Additional Problems 15
Visualizing Chemistry
Problem 15-13
Give IUPAC names for the following substances (red = O, blue = N):
(a)
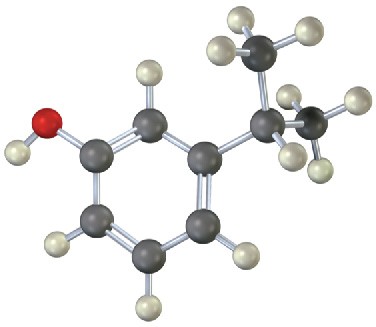
(b)
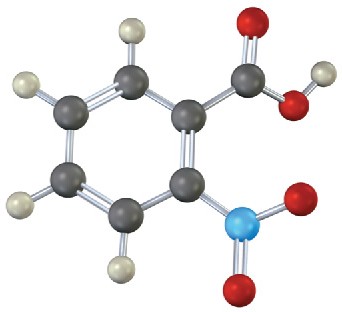
Problem 15-14
All-cis cyclodecapentaene is a stable molecule that shows a single absorption in its 1H NMR spectrum at 5.67 δ. Tell whether it is aromatic, and explain its NMR spectrum.
Problem 15-15
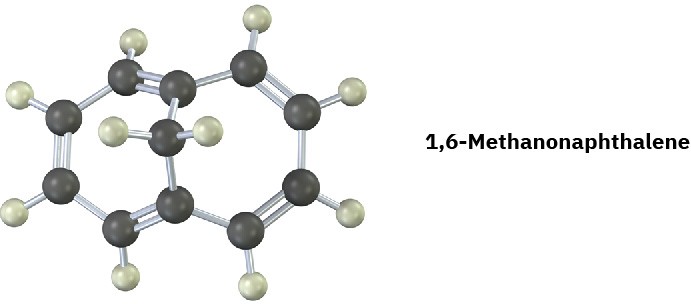
1,6-Methanonaphthalene has an interesting 1H NMR spectrum in which the eight hydrogens around the perimeter absorb at 6.9 to 7.3 δ, while the two CH2 protons absorb at
–0.5 δ. Tell whether it is aromatic, and explain its NMR spectrum.
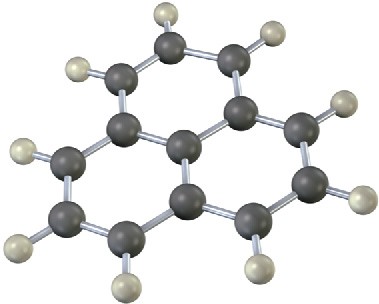
Problem 15-16
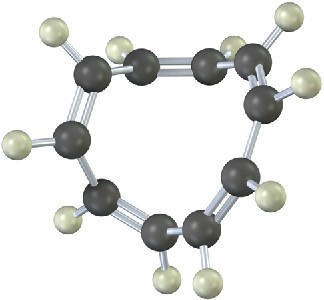
The following molecular model is that of a carbocation. Draw two resonance structures for the carbocation, indicating the positions of the double bonds.
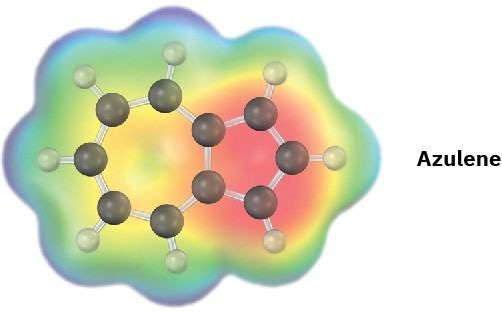
Problem 15-17
Azulene, an isomer of naphthalene, has a remarkably large dipole moment for a hydrocarbon (μ = 1.0 D). Explain, using resonance structures.
