Additional Problems 6
Visualizing Chemistry
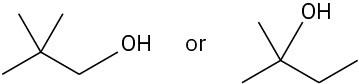
Problem 6.7
Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides (green = Cl):
(a)
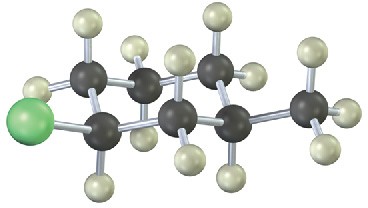
(b)
Problem 6.8
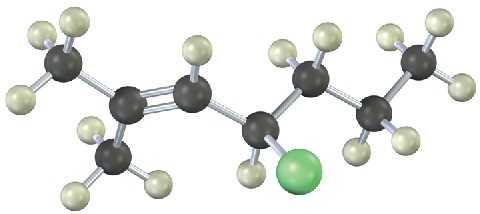
The following alkyl bromide can be prepared by reaction of the alcohol (S)-2-pentanol with PBr3. Name the compound, assign (R) or (S) stereochemistry, and tell whether the reaction of the alcohol results in the same stereochemistry or a change in stereochemistry (reddish brown = Br).
Mechanism Problems
Problem 6.9
In light of the fact that tertiary alkyl halides undergo spontaneous dissociation to yield a carbocation plus halide ion (see Problem 10-41), propose a mechanism for the following reaction.
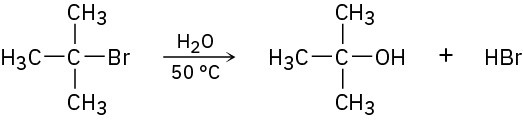
Naming Alkyl Halides
Problem 6.10
Name the following alkyl halides:
(a)
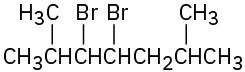
(b)
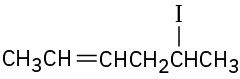
(c)
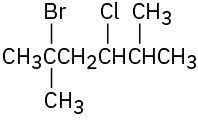
(d)
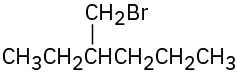
(e)
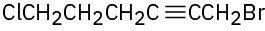
Problem 6.11
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
(a) 2,3-Dichloro-4-methylhexane
(b) 4-Bromo-4-ethyl-2-methylhexane
(c) 3-Iodo-2,2,4,4-tetramethylpentane
(d) cis-1-Bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane
Problem 6.12
Draw and name all the monochlorination products you might obtain from radical chlorination of the following compounds. Which of the products are chiral? Are any of the products optically active?
(a) methylbutane
(b) methylcyclopropane
(c) 2,2-dimethylpentane
Synthesizing Alkyl Halides
Problem 6.13
How would you prepare the following compounds, starting with cyclopentene and any other reagents needed?
(a) Chlorocyclopentane
(b) Cyclopentanol
Problem 6.14
Predict the product(s) of the following reactions:
(a)
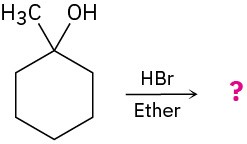
(b)
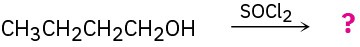
(c)
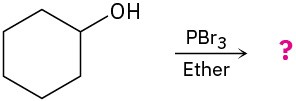
(d)
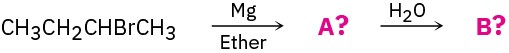
Oxidation and Reduction
Problem 6.15
Rank the compounds in each of the following series in order of increasing oxidation level:
(a) but-2-ene, but-1-ene, butanal, butanoic acid
(b)
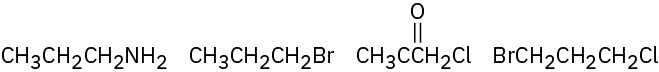
Problem 6.16
Which of the following compounds have the same oxidation level, and which have different levels?
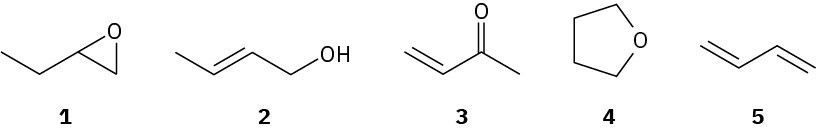
Problem 6.17
Tell whether each of the following reactions is an oxidation, a reduction, or neither:
(a)
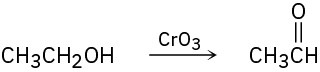
(b)
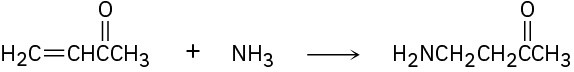
(c)
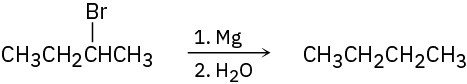
General Problems
Problem 6.18
Draw resonance structures for the following species:
(a)
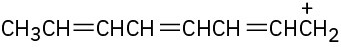
(b)
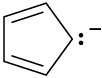
(c)
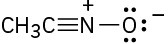
Problem 6.19
(S)-3-Methylhexane undergoes radical bromination to yield optically inactive 3-bromo-3- methylhexane as the major product. Is the product chiral? What conclusions can you draw about the radical intermediate?
Problem 6.20
Assume that you have carried out a radical chlorination reaction on (R)-2-chloropentane and have isolated (in low yield) 2,4-dichloropentane. How many stereoisomers of the product are formed, and in what ratio? Are any of the isomers optically active?
Problem 6.21
The synthesis shown here are unlikely to occur as written. What is wrong with it?
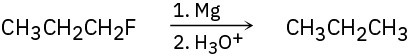
Problem 6.22
Why do you suppose it’s not possible to prepare a Grignard reagent from a bromo alcohol such as 4-bromo-1-pentanol? Give another example of a molecule that is unlikely to form a Grignard reagent.
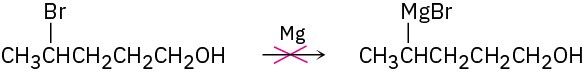
Problem 6.23
Addition of HBr to a double bond with an ether (−OR) substituent occurs regiospecifically to give a product in which the −Br and −OR are bonded to the same carbon. Draw the two possible carbocation intermediates in this electrophilic addition reaction, and explain using resonance why the observed product is formed.
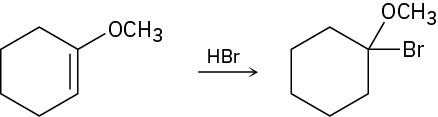
Problem 6.24
Tertiary alkyl halides, R3CX, undergo spontaneous dissociation to yield a carbocation, R3C+, plus halide ion. Which do you think reacts faster, (CH3)3CBr or H2C=CHC(CH3)2Br? Explain.
Problem 6.25
Carboxylic acids (RCO2H; pKa ≈ 5) are approximately 1011 times more acidic than alcohols (ROH; pKa ≈ 16). In other words, a carboxylate ion (RCO2−) is more stable than an alkoxide ion (RO−). Explain, using resonance.
Problem 6.26
Choose the alcohol from each pair below that would react faster with HX to form the corresponding alkyl halide.
(a)
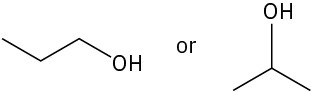
(b)
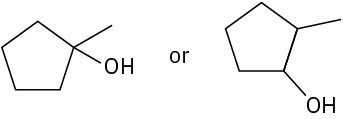
(c)