Key Terms
- anti stereochemistry
- bromonium ion
- carbene, R2C
- chain-growth polymer
- epoxide
- glycol
- halohydrin
- hydroboration
- hydrogenated
- hydroxylation
- monomer
- oxidation
- oxirane
- oxymercuration–demercuration
- ozonide
- polymer
- reduction
- Simmons–Smith reaction
- stereospecific
- syn stereochemistry
Summary of Reactions 8 • Summary of Reactions 8 • Summary of Reactions
No stereochemistry is implied unless specifically indicated with wedged, solid, and dashed lines.
- Addition reactions of alkenes
- Addition of HCl, HBr, and HI (Section 7.7 and Section 7.8)
Markovnikov regiochemistry occurs, with H adding to the less highly substituted alkene carbon and halogen adding to the more highly substituted carbon.
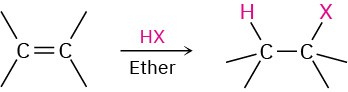
- Addition of halogens Cl2 and Br2 (Section 8.2)
Anti addition is observed through a halonium ion intermediate.
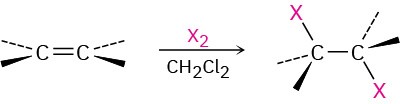
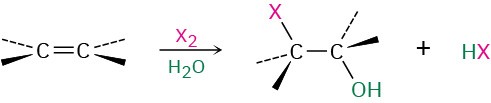
- Halohydrin formation (Section 8.3)
Markovnikov regiochemistry and anti stereochemistry occur.
- Addition of water by oxymercuration–demercuration (Section 8.4) Markovnikov regiochemistry occurs.
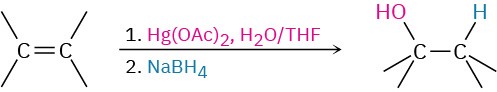
- Addition of water by hydroboration–oxidation (Section 8.5) Non-Markovnikov syn addition occurs.
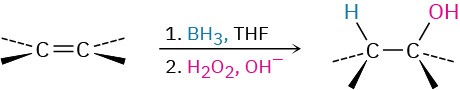
- Catalytic hydrogenation (Section 8.6) Syn addition occurs.
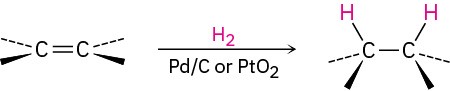
- Epoxidation with a peroxyacid (Section 8.7) Syn addition occurs.
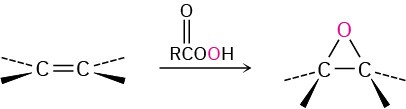
- Hydroxylation with OsO4 (Section 8.7) Syn addition occurs.
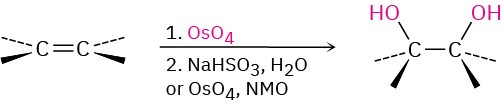
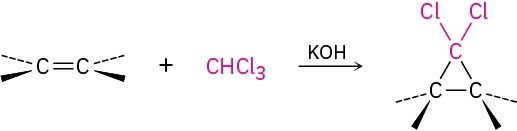
- Addition of carbenes to yield cyclopropanes (Section 8.9)
- Dichlorocarbene addition
- Simmons–Smith reaction
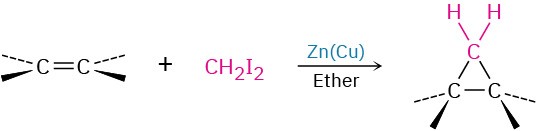
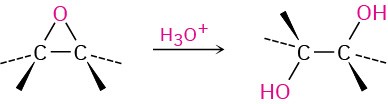
- Hydroxylation by acid-catalyzed epoxide hydrolysis (Section 8.7) Anti stereochemistry occurs.
- Oxidative cleavage of alkenes (Section 8.8)
- Reaction with ozone followed by zinc in acetic acid
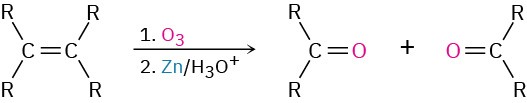
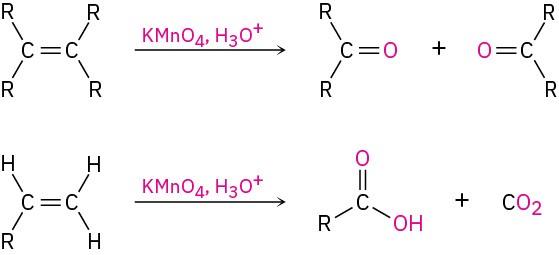
- Reaction with KMnO4 in acidic solution
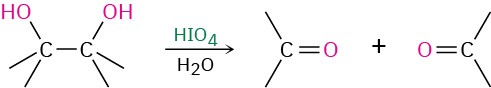
- Cleavage of 1,2-diols (Section 8.8)