5.12 Reduction of Alkynes
Alkynes are reduced to alkanes by addition of H2 over a metal catalyst. The reaction occurs in two steps through an alkene intermediate.
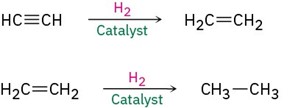
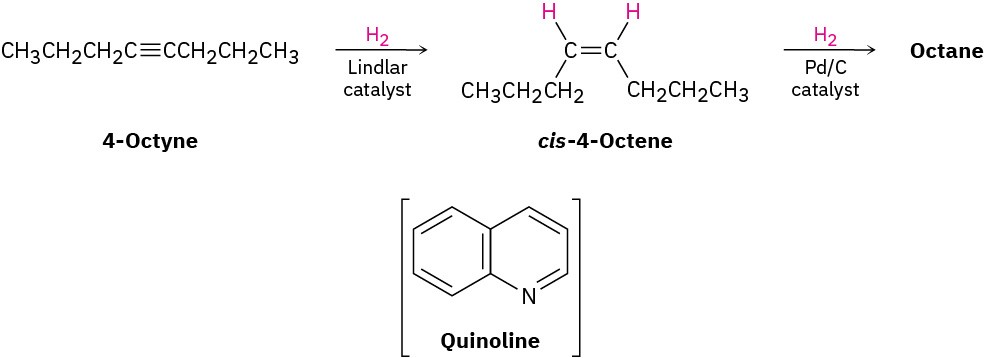
Complete reduction to the alkane occurs when palladium on carbon (Pd/C) is used as catalyst, but hydrogenation can be stopped at the alkene stage if the less active Lindlar catalyst is used. The Lindlar catalyst is a finely divided palladium metal that has been precipitated onto a calcium carbonate support and then deactivated by treatment with lead acetate and quinoline, an aromatic amine. The hydrogenation occurs with syn stereochemistry, giving a cis alkene product.
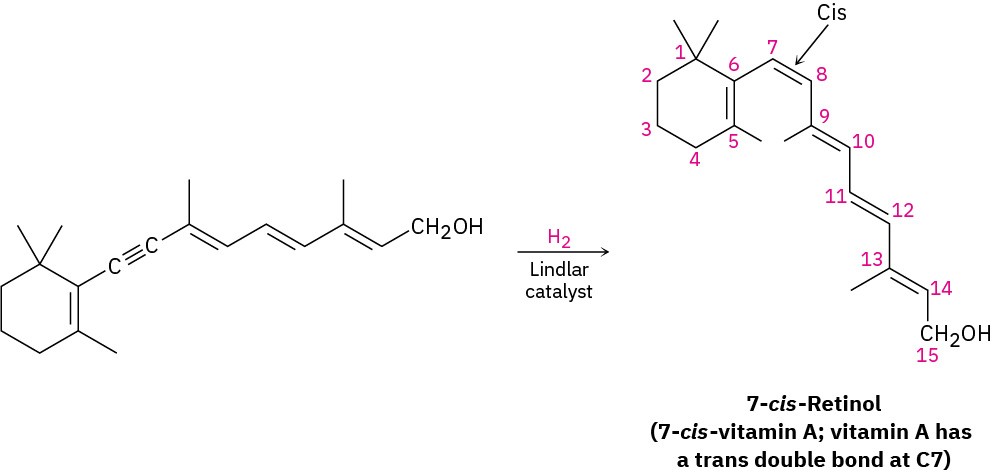
 The alkyne hydrogenation reaction has been explored extensively by the Hoffmann–LaRoche pharmaceutical company, where it is used in the commercial synthesis of vitamin A. The cis isomer of vitamin A produced initially on hydrogenation is converted to the trans isomer by heating.
The alkyne hydrogenation reaction has been explored extensively by the Hoffmann–LaRoche pharmaceutical company, where it is used in the commercial synthesis of vitamin A. The cis isomer of vitamin A produced initially on hydrogenation is converted to the trans isomer by heating.