Module 4: Molecular Weight
4.0 Introduction and Study Guide

In this short module, we will learn all about molecular weight (MW), MW distributions, and polydispersity. Extent of reaction will be introduced. You will learn to complete MW calculations. You will practice calculating MW, PDI, and p. The variables and equations can be confusing, but remember you have been calculating number averages since you were in elementary school! In TE 200, there is a 100% chance that you will be asked to calculate MW on the first exam and again on the final.
Read Section 2.2: Molecular Weight – Definitions in Chapter 2: Microstructure and Molecular Weight of the Polymer Science and Engineering eBook (or the equivalent in a print version).
Study Guide for Module 4: Molecular Weight
By the end of the module, can you do the following?
- Given the equation, calculate the number-average molecular weight,
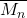 .
. - Given the equation, calculate the weight-average molecular weight,
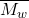 .
. - Calculate the number average degree of polymerization,
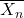 .
. - Calculate the weight average degree of polymerization,
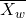 .
. - Identify key aspects of a MW distribution plot (e.g., a narrow distribution versus a broad one, which curve has a higher
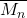 or
or 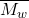 , etc.).
, etc.). - Explain the importance of the polydispersity index.
- Calculate polydispersity.
- Use your knowledge of polydispersity to convert from weight average to number average, and vice versa.
- Given the appropriate equations, calculate the polydispersity,
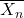 , and
, and 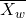 from the extent of reaction (p) for step growth polymers (and vice versa).
from the extent of reaction (p) for step growth polymers (and vice versa). - Explain why the polydispersity of step growth polymers is ca. 2.
Get your own copy of the Module 04 Study Guide and Checklist (link goes to a “force copy” Google Doc).