Naming Aromatic Compounds
Problem 15-18
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:
(a)
(b)
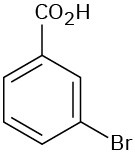
(c)
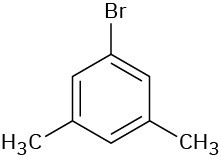
(d)
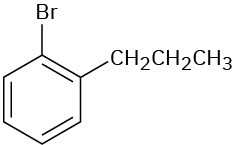
(e)
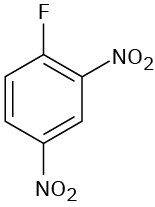
(f)
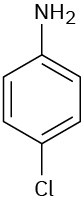
Problem 15-19
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
(a) 3-Methyl-1,2-benzenediamine
(b)
1,3,5-Benzenetriol
(c) 3-Methyl-2-phenylhexane
(d) o-Aminobenzoic acid
(e) m-Bromophenol
(f) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (picric acid)
Problem 15-20
Draw and name all possible isomers of the following:
(a) Dinitrobenzene
(b) Bromodimethylbenzene
(c) Trinitrophenol
Problem 15-21
Draw and name all possible aromatic compounds with the formula C7H7Cl.
Problem 15-22
Draw and name all possible aromatic compounds with the formula C8H9Br. (There are 14.)
Structure of Aromatic Compounds
Problem 15-23
Propose structures for aromatic hydrocarbons that meet the following descriptions:
(a) C9H12; gives only one C9H11Br product on substitution of a hydrogen on the aromatic ring with bromine
(b) C10H14; gives only one C10H13Cl product on substitution of a hydrogen on the aromatic ring with chlorine
(c) C8H10; gives three C8H9Br products on substitution of a hydrogen on the aromatic ring with bromine
(d) C10H14; gives two C10H13Cl products on substitution of a hydrogen on the aromatic ring with chlorine
Problem 15-24
Look at the three resonance structures of naphthalene shown in Section 15.6, and account for the fact that not all carbon–carbon bonds have the same length. The C1–C2 bond is 136 pm long, whereas the C2–C3 bond is 139 pm long.
Problem 15-25
Anthracene has four resonance structures, one of which is shown. Draw the other three.
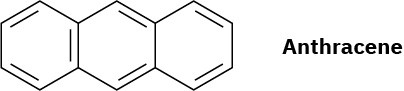
Problem 15-26
Phenanthrene has five resonance structures, one of which is shown. Draw the other four.
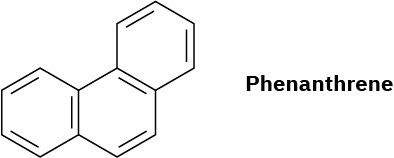
Problem 15-27
Look at the five resonance structures for phenanthrene (Problem 26), and predict which of its carbon–carbon bonds is shortest.
Problem 15-28
In 1932, A. A. Levine and A. G. Cole studied the ozonolysis of o-xylene and isolated three products: glyoxal, 2,3-butanedione, and pyruvaldehyde:
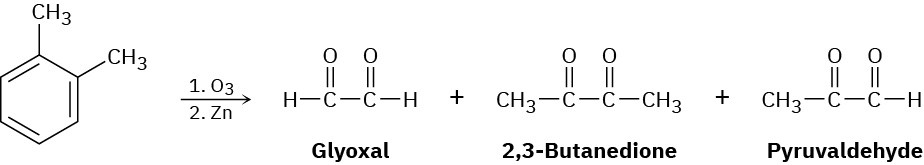
In what ratio would you expect the three products to be formed if o-xylene is a resonance hybrid of two structures? The actual ratio found was 3 parts glyoxal, 1 part 2,3- butanedione, and 2 parts pyruvaldehyde. What conclusions can you draw about the structure of o-xylene?
Aromaticity and Hückel’s Rule
Problem 15-29
3-Chlorocyclopropene, on treatment with AgBF4, gives a precipitate of AgCl and a stable solution of a product that shows a single 1H NMR absorption at 11.04 δ. What is a likely structure for the product, and what is its relation to Hückel’s rule?

