Module 8: Structure and Morphology
8.0 Introduction & Study Guide
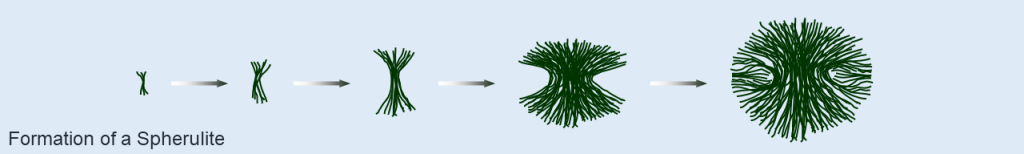
In this short module, we will learn about polymer conformations, the end-to-end distance, the overall shape and form of polymer crystals (crystal morphology), and the conditions required for the formation of these crystalline morphologies. Chapter 8 in the Polymer Science and Engineering eBook goes into much more detail than we will. Instead of starting with a chapter reading, watch the lecture and use the reading to supplement and/or clarify the lecture. If content is not in the Study Guide, you are not responsible for it.
Use Chapter 8: Structure and Morphology of the Polymer Science and Engineering eBook (or the equivalent in a print version) as a reference for studying the content covered in the lecture. The textbook goes into much greater depth than we will. Use the study guide, lecture, and lecture notes as your primary materials and the chapter as a supplement.
Study Guide for Module 8: Structure & Morphology
By the end of the module, can you do the following?
- Define and/or describe the following as they relate to polymers:
- Morphology
- Fringed micelle
- Lamella
- Spherulite
- Row nucleated structures
- Conformations
- End-to-end distance
- Tie molecules (V, VI)
- Describe and discuss polymer conformations and how many conformations are possible.
- Recognize that if each bond in the backbone has X possible confirmations and Y bonds in the backbone, then there are XY possible conformations (ignoring redundancies). A student should be able to explain why it is multiplicative and not additive. (?)
- Explain how a polymer’s end-to-end distance changes with:
- Solvent quality
- Molecular weight
- Backbone stiffness (VI)
- Describe the overall shape and form of polymer crystals, specifically:
- Single crystals
- Spherulites
- Row nucleated structures (V)
- Describe how increasing (or decreasing) the degree of crystallinity affects the following properties:
- Strength
- Stiffness
- Toughness
- Brittleness
- Optical clarity
- Barrier properties
- Solubility (VI)
- Given a set of conditions, predict the morphology of the polymer. For example, if a crystallizable polymer is slowly cooled from the melt in a cooling dish, then one would predict the sample would crystallize forming spherulites. (IV, V)
Get your own copy of the Module 08 Study Guide and Checklist (link goes to a “force copy” Google Doc).
