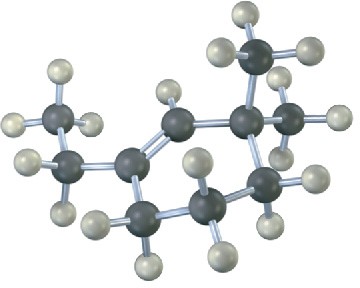
Problem 4.23
Assign E or Z stereochemistry to the double bonds in each of the following alkenes, and convert each drawing into a skeletal structure (red = O, green = Cl):
(a)
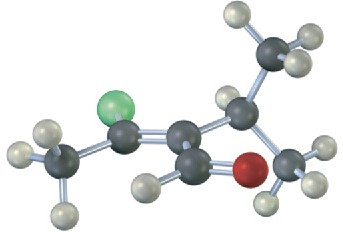
(b)
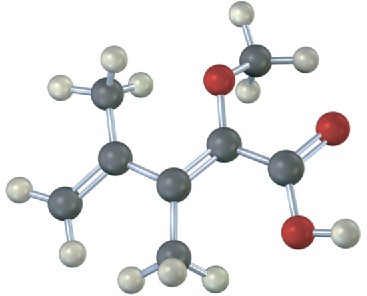
Problem 4.24
The following alkyl halide can be prepared by addition of HBr to two different alkenes. Draw the structures of both (reddish-brown = Br).
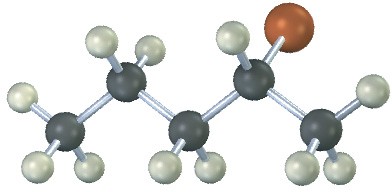
Problem 4.25
The following structure represents the carbocation intermediate formed in the addition reaction of HBr to two different alkenes. Draw the structures of both.
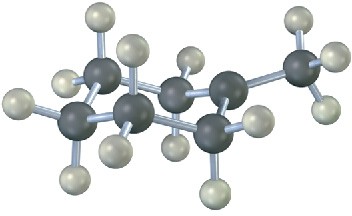
Problem 4.26
Electrostatic potential maps of (a) formaldehyde (CH2O) and (b) methanethiol (CH3SH) are shown. Is the formaldehyde carbon atom likely to be electrophilic or nucleophilic? What about the methanethiol sulfur atom? Explain.
(a)
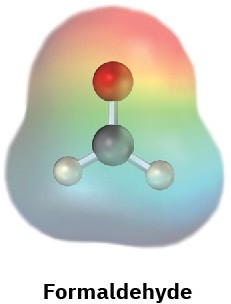
(b)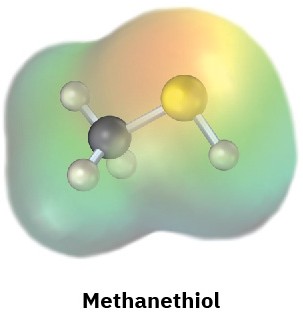
Problem 4.27
Look at the following energy diagram:
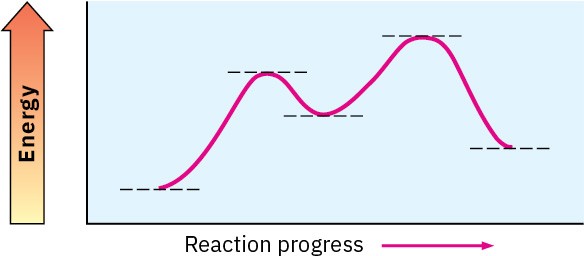
(a) Is ΔG° for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram.
(b) How many steps are involved in the reaction?
(c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram.
Problem 4.28
Look at the following energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction:
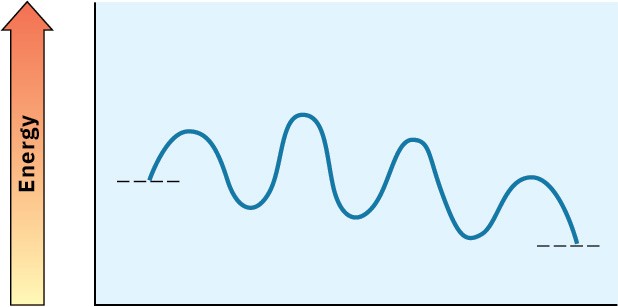
(a) How many steps are involved?