Problem 15-30
Draw an energy diagram for the three molecular orbitals of the cyclopropenyl system (C3H3). How are these three molecular orbitals occupied in the cyclopropenyl anion, cation, and radical? Which of the three substances is aromatic according to Hückel’s rule?
Problem 15-31
Cyclopropanone is highly reactive because of its large amount of angle strain. Methylcyclopropenone, although even more strained than cyclopropanone, is nevertheless quite stable and can even be distilled. Explain, taking the polarity of the carbonyl group into account.
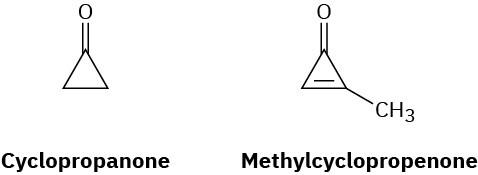
Problem 15-32
Cycloheptatrienone is stable, but cyclopentadienone is so reactive that it can’t be isolated. Explain, taking the polarity of the carbonyl group into account.
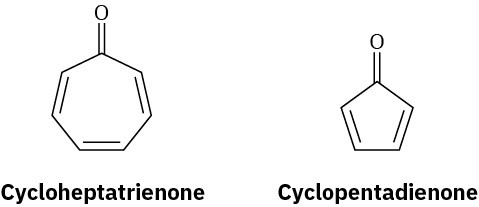
Problem 15-33
Which would you expect to be most stable, cyclononatetraenyl radical, cation, or anion? (Cyclononatetraene has a ring of nine carbons and four double bonds.)
Problem 15-34
How might you convert 1,3,5,7-cyclononatetraene to an aromatic substance?
Problem 15-35
Calicene, like azulene (Problem 17), has an unusually large dipole moment for a hydrocarbon. Explain, using resonance structures.
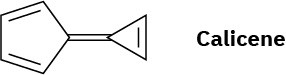
Problem 15-36
Pentalene is a most elusive molecule that has been isolated only at liquid-nitrogen temperature. The pentalene dianion, however, is well known and quite stable. Explain.
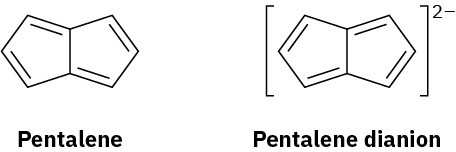
Problem 15-37
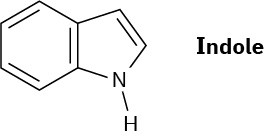
Indole is an aromatic heterocycle that has a benzene ring fused to a pyrrole ring. Draw an orbital picture of indole.
(a) How many π electrons does indole have?
(b)What is the electronic relationship of indole to naphthalene?
Problem 15-38
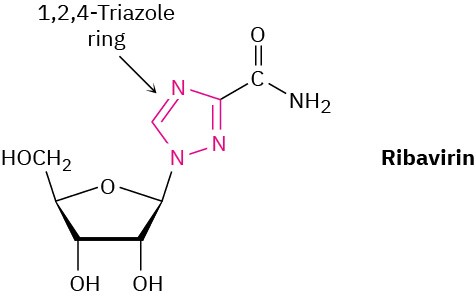
Ribavirin, an antiviral agent used against hepatitis C and viral pneumonia, contains a 1,2,4- triazole ring. Why is the ring aromatic?
Spectroscopy
Problem 15-39
Compound A, C8H10, yields three substitution products, C8H9Br, on reaction with Br2. Propose two possible structures for A. The 1H NMR spectrum of A shows a complex four- proton multiplet at 7.0 δ and a six-proton singlet at 2.30 δ. What is the structure of A?
Problem 15-40
What is the structure of a hydrocarbon that has M+ = 120 in its mass spectrum and has the following 1H NMR spectrum?
