1.9 sp Hybrid Orbitals and the Structure of Acetylene
In addition to forming single and double bonds by sharing two and four electrons, respectively, carbon can also form a triple bond by sharing six electrons. To account for the triple bond in a molecule such as acetylene, H−C≡C−H, we need a third kind of hybrid orbital, an sp hybrid. Imagine that, instead of combining with two or three p orbitals, a carbon 2s orbital hybridizes with only a single p orbital. Two sp hybrid orbitals result, and two p orbitals remain unchanged. The two sp orbitals are oriented 180° apart on the right-left (x) axis, while the p orbitals are perpendicular on the up-down (y) axis and the in-out (z) axis, as shown in Figure 1.17.
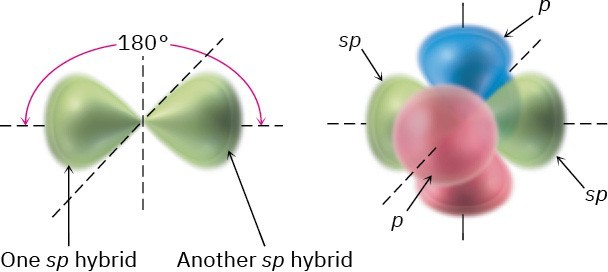
Figure 1.17 sp Hybridization. The two sp hybrid orbitals are oriented 180° away from each other, perpendicular to the two remaining p orbitals (red/blue).
When two sp-hybridized carbon atoms approach each other, sp hybrid orbitals on each carbon overlap head-on to form a strong sp–sp σ bond. At the same time, the pz orbitals from each carbon form a pz–pz π bond by sideways overlap, and the py orbitals overlap similarly to form a py–py π bond. The net effect is the sharing of six electrons and formation of a carbon–carbon triple bond. Each of the two remaining sp hybrid orbitals forms a σ bond with hydrogen to complete the acetylene molecule (Figure 1.18).
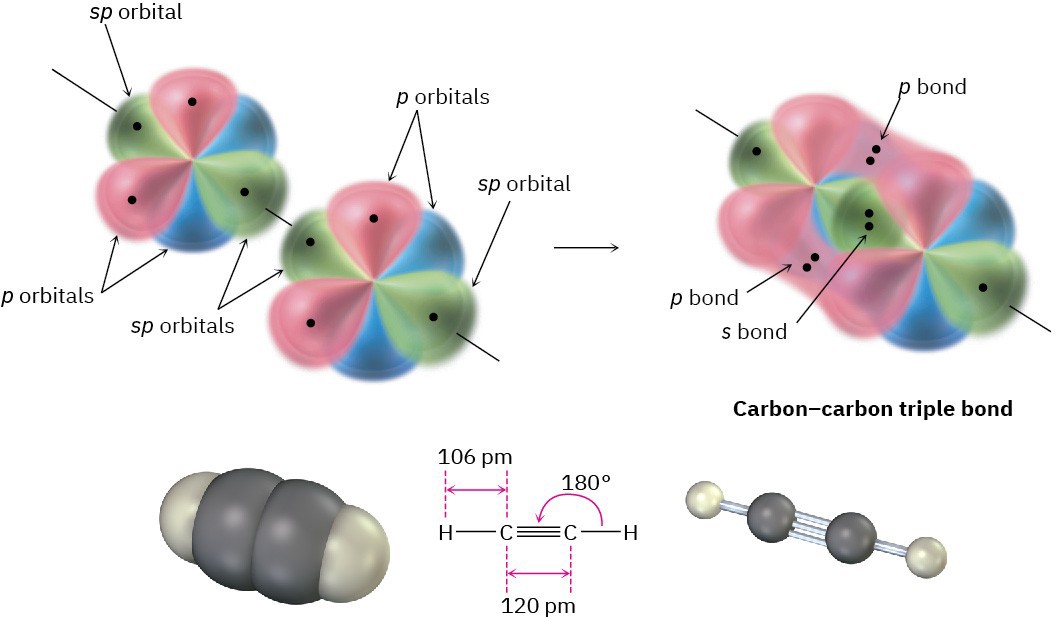
Figure 1.18 The structure of acetylene. The two carbon atoms are joined by one sp–sp σ bond and two p–p π bonds.
As suggested by sp hybridization, acetylene is a linear molecule with H–C–C bond angles of 180°. The C–H bonds have a length of 106 pm and a strength of 558 kJ/mol (133 kcal/mol). The C–C bond length in acetylene is 120 pm, and its strength is about 965 kJ/mol (231 kcal/mol), making it the shortest and strongest of any carbon–carbon bond. A comparison of sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridization is given in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2 Comparison of C−C and C−H Bonds in Methane, Ethane, Ethylene, and Acetylene
|
Bond |
Bond strength |
Bond length (pm)
|
||
|
(kJ/mol) |
(kcal/mol) |
|||
|
Methane, CH4 |
(sp3) C−H |
439 |
105 |
109 |
|
Ethane, CH3CH3 |
(sp3) C−C (sp3) |
377 |
90 |
153 |
|
(sp3) C−H |
421 |
101 |
109 |
|
|
Ethylene, H2C=CH2 |
(sp2) C=C (sp2) |
728 |
174 |
134 |
|
(sp2) C−H |
464 |
111 |
109 |
|
|
Acetylene, HC≡CH |
(sp) C≡C (sp) |
965 |
231 |
120 |
|
(sp) C−H |
558 |
133 |
106 |
|
Problem 1.13