(b) Which step is most exergonic?
(c) Which step is slowest?
Naming Alkenes
Problem 4.29
Name the following alkenes:
(a)
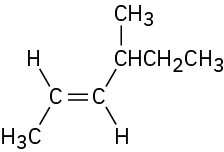
(b)
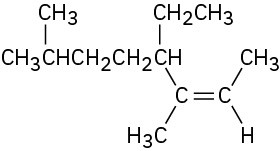
(c)
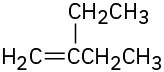
(d)
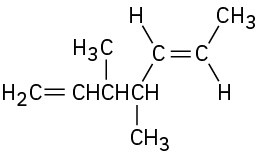
(e)
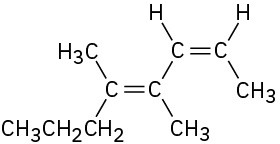
(f) 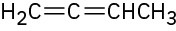
Problem 4.30
Draw structures corresponding to the following systematic names:
(a) (4E)-2,4-Dimethyl-1,4-hexadiene
(b) cis-3,3-Dimethyl-4-propyl-1,5-octadiene
(c) 4-Methyl-1,2-pentadiene
(d) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene
(e) 3-Butyl-2-heptene
(f) trans-2,2,5,5-Tetramethyl-3-hexene
Problem 4.31
Name the following cycloalkenes:
(a)
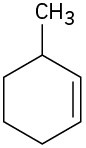
(b)
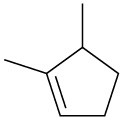
(c)
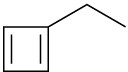
(d)
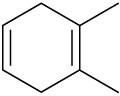
(e)
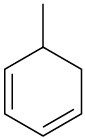
(f)
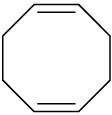
Problem 4.32
Ocimene is a triene found in the essential oils of many plants. What is its IUPAC name, including stereochemistry?
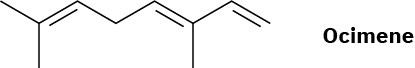
Problem 4.33
α-Farnesene is a constituent of the natural wax found on apples. What is its IUPAC name, including stereochemistry?
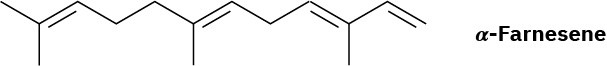
Problem 4.34
Menthene, a hydrocarbon found in mint plants, has the systematic name 1-isopropyl-4- methylcyclohexene. Draw its structure.
Problem 4.35
Draw and name the six alkene isomers, C5H10, including E,Z isomers.
Naming Alkynes
Problem 4.36
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:
(a)
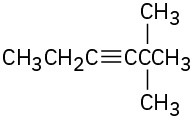
(b)
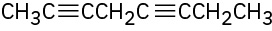
(c)
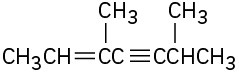
(d)
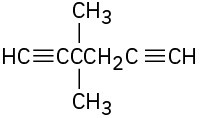
(e)
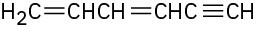
(f)
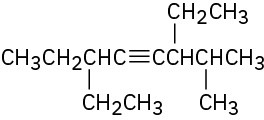
Problem 4.37
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
(a) 3,3-Dimethyl-4-octyne
(b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne
(c) 2,2,5,5-Tetramethyl-3-hexyne
(d) 3,4-Dimethylcyclodecyne
(e) 3,5-Heptadien-1-yne
(f) 3-Chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonen-6-yne
(g) 3-sec–Butyl-1-heptyne
(h) 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne
Problem 4.38
The following two hydrocarbons have been isolated from various plants in the sunflower family. Name them according to IUPAC rules.