7.25 δ (5 H, broad singlet); 2.90 δ (1 H, septet, J = 7 Hz); 1.22 δ (6 H, doublet, J = 7 Hz) Problem 15-41
Propose structures for compounds that fit the following descriptions:
(a) C10H14
1H NMR: 7.18 δ (4 H, broad singlet); 2.70 δ (4 H, quartet, J = 7 Hz); 1.20 δ (6 H, triplet, J = 7 Hz)
IR absorption at 745 cm–1 (b)
C10H14
1H NMR: 7.0 δ (4 H, broad singlet); 2.85 δ (1 H, septet, J = 8 Hz); 2.28 δ (3 H, singlet); 1.20 δ
(6 H, doublet, J = 8 Hz)
IR absorption at 825 cm–1
General Problems
Problem 15-42
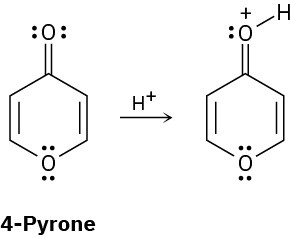
On reaction with acid, 4-pyrone is protonated on the carbonyl-group oxygen to give a stable cationic product. Using resonance structures and the Hückel 4n + 2 rule, explain why the protonated product is so stable.
Problem 15-43
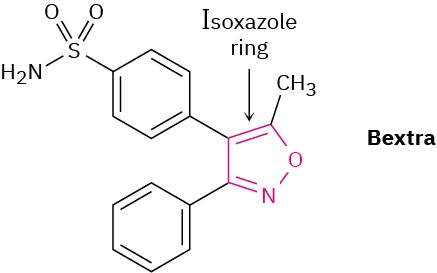
Bextra, a COX-2 inhibitor once used in the treatment of arthritis, contains an isoxazole ring. Why is the ring aromatic?
Problem 15-44
N-Phenylsydnone, so-named because it was first studied at the University of Sydney, Australia, behaves like a typical aromatic molecule. Explain, using the Hückel 4n + 2 rule.
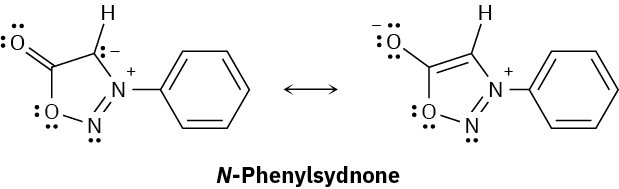
Problem 15-45
Show the relative energy levels of the seven π molecular orbitals of the cycloheptatrienyl system. Tell which of the seven orbitals are filled in the cation, radical, and anion, and account for the aromaticity of the cycloheptatrienyl cation.
Problem 15-46
1-Phenyl-2-butene has an ultraviolet absorption at λmax = 208 nm (ε = 8000). On treatment with a small amount of strong acid, isomerization occurs and a new substance with λmax = 250 nm (ε = 15,800) is formed. Propose a structure for this isomer, and suggest a mechanism for its formation.
