2.6 Drawing Resonance Forms
Look back at the resonance forms of the acetate ion and the acetone anion shown in the previous section. The pattern seen there is a common one that leads to a useful technique for drawing resonance forms. In general, any three-atom grouping with a p orbital on each atom has two resonance forms:
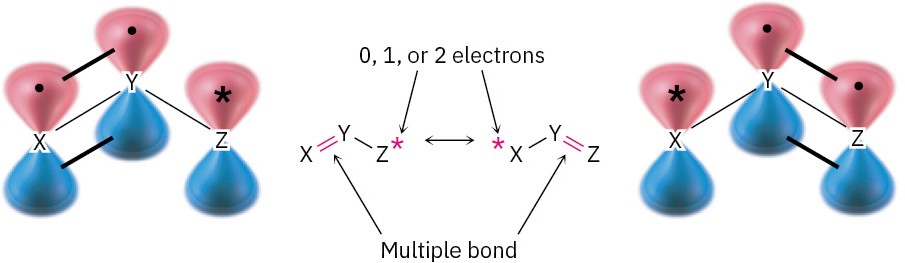
The atoms X, Y, and Z in the general structure might be C, N, O, P, S, or others, and the asterisk (*) might mean that the p orbital on atom Z is vacant, that it contains a single electron, or that it contains a lone pair of electrons. The two resonance forms differ simply by an exchange in position of the multiple bond and the asterisk from one end of the three- atom grouping to the other.
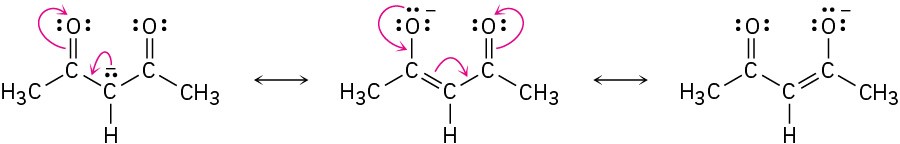
By learning to recognize such three-atom groupings within larger structures, resonance forms can be systematically generated. Look, for instance, at the anion produced when H+ is removed from 2,4-pentanedione by reaction with a base. How many resonance structures does the resultant anion have?
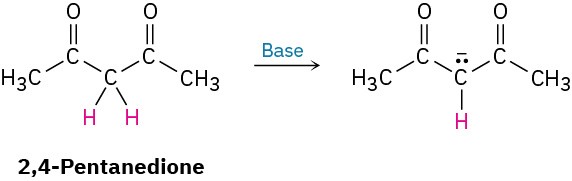
The 2,4-pentanedione anion has a lone pair of electrons and a formal negative charge on the central carbon atom, next to a C=O bond on the left. The O=C–C:− grouping is a typical one for which two resonance structures can be drawn.
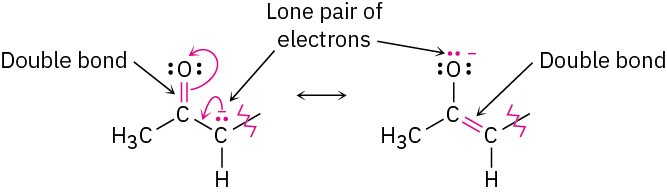
Just as there is a C=O bond to the left of the lone pair, there is a second C=O bond to the right. Thus, we can draw a total of three resonance structures for the 2,4-pentanedione anion.
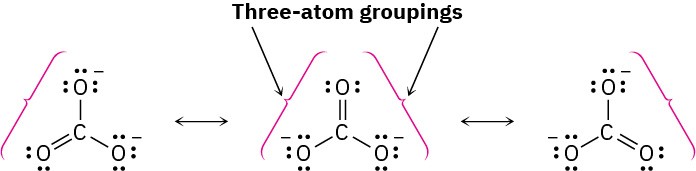
Worked Example 2.2Drawing Resonance Forms for an AnionDraw three resonance structures for the carbonate ion, CO32–.
 StrategyLook for three-atom groupings that contain a multiple bond next to an atom with a p orbital. Then exchange the positions of the multiple bond and the electrons in the p orbital. In the carbonate ion, each singly bonded oxygen atom with three lone pairs and a negativecharge is adjacent to the C=O double bond, giving the grouping.SolutionExchanging the position of the double bond and an electron lone pair in each grouping generates three resonance structures.
StrategyLook for three-atom groupings that contain a multiple bond next to an atom with a p orbital. Then exchange the positions of the multiple bond and the electrons in the p orbital. In the carbonate ion, each singly bonded oxygen atom with three lone pairs and a negativecharge is adjacent to the C=O double bond, giving the grouping.SolutionExchanging the position of the double bond and an electron lone pair in each grouping generates three resonance structures.
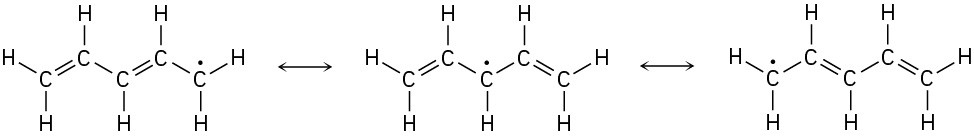
Worked Example 2.3Drawing Resonance Forms for a RadicalDraw three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical, where a radical is a substance that contains a single, unpaired electron in one of its orbitals, denoted by a dot (·).
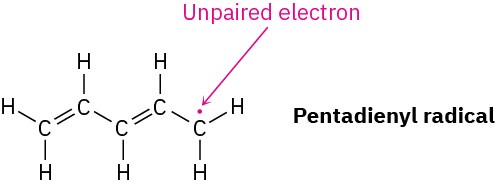 StrategyFind the three-atom groupings that contain a multiple bond next to an atom with a porbital.
StrategyFind the three-atom groupings that contain a multiple bond next to an atom with a porbital.
SolutionThe unpaired electron is on a carbon atom next to a C=C bond, giving a typical three-atom grouping that has two resonance forms.
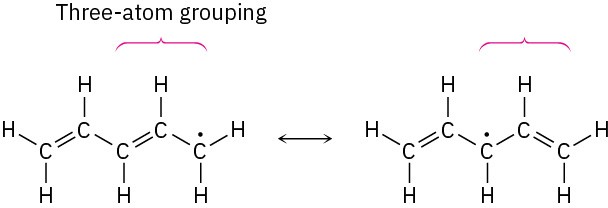
In the second resonance form, the unpaired electron is next to another double bond, giving another three-atom grouping and leading to another resonance form.

Thus, the three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical are:
Problem 2-9
Which of the following pairs of structures represent resonance forms, and which do not? Explain.
(a) 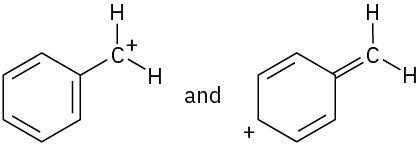 (b)
(b) 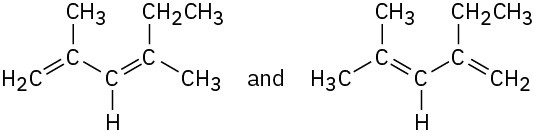
Problem 2-10
Draw the indicated number of resonance forms for each of the following substances: (a)
The methyl phosphate anion, CH3OPO32– (3) (b)
The nitrate anion, NO3– (3) (c)
The allyl cation, H2C=CH–CH2+ (2)
(d)
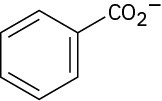
The benzoate anion (2)