(a) CH3CH=CHC≡CC≡CCH=CHCH=CHCH=CH2 (all trans)
(b) CH3C≡CC≡CC≡CC≡CC≡CCH=CH2
Alkene Isomers and Their Stability
Problem 4.39
Rank the following sets of substituents according to the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog sequence rules:
(a) 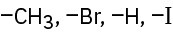
(b) 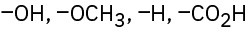
(c) 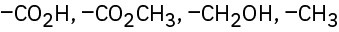
(d) 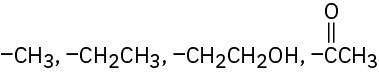
(e) 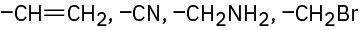
(f) 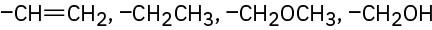
Problem 4.40
Assign E or Z configuration to each of the following compounds:
(a)
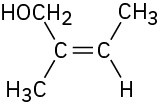
(b)
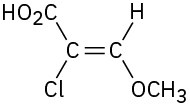
(c)
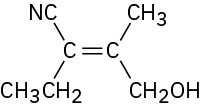
(d)
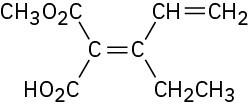
Problem 4.41
Which of the following E,Z designations are correct, and which are incorrect?
(a)
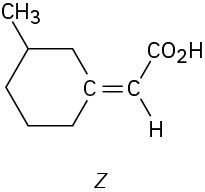
(b)
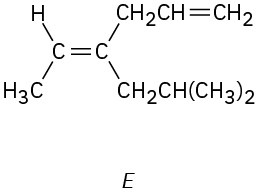
(c)
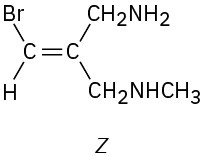
(d)
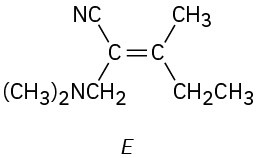
(e)
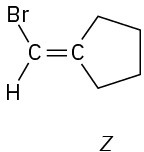
(f)
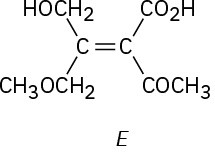
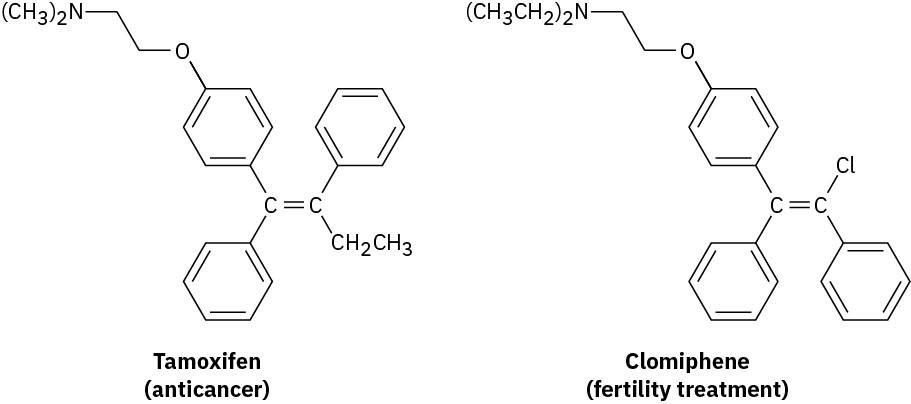
Problem 4.42
Tamoxifen, a drug used in the treatment of breast cancer, and clomiphene, a drug used in fertility treatment, have similar structures but very different effects. Assign E or Z configuration to the double bonds in both compounds.
Energy Diagrams and Reaction Mechanisms
Problem 4.43
What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate?
Problem 4.44
Draw the complete mechanism for each of the following polar reactions.