Problem 15-47
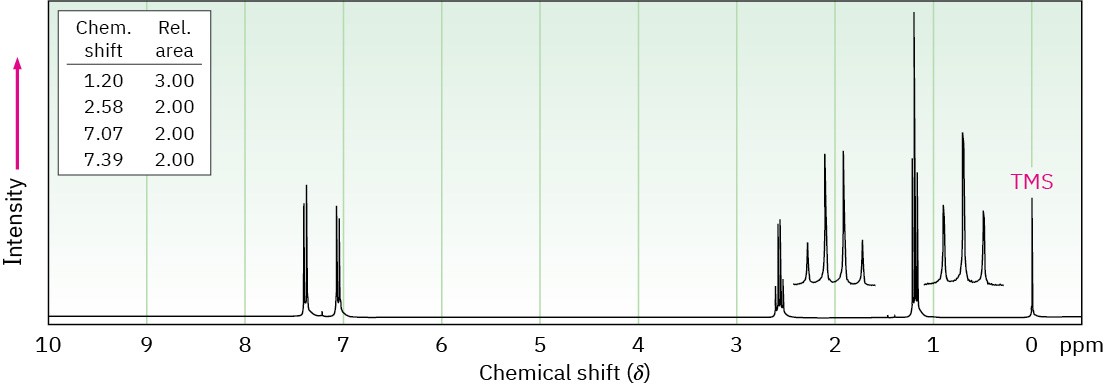
Propose structures for aromatic compounds that have the following 1H NMR spectra:
(a) C8H9Br
IR absorption at 820 cm–1
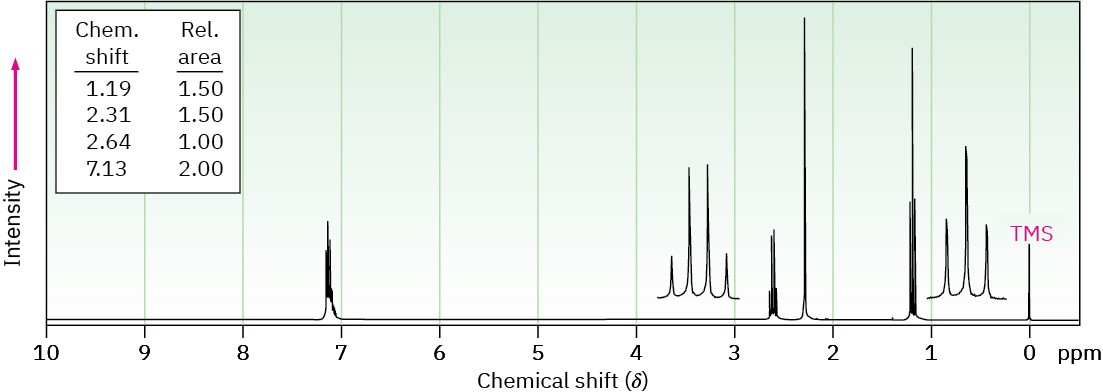
(b) C9H12
IR absorption at 750 cm–1
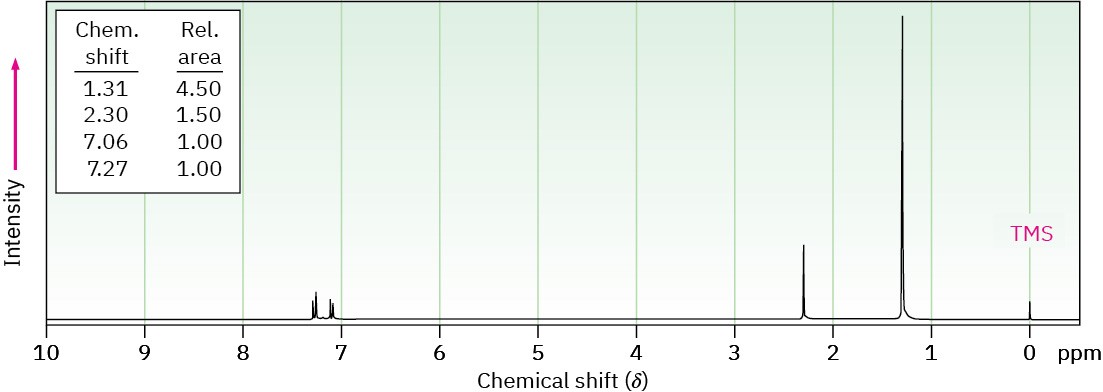
(c) C11H16
IR absorption at 820 cm–1
Problem 15-48
Propose a structure for a molecule C14H12 that has the following 1H NMR spectrum and has IR absorptions at 700, 740, and 890 cm–1:
