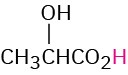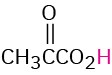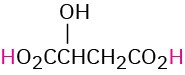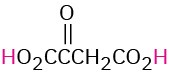20.1 Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
Carboxylic Acids, RCO2H
Simple carboxylic acids derived from open-chain alkanes are systematically named by replacing the terminal –e of the corresponding alkane name with –oic acid. The –CO2H carbon atom is numbered C1.
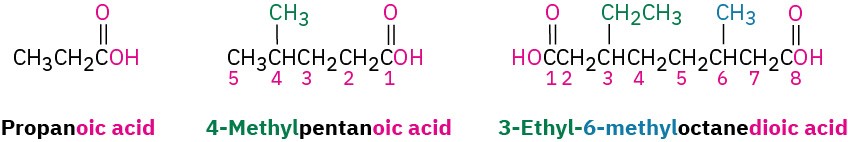
Compounds that have a –CO2H group bonded to a ring are named using the suffix – carboxylic acid. The CO2H carbon is attached to C1 in this system and is not itself numbered. As a substituent, the CO2H group is called a carboxyl group.

Because many carboxylic acids were among the first organic compounds to be isolated and purified, quite a few common names exist (Table 20.1). Biological chemists, in particular, make frequent use of these names, so you may find yourself referring back to this list on occasion. We’ll use systematic names in this book, with a few exceptions such as formic (methanoic) acid and acetic (ethanoic) acid, whose names are accepted by IUPAC and are so well known that it makes little sense to refer to them any other way.
Also listed in Table 20.1 are the names of acyl groups 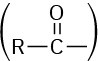 derived from the parent acids. Except for the eight entries at the top of Table 20.1, whose names have a –yl ending, all other acyl groups are named using an –oyl ending.
derived from the parent acids. Except for the eight entries at the top of Table 20.1, whose names have a –yl ending, all other acyl groups are named using an –oyl ending.
Table 20.1 Common Names of Some Carboxylic Acids and Acyl Groups
|
Structure |
Name |
Acyl group |
|
HCO2H |
Formic |
Formyl |
|
CH3CO2H |
Acetic |
Acetyl |
|
CH3CH2CO2H |
Propionic |
Propionyl |
|
CH3CH2CH2CO2H |
Butyric |
Butyryl |
|
HO2CCO2H |
Oxalic |
Oxalyl |
|
HO2CCH2CO2H |
Malonic |
Malonyl |
|
Name |
Acyl group |
|
|
HO2CCH2CH2CO2H |
Succinic |
Succinyl |
|
HO2CCH2CH2CH2CO2H |
Glutaric |
Glutaryl |
|
HO2CCH2CH2CH2CH2CO2H |
Adipic |
Adipoyl |
|
H2C═CHCO2H |
Acrylic |
Acryloyl |
|
HO2CCH═CHCO2H |
Maleic (cis) Fumaric (trans) |
Maleoyl Fumaroyl |
|
HOCH2CO2H |
Glycolic |
Glycoloyl |
|
|
Lactic |
Lactoyl |
|
|
Pyruvic |
Pyruvoyl |
|
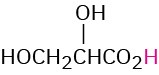
|
Glyceric |
Glyceroyl |
|
|
Malic |
Maloyl |
|
|
Oxaloacetic |
Oxaloacetyl |
|
|
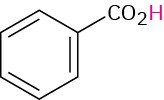
Benzoic |
Benzoyl |
|
|
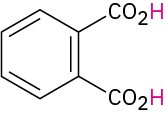
Phthalic |
Phthaloyl |
Nitriles, RC≡N
Compounds containing the –C≡N functional group are called nitriles and can undergo some chemistry similar to that of carboxylic acids. Simple open-chain nitriles are named by adding –nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name, with the nitrile carbon numbered C1.

Nitriles can also be named as derivatives of carboxylic acids by replacing the –ic acid or –oic acid ending with –onitrile, or by replacing the –carboxylic acid ending with –carbonitrile. The nitrile carbon atom is attached to C1 but is not itself numbered.
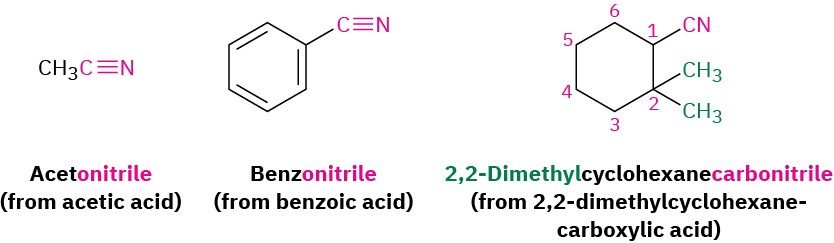
If another carboxylic acid derivative is present in the same molecule, the prefix cyano– is used for the C≡N group.

Problem 20-1
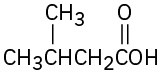 Give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (a)
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (a)
(b)
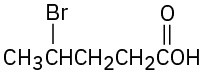
(c)
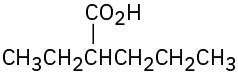
(d)
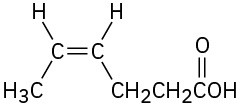
(e)
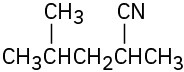
(f)
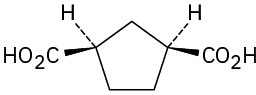
Problem 20-2
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a)
2,3-Dimethylhexanoic acid (b)
4-Methylpentanoic acid
(c)
trans-1,2-Cyclobutanedicarboxylic acid (d)
o-Hydroxybenzoic acid (e)
(9Z,12Z)-9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (f)
2-Pentenenitrile