(a)
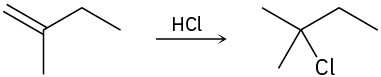
(b)
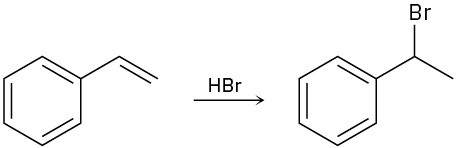
(c)
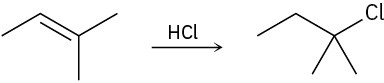
Polar Reactions
Problem 4.45
Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each:
(a) 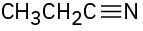
(b)
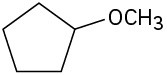
(c)
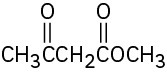
(d)
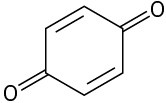
(e)
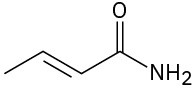
(f)
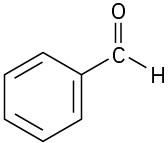
Problem 4.46
Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements:
(a) 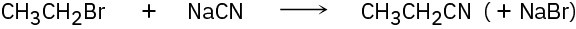
(b)
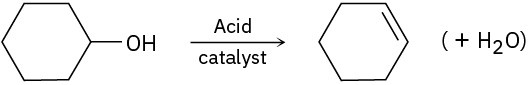
(c)
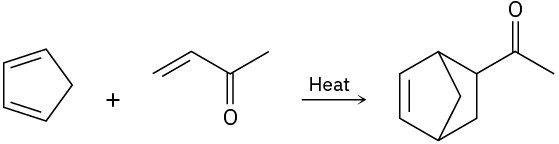
(d)
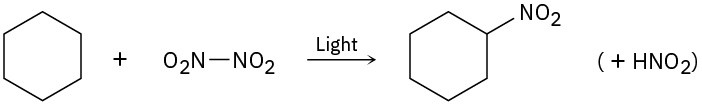
Problem 4.47
Identify the likely electrophilic and nucleophilic sites in each of the following molecules:
(a)
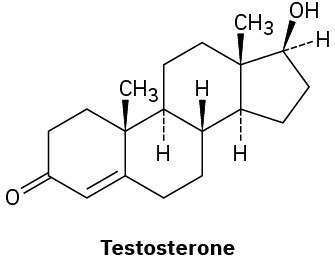
(b)
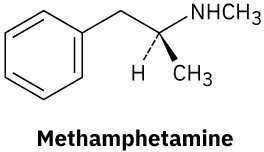
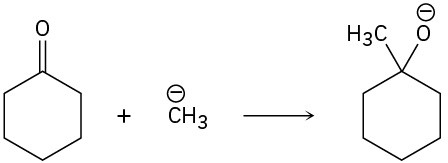
Problem 4.48
Identify the electrophile and the nucleophile.
(a)
![]()
(b)
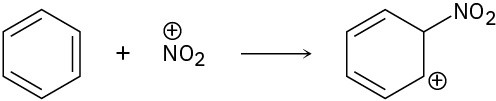
(c)
Problem 4.49
Follow the flow of electrons indicated by the curved arrows in each of the following polar reactions, and predict the products that result:
(a)
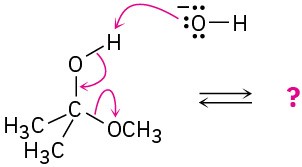
(b)
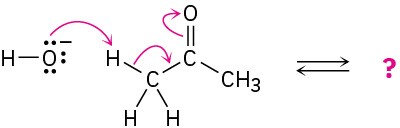
(c)
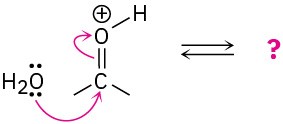
(d)
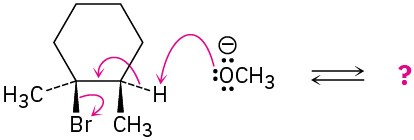
Problem 4.50
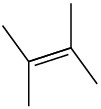
Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+.
(a)
![]()
(b)
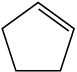
(c)
General Problems
Problem 4.51
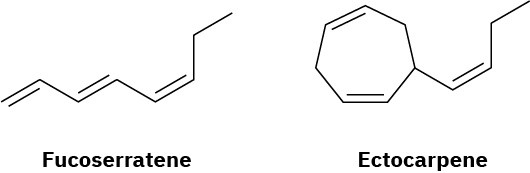
Fucoserratene and ectocarpene are sex pheromones produced by marine brown algae. What are their systematic names? (Ectocarpene is difficult; make your best guess, and then check your answer in the Student Solutions Manual.)
Problem 4.52
Draw an energy diagram for the addition of HBr to 1-pentene. Let one curve on your diagram show the formation of 1-bromopentane product and another curve on the same diagram show the formation of 2-bromopentane product. Label the positions for all reactants, intermediates, and products. Which curve has the higher-energy carbocation intermediate? Which curve has the higher-energy first transition state?