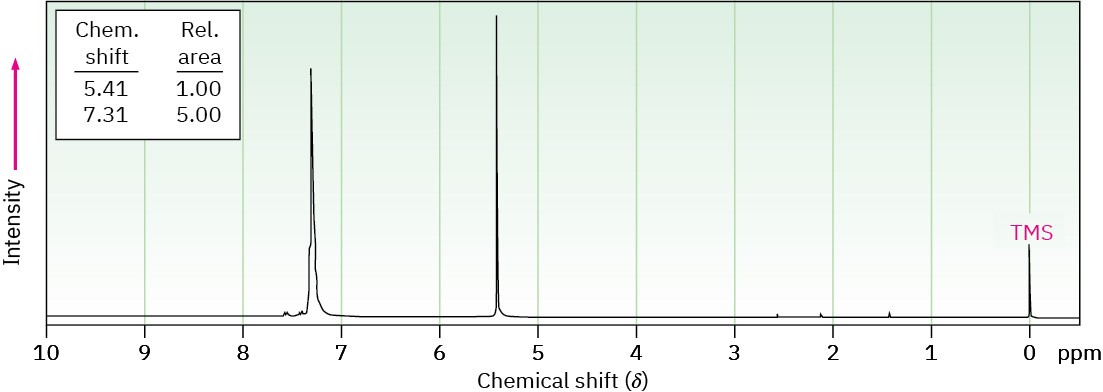
Problem 15-49
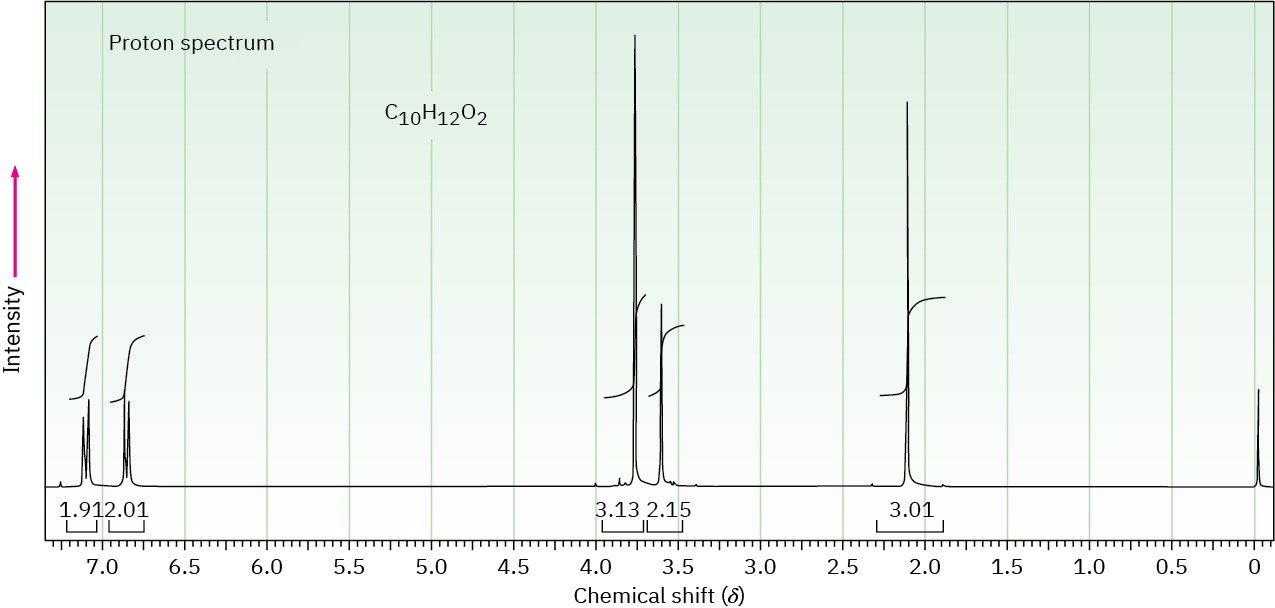
The proton NMR spectrum for a compound with formula C10H12O2 is shown. The infrared spectrum has a strong band at 1711 cm–1. The normal carbon-13 NMR spectral results are tabulated along with the DEPT-135 and DEPT-90 information. Draw the structure of this compound.
