21 Why This Chapter?

Figure 21.1 The lives of rock climbers depend on their ropes, typically made of a nylon polymer prepared by a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. (credit: modification of work “110823-A-NR754-001” by USASOC News Service/Flickr, CC BY 2.0)
Carboxylic acid derivatives are among the most widely occurring of all molecules, both in laboratory chemistry and in biological pathways. Thus, a study of them and their primary reaction—nucleophilic acyl substitution—is fundamental to understanding organic chemistry. We’ll begin this chapter by first learning about carboxylic acid derivatives, and we’ll then explore the chemistry of acyl substitution reactions.
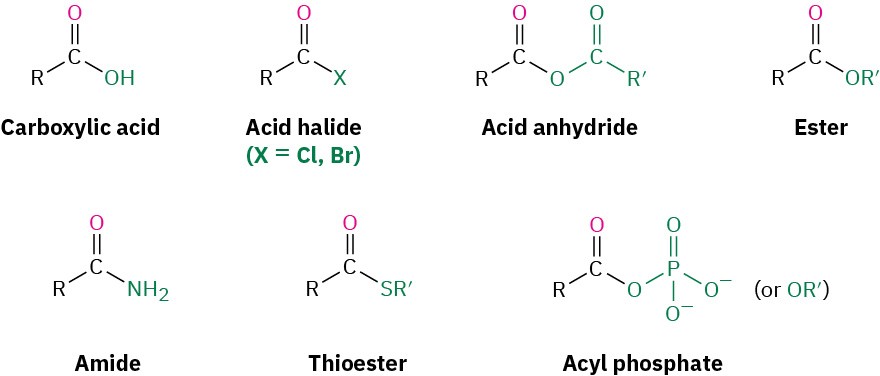
Closely related to the carboxylic acids and nitriles discussed in the previous chapter are the carboxylic acid derivatives, compounds in which an acyl group is bonded to an electronegative atom or substituent that can act as a leaving group in the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction that we saw briefly in the Preview of Carbonyl Chemistry:

Many kinds of acid derivatives are known, but we’ll be concerned primarily with four of the most common ones: acid halides, acid anhydrides, esters, and amides. Acid halides and acid anhydrides are used only in the laboratory, while esters and amides are common in both laboratory and biological chemistry. In addition, carboxylic acid derivatives called thioesters and acyl phosphates are encountered primarily in biological chemistry. Note the structural similarity between acid anhydrides and acyl phosphates.