|
Normal Carbon |
DEPT-135 |
DEPT-90 |
|
29 ppm |
Positive |
No peak |
|
50 |
Negative |
No peak |
|
55 |
Positive |
No peak |
|
114 |
Positive |
Positive |
|
126 |
No peak |
No peak |
|
130 |
Positive |
Positive |
|
159 |
No peak |
No peak |
|
207 |
No peak |
No peak |
Problem 15-50
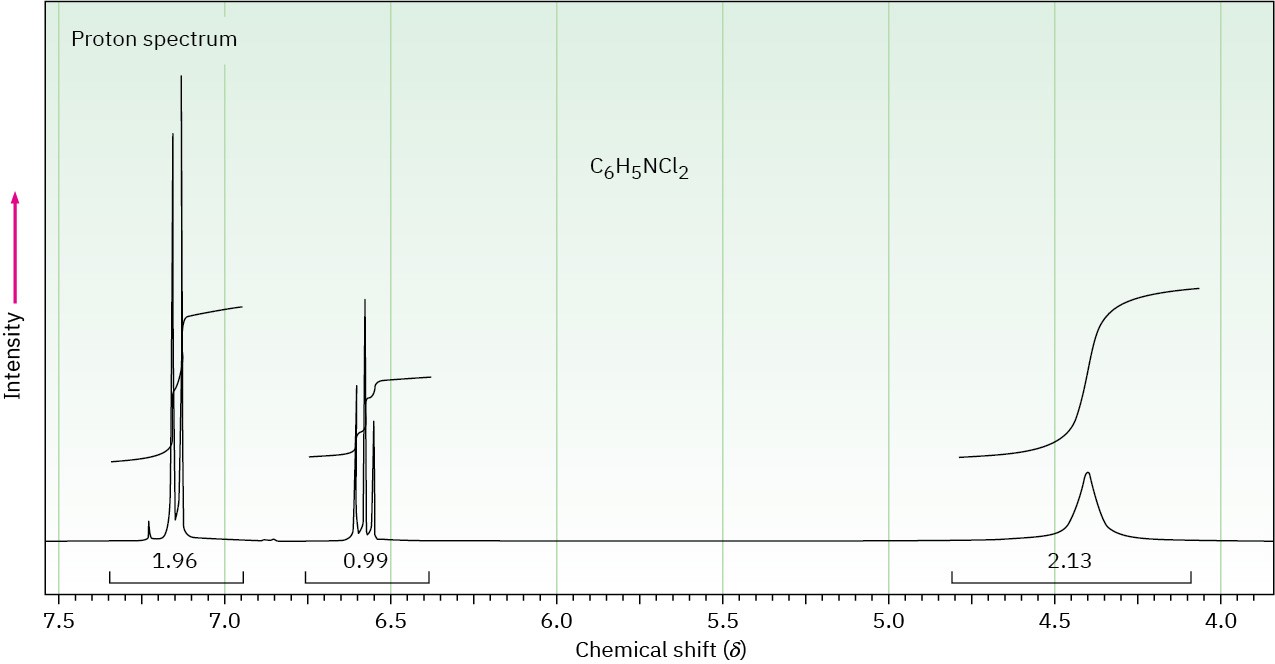
The proton NMR spectrum of a compound with formula C6H5NCl2 is shown. The normal carbon-13 and DEPT experimental results are tabulated. The infrared spectrum shows peaks at 3432 and 3313 cm–1 and a series of medium-sized peaks between 1618 and 1466 cm–1. Draw the structure of this compound.
|
Normal Carbon |
DEPT-135 |
DEPT-90 |
|
118.0 ppm |
Positive |
Positive |
|
119.5 |
No peak |
No peak |
|
128.0 |
Positive |
Positive |
|
140.0 |
No peak |
No peak |
Problem 15-51
Aromatic substitution reactions occur by addition of an electrophile such as Br+ to an aromatic ring to yield an allylic carbocation intermediate, followed by loss of H+. Show the structure of the intermediate formed by reaction of benzene with Br+.
Problem 15-52
The substitution reaction of toluene with Br2 can, in principle, lead to the formation of three isomeric bromotoluene products. In practice, however, only o– and p-bromotoluene are formed in substantial amounts. The meta isomer is not formed. Draw the structures of the three possible carbocation intermediates (Problem 51), and explain why ortho and para products predominate over meta products.
Problem 15-53
Look at the following aromatic anions and their linear counterparts, and draw all of the resonance forms for each. What patterns emerge?
(a)
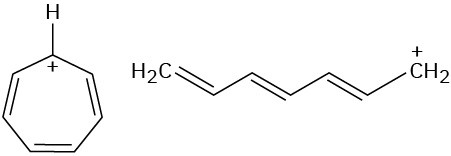
(b)
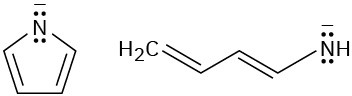
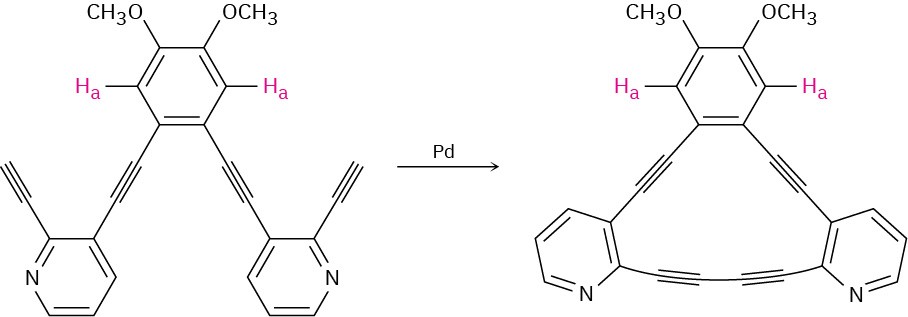
Problem 15-54
After the following reaction, the chemical shift of Ha moves downfield from 6.98 ppm to
7.30 ppm. Explain.
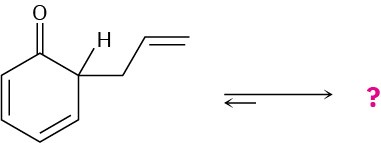
Problem 15-55
The following compound is the product initially formed in a Claisen rearrangement, which we’ll see in Section 18.4. This product is not isolated, but tautomerizes to its enol form. Give the structure of the enol and provide an explanation as to why the enol tautomer is favored.
Problem 15-56
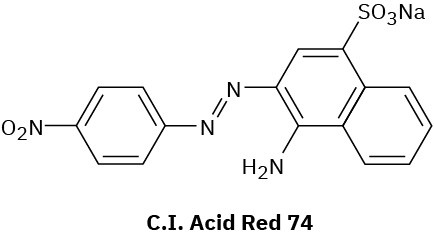
Compounds called azo dyes are the major source of artificial color in textiles and food. Part of the reason for their intense coloring is the conjugation from an electron-donating group through the diazo bridge (−N=N−) to an electron-withdrawing group on the other side. For the following azo dyes, draw a resonance form that shows how the electron-donating group is related to the electron-withdrawing group on the other side of the diazo bridge. Used curved arrows to show how the electrons are reorganized.
(a)
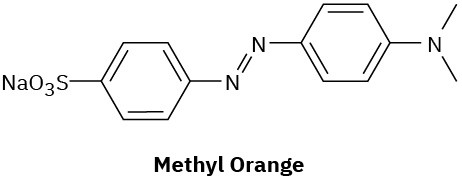
